| Date | May 2011 | Marks available | 5 | Reference code | 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | State and Suggest | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction include particle size, concentration of reactants and the temperature of the reaction.
Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol are two structural isomers of \({{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}\).
Define the term rate of a chemical reaction.
List the three characteristic properties of reactant particles which affect the rate of reaction as described by the collision theory.
On the axes below sketch two Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curves for the same sample of gas, one at a temperature \(T\) and another at a higher temperature \(T'\). Label both axes. Explain why raising the temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction.

Explain why coal dust burns much faster than a large piece of coal with the same mass.
State the equation for the complete combustion of \({{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}\).
Both propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol can be oxidized in aqueous solution by potassium dichromate(VI). State any necessary conditions for the oxidation to occur and describe the colour change during the oxidation process.
State the name(s) and structure(s) of the organic product(s) that can be formed when each of the alcohols is oxidized and suggest why one of the alcohols gives two organic products and the other only gives one organic product.
Markscheme
increase in concentration of product per unit time / decrease in concentration of reactant per unit time;
Accept change instead of increase/decrease and mass/amount/volume instead of concentration.
frequency of collisions;
kinetic energy/speed of reactant particles;
collision geometry/orientation;
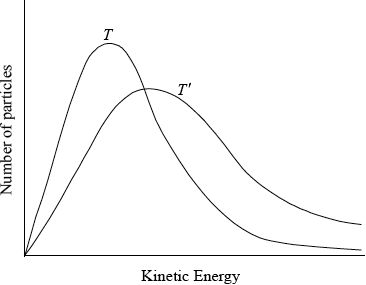
correctly labelled axes showing number of particles/frequency against (kinetic) energy;
correctly shaped graph for \(T\) (curve must not touch or cross x axes);
\(T'\) curve to the right of \(T\) and with a peak lower than \(T\);
increasing the temperature increases the (kinetic) energy of the particles / more particles will possess the necessary activation energy;
there will be more collisions per unit time / the frequency of collisions increases / there are more successful collisions;
the dust has a greatly increased surface area / more of the coal can come into contact with the oxygen molecules when it is in dust form / OWTTE;
\({{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_8}{\text{O}} + {\text{4}}\frac{1}{2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{3C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}/{\text{2}}{{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_8}{\text{O}} + {\text{9}}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{6C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{8}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\)
Award [1] for correct products and reactants and [1] for correct balancing.
Ignore state symbols.
acidic solution / \({{\text{H}}^ + }\) / sulfuric acid;
warm / heat / reflux;
(the solution changes) from orange to green;
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO}}\) and propanal;
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}\) and propanoic acid;
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_3}\) and propanone/acetone;
Award [1] for 2 or 3 correct names or structures, award [2] for 4 or 5 correct names or structures.
propan-1-ol gives propanal and propanoic acid and propan-2-ol gives propanone;
propan-1-ol has two H atoms bonded to the C containing the –OH whereas propan-2-ol only has one / propan-1-ol is a primary alcohol and propan-2-ol is a secondary alcohol;
Examiners report
This question began with kinetics and although many did well, there were also a lot of marks lost. Some did not have a correct definition of rate of reaction and many misread the question that asked for the properties of reactant particles that affect rate. Many candidates talked about surface area, concentration etc as opposed to collision frequency, collision geometry and reactant particle kinetic energy. The Maxwell-Bolzmann energy curves were drawn very badly and even candidates who could do it lost marks for the sloppy drawing of the curves e.g curves did not start at the origin or they crossed the x axis.
Also candidates could not label the axes correctly. However most could suggest that coal dust burns faster as it has a larger surface area.
This question began with kinetics and although many did well, there were also a lot of marks lost. Some did not have a correct definition of rate of reaction and many misread the question that asked for the properties of reactant particles that affect rate. Many candidates talked about surface area, concentration etc as opposed to collision frequency, collision geometry and reactant particle kinetic energy. The Maxwell-Bolzmann energy curves were drawn very badly and even candidates who could do it lost marks for the sloppy drawing of the curves e.g curves did not start at the origin or they crossed the x axis.
Also candidates could not label the axes correctly. However most could suggest that coal dust burns faster as it has a larger surface area.
This question began with kinetics and although many did well, there were also a lot of marks lost. Some did not have a correct definition of rate of reaction and many misread the question that asked for the properties of reactant particles that affect rate. Many candidates talked about surface area, concentration etc as opposed to collision frequency, collision geometry and reactant particle kinetic energy. The Maxwell-Bolzmann energy curves were drawn very badly and even candidates who could do it lost marks for the sloppy drawing of the curves e.g curves did not start at the origin or they crossed the x axis.
Also candidates could not label the axes correctly. However most could suggest that coal dust burns faster as it has a larger surface area.
This question began with kinetics and although many did well, there were also a lot of marks lost. Some did not have a correct definition of rate of reaction and many misread the question that asked for the properties of reactant particles that affect rate. Many candidates talked about surface area, concentration etc as opposed to collision frequency, collision geometry and reactant particle kinetic energy. The Maxwell-Bolzmann energy curves were drawn very badly and even candidates who could do it lost marks for the sloppy drawing of the curves e.g curves did not start at the origin or they crossed the x axis.
Also candidates could not label the axes correctly. However most could suggest that coal dust burns faster as it has a larger surface area.
Part (b) was based on organic chemistry and most candidates knew that the products of combusting propan-2-ol were carbon dioxide and water- although few could balance the equation correctly. In the next part of the question the colour change from orange to green was well known, but the necessary conditions of reflux and acidifying the dichromate were not. The final part of this question was often done very well and many candidates could draw the structures of the 3 oxidation products and name them.
Part (b) was based on organic chemistry and most candidates knew that the products of combusting propan-2-ol were carbon dioxide and water- although few could balance the equation correctly. In the next part of the question the colour change from orange to green was well known, but the necessary conditions of reflux and acidifying the dichromate were not. The final part of this question was often done very well and many candidates could draw the structures of the 3 oxidation products and name them.
Part (b) was based on organic chemistry and most candidates knew that the products of combusting propan-2-ol were carbon dioxide and water- although few could balance the equation correctly. In the next part of the question the colour change from orange to green was well known, but the necessary conditions of reflux and acidifying the dichromate were not. The final part of this question was often done very well and many candidates could draw the structures of the 3 oxidation products and name them.

