| Date | May 2010 | Marks available | 8 | Reference code | 10M.2.sl.TZ2.7 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Deduce and Determine | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Alkenes are an economically and chemically important family of organic compounds.
The reaction of alkenes with bromine water provides a test for unsaturation in the laboratory. Describe the colour change when bromine water is added to chloroethene.
Deduce the Lewis structure of chloroethene and identify the formula of the repeating unit of the polymer poly(chloroethene).
(i) Deduce the structural formulas of the two alcohol isomers of molecular formula \({{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}\). Name each isomer and identify each as either a primary or a secondary alcohol.
(ii) Oxidation of the alcohol isomers lead to the formation of different organic products. Determine the structures of the organic products formed from the oxidation of each alcohol isomer in (c) (i) above and list the conditions required to obtain the different products.
Markscheme
colour change from yellow/orange/rust colour/red/brown to colourless;
No mark for change to clear, or for decolourized with no reference to original colour.
Chloroethene:
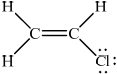 ;
;
No mark if the lone pairs missing on Cl.
Accept lines, dots or crosses for e– pairs.
Poly(chloroethene):
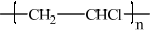 ;
;
n and square brackets are not required.
Continuation bonds must be shown.
(i) \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\), propan-1-ol/1-propanol;
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH(OH)C}}{{\text{H}}_3}\), propan-2-ol/2-propanol;
Need both formula and name for mark.
Accept either condensed or full structural formulas.
CH3CH2CH2OH: primary and CH3CH(OH)CH3: secondary;
(ii) \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO}}\);
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}\);
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_3}\);
Accept either condensed or full structural formulas.
from propan-1-ol: \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO}}\) (propanal) obtained by distillation (as product is formed);
propan-1-ol gives \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}\) (propanoic acid) by (heating under) reflux;
Award [1] if CH3CH2CHO and CH3CH2COOH identified but conditions not
given/incorrect.
propan-2-ol gives \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_3}\) by (heating under) reflux;
Examiners report
Although this was the least popular question it was generally accessible with candidates often scoring high marks. The colour change when bromine water is added to an alkene was well answered by most candidates although some either did not state the colour of bromine or stated that it becomes clear, rather than colourless.
Most candidates deduced the correct Lewis structure of chloroethene although some did not include the lone electron pairs on the Cl atom. The formula of the repeating unit of the polymer poly(chloroethene) was generally done well.
(c) was generally well answered.
The most common error in (c) (i) was just giving ‘propanol’ with no reference to the position of the OH group. The structures of the organic products were well known although the experimental conditions needed to extract the products were less familiar.

