| Date | November 2013 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 13N.2.sl.TZ0.6 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 6 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
2-methylbutan-2-ol, \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C(OH)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\), is a liquid with a smell of camphor that was formerly used as a sedative. One way of producing it starts with 2-methylbut-2-ene.
2-chloro-2-methylbutane contains some molecules with a molar mass of approximately \({\text{106 g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\) and some with a molar mass of approximately \({\text{108 g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\).
Draw the structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene.
State the other substances required to convert 2-methylbut-2-ene to 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
Explain whether you would expect 2-methylbutan-2-ol to react with acidified potassium dichromate(VI).
Explain why 2-methylbut-2-ene is less soluble in water than 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
Outline why there are molecules with different molar masses.
Markscheme
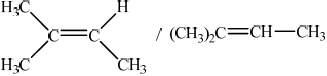 ;
;
Accept condensed formula such as (CH3)2CCHCH3.
water/\({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\);
Accept steam.
(concentrated) sulfuric acid/\({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\) (catalyst);
Accept phosphoric acid/H3PO4.
Award [2] for HBr and NaOH, (2 stage process via the halogenoalkane).
not react;
tertiary alcohol (not easily oxidized);
2-methylbutan-2-ol has hydroxyl/OH group;
Do not accept “hydroxide group”.
Allow 2-methylbutan-2-ol is an alcohol.
2-methylbutan-2-ol can form H-bonds (to water) / 2-methylbut-2-ene cannot form H-bonds (to water);
chlorine can be \(^{{\text{35}}}{\text{Cl}}\)/Cl–35 or \(^{{\text{37}}}{\text{Cl}}\)/Cl–37;
Accept “chlorine can exist as two isotopes”.
Answer must refer to chlorine rather than isotopes in general.
Examiners report
This was the second most popular question answered in Section B. This question was focussed on organic chemistry and attempted by many candidates.
Most candidates were able to draw the correct structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene in part (a). In part (b), water and sulfuric acid were stated correctly as the reagents. In part (c), most candidates knew that tertiary alcohols do not react. In part (d), the most common mistake was some candidates thinking that the hydroxyl group in an alcohol was a hydrogen bond. Some other candidates could not write that the alcohol forms hydrogen bonds with water. In part (e), many candidates got \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\), though an odd few candidates identified the mechanism as \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\). In part (e) (ii), the mechanisms proved a problem for several candidates. The use of curly arrows in reaction mechanisms continues to be poorly understood, the arrow often pointing in the wrong direction. Candidates must take care to accurately draw the position of the curly arrows illustrating the movement of electrons. Some candidates forgot to include the lone pair for the curly arrow going from the lone pair on O to \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Some candidates had the lone pair incorrectly located on the H and others had the curly arrow going to an atom instead of between the O and the \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Part (iii) was well answered.
Part (f) proved challenging for candidates and very few referred to chlorines isotopes. In addition, the majority of candidates did not state that the same rate could be applied as the isotopes have the same chemical properties. In part (g), many candidates scored three out of five marks. Some candidates forgot to state that the sample is converted to the gaseous state for the vaporization stage. Many candidates although knew about detection but only few stated that the ions hit the counter and an electrical signal is generated.
This was the second most popular question answered in Section B. This question was focussed on organic chemistry and attempted by many candidates.
Most candidates were able to draw the correct structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene in part (a). In part (b), water and sulfuric acid were stated correctly as the reagents. In part (c), most candidates knew that tertiary alcohols do not react. In part (d), the most common mistake was some candidates thinking that the hydroxyl group in an alcohol was a hydrogen bond. Some other candidates could not write that the alcohol forms hydrogen bonds with water. In part (e), many candidates got \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\), though an odd few candidates identified the mechanism as \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\). In part (e) (ii), the mechanisms proved a problem for several candidates. The use of curly arrows in reaction mechanisms continues to be poorly understood, the arrow often pointing in the wrong direction. Candidates must take care to accurately draw the position of the curly arrows illustrating the movement of electrons. Some candidates forgot to include the lone pair for the curly arrow going from the lone pair on O to \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Some candidates had the lone pair incorrectly located on the H and others had the curly arrow going to an atom instead of between the O and the \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Part (iii) was well answered.
Part (f) proved challenging for candidates and very few referred to chlorines isotopes. In addition, the majority of candidates did not state that the same rate could be applied as the isotopes have the same chemical properties. In part (g), many candidates scored three out of five marks. Some candidates forgot to state that the sample is converted to the gaseous state for the vaporization stage. Many candidates although knew about detection but only few stated that the ions hit the counter and an electrical signal is generated.
This was the second most popular question answered in Section B. This question was focussed on organic chemistry and attempted by many candidates.
Most candidates were able to draw the correct structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene in part (a). In part (b), water and sulfuric acid were stated correctly as the reagents. In part (c), most candidates knew that tertiary alcohols do not react. In part (d), the most common mistake was some candidates thinking that the hydroxyl group in an alcohol was a hydrogen bond. Some other candidates could not write that the alcohol forms hydrogen bonds with water. In part (e), many candidates got \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\), though an odd few candidates identified the mechanism as \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\). In part (e) (ii), the mechanisms proved a problem for several candidates. The use of curly arrows in reaction mechanisms continues to be poorly understood, the arrow often pointing in the wrong direction. Candidates must take care to accurately draw the position of the curly arrows illustrating the movement of electrons. Some candidates forgot to include the lone pair for the curly arrow going from the lone pair on O to \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Some candidates had the lone pair incorrectly located on the H and others had the curly arrow going to an atom instead of between the O and the \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Part (iii) was well answered.
Part (f) proved challenging for candidates and very few referred to chlorines isotopes. In addition, the majority of candidates did not state that the same rate could be applied as the isotopes have the same chemical properties. In part (g), many candidates scored three out of five marks. Some candidates forgot to state that the sample is converted to the gaseous state for the vaporization stage. Many candidates although knew about detection but only few stated that the ions hit the counter and an electrical signal is generated.
This was the second most popular question answered in Section B. This question was focussed on organic chemistry and attempted by many candidates.
Most candidates were able to draw the correct structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene in part (a). In part (b), water and sulfuric acid were stated correctly as the reagents. In part (c), most candidates knew that tertiary alcohols do not react. In part (d), the most common mistake was some candidates thinking that the hydroxyl group in an alcohol was a hydrogen bond. Some other candidates could not write that the alcohol forms hydrogen bonds with water. In part (e), many candidates got \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\), though an odd few candidates identified the mechanism as \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\). In part (e) (ii), the mechanisms proved a problem for several candidates. The use of curly arrows in reaction mechanisms continues to be poorly understood, the arrow often pointing in the wrong direction. Candidates must take care to accurately draw the position of the curly arrows illustrating the movement of electrons. Some candidates forgot to include the lone pair for the curly arrow going from the lone pair on O to \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Some candidates had the lone pair incorrectly located on the H and others had the curly arrow going to an atom instead of between the O and the \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Part (iii) was well answered.
Part (f) proved challenging for candidates and very few referred to chlorines isotopes. In addition, the majority of candidates did not state that the same rate could be applied as the isotopes have the same chemical properties. In part (g), many candidates scored three out of five marks. Some candidates forgot to state that the sample is converted to the gaseous state for the vaporization stage. Many candidates although knew about detection but only few stated that the ions hit the counter and an electrical signal is generated.
This was the second most popular question answered in Section B. This question was focussed on organic chemistry and attempted by many candidates.
Most candidates were able to draw the correct structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene in part (a). In part (b), water and sulfuric acid were stated correctly as the reagents. In part (c), most candidates knew that tertiary alcohols do not react. In part (d), the most common mistake was some candidates thinking that the hydroxyl group in an alcohol was a hydrogen bond. Some other candidates could not write that the alcohol forms hydrogen bonds with water. In part (e), many candidates got \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\), though an odd few candidates identified the mechanism as \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\). In part (e) (ii), the mechanisms proved a problem for several candidates. The use of curly arrows in reaction mechanisms continues to be poorly understood, the arrow often pointing in the wrong direction. Candidates must take care to accurately draw the position of the curly arrows illustrating the movement of electrons. Some candidates forgot to include the lone pair for the curly arrow going from the lone pair on O to \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Some candidates had the lone pair incorrectly located on the H and others had the curly arrow going to an atom instead of between the O and the \({{\text{C}}^ + }\). Part (iii) was well answered.
Part (f) proved challenging for candidates and very few referred to chlorines isotopes. In addition, the majority of candidates did not state that the same rate could be applied as the isotopes have the same chemical properties. In part (g), many candidates scored three out of five marks. Some candidates forgot to state that the sample is converted to the gaseous state for the vaporization stage. Many candidates although knew about detection but only few stated that the ions hit the counter and an electrical signal is generated.

