| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.sl.TZ1.4 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Suggest and Show | Question number | 4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid.
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
The results of a series of experiments in which the concentration of HCl was varied are shown below.
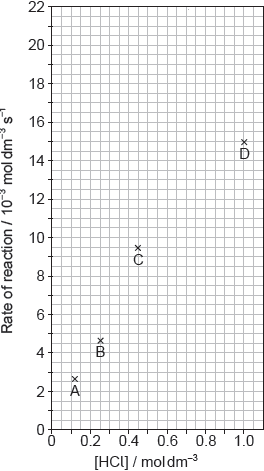
Outline two ways in which the progress of the reaction can be monitored. No practical details are required.
Suggest why point D is so far out of line assuming human error is not the cause.
Suggest the relationship that points A, B and C show between the concentration of the acid and the rate of reaction.
Markscheme
Any two of:
loss of mass «of reaction mixture/CO2»
«increase in» volume of gas produced
change of conductivity
change of pH
change in temperature
Do not accept “disappearance of calcium carbonate”.
Do not accept “gas bubbles”.
Do not accept “colour change” or “indicator”.
[2 marks]
reaction is fast at high concentration AND may be difficult to measure accurately
OR
so many bubbles of CO2 produced that inhibit contact of HCl(aq) with CaCO3(s)
OR
insufficient change in conductivity/pH at high concentrations
OR
calcium carbonate has been used up/is limiting reagent/there is not enough calcium carbonate «to react with the high concentration of HCl»
OR
HCl is in excess
OR
so many bubbles of CO2 produced that inhibit contact of HCl(aq) with CaCO3(s)
[1 mark]
«directly» proportional
Accept “first order” or “linear”.
Do not accept “rate increases as concentration increases” or “positive correlation”
[1 mark]
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 18M.3.sl.TZ2.16c: Explain why aspirin is not stored in a hot, humid location.
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.2b.i: Sketch a curve on the graph to show the volume of gas produced over time if the same mass of...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.2a: Sketch a Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution curve for a chemical reaction showing the activation...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.17: Which factors can affect the rate of reaction? I. Particle size of solid...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.16: The potential energy profile for the reversible reaction, X + Y \( \rightleftharpoons \) Z...
- 18M.3.sl.TZ1.2c.ii: State a factor, that has a significant effect on reaction rate, which could vary between...
- 18M.3.sl.TZ1.2c.i: Deduce, giving a reason, which of the two methods would be least affected by the chips not...
- 18M.3.sl.TZ1.2b: Neither method actually gives the initial rate. Outline a method that would allow the initial...
- 18M.3.sl.TZ1.1b.i: Suggest why there is a small increase in the surface pressure as the area is reduced to about...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.4b.i: Suggest why point D is so far out of line assuming human error is not the cause.
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.4a: Outline two ways in which the progress of the reaction can be monitored. No practical details...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.17: Which statements are correct? I. The activation energy of a reaction is not...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.16: Which change increases the rate of formation of hydrogen when zinc reacts with excess...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.4b.iii: Suggest the relationship that points A, B and C show between the concentration of the acid...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.4b.i: Suggest why point D is so far out of line assuming human error is not the cause.
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.4a: Outline two ways in which the progress of the reaction can be monitored. No practical details...
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.2b: Suggest two variables, besides the time of reaction, which the student should have controlled...
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.1e.ii: Suggest one possible reason for the differences between curves X and Y.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.1e.i: Explain the shape of curve X in terms of the collision theory.
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.17: Excess magnesium powder was added to a beaker containing hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq). The...
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.16: The diagram shows the energy profile for a catalysed and uncatalysed reaction.Which...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.1b: The student then carried out the experiment at other acid concentrations with all...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.1a.ii: A student produced these results with [H+] = 0.15 mol\(\,\)dm−3. Propanone and acid were in...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.1a.i: Suggest how the change of iodine concentration could be followed.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.17: 100 cm3 of 10% hydrogen peroxide solution decomposes at 298 K to form water and...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.16: Copper catalyses the reaction between zinc and dilute sulfuric acid. Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) →...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.3g: Suggest one reason why the values of rates of reactions obtained at higher temperatures may...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.3f: An additional experiment was carried out at a higher temperature, T2. (i) On the same axes,...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.3e: A student decided to carry out another experiment using 0.075 mol dm-3 solution of sodium...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.3d: Draw the best fit line of \(\frac{1}{{\rm{t}}}\) against concentration of sodium thiosulfate...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.17: Which experimental methods could be used to observe the progress of the following...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.16: For the reaction R → P, which letter represents the activation energy for the catalysed...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.3b: The enthalpy change for the reaction between nitrogen monoxide and hydrogen is −664 kJ and...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.3a: (i) State the equation for the overall reaction. (ii) Deduce the rate expression consistent...
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.3b: (i) Sketch the potential energy profile for the synthesis of phosgene, using the axes given,...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.17: Graph 1 shows a plot of volume...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.16: Which conditions must be met for a reaction to take place? I. Reactants collide with...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.3a: Define the term rate of reaction.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.3b: Describe the collision theory.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.2a: Define the term rate of reaction.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.2b: Explain why increasing the particle size of a solid reactant decreases the rate of reaction.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.iii: Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\).
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.7b: Ammonia is manufactured by the Haber process in which iron is used as a catalyst. Explain...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.18: Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas according to the following...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.17: Which variable is best to use when determining the rate of decomposition of hydrogen...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.17: Which is a correct unit for expressing the rate of a reaction? A. ...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.18: \({\text{100 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of a...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.3a: Define the term rate of reaction.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.3b: Describe the collision theory.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.5d.ii: Ammonia is manufactured by the Haber process in which iron is used as a catalyst. Explain the...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.5d.iii: Sketch the Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curve for a reaction, labelling both axes...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.7d.ii: Describe how a catalyst increases the rate of a reaction.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.5d.i: Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\).
- 14M.1.hl.TZ2.22: Which pair of graphs shows a decomposition reaction of \(X\) that obeys first-order kinetics?
- 14M.1.hl.TZ2.8: Which statements explain why a catalyst is used in the Contact process (shown...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.2a: Deduce, with a reason, the order of reaction with respect to each reactant.
- 14M.2.hl.TZ2.1d: Outline how you could establish that the system had reached equilibrium at the end of one week.
- 14M.2.hl.TZ2.1e: Outline why changing the temperature has only a very small effect on the value of the...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ2.6a: (i) State the volumes of the liquids that should be mixed. (ii) State why it is...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ2.6c: (i) Sketch and label, indicating an approximate activation energy, the Maxwell–Boltzmann...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ1.17: Why does the rate of a reaction increase when the temperature is increased? I. The...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.18: Which is not affected by an increase in temperature? A. Rate of reaction B. ...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.1a: (i) The graph shows the volume of hydrogen produced against time under these experimental...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ1.18: The diagram represents the Maxwell‒Boltzmann energy distribution curve of the reactants for a...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.17: Which change increases the rate of a chemical reaction? A. Increasing the size of solid...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.1b: The hydrochloric acid does not appear in the balanced equation for the reaction. State its...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.1g: Outline how you could establish that the system had reached equilibrium at the end of one week.
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.1h: Outline why changing the temperature has only a very small effect on the value of the...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.5b: (i) State the volumes of the liquids that should be mixed. (ii) State why it is...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.5c: (i) Sketch and label, indicating an approximate activation energy, the Maxwell–Boltzmann...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.5e: (i) Calculate the volume of sulfur dioxide, in \({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\),...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.11a.ii: Explain how and why the rate of reaction changes with time.
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.11b: A Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curve is drawn below. Label both axes and explain, by...
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.17: Consider the following reaction between hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen ions and iodide...
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.18: Which quantity can be changed by the use of a catalyst? A. I and II only B. I and...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.5b: The Contact process operates at a temperature of 450 °C and a pressure of 2 atm as optimum...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.8e: (i) The experiment is repeated with the same amount of a more effective catalyst,...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.1a: The concentration of iodide ions, \({{\text{I}}^ - }\), is assumed to be constant. Outline...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.20: The diagram below shows the energy changes for a reaction with and without a catalyst. Which...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.1b: For this mixture the concentration of hydrogen peroxide,...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.1e: The colour change occurs when \(1.00 \times {10^{ - 4}}{\text{ mol}}\) of iodine has been...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.1g: In another experiment, 0.100 g of a black powder was also added while all other...
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.18: The diagram below shows the energy changes for a reaction with and without a catalyst. Which...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.1j: In a third experiment, 0.100 g of a black powder was also added while all other...
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.17: Which factors can increase the rate of a chemical reaction? I. Increasing the pressure...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.1d: For this mixture the concentration of hydrogen peroxide,...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.1i: In a second experiment, the concentration of the hydrogen peroxide was decreased to...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.1c: The concentration of iodide ions, \({{\text{I}}^ - }\), is assumed to be constant. Outline...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.1h: The colour change occurs when \(1.00 \times {10^{ - 4}}{\text{ mol}}\) of iodine has been...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.1k: Explain why increasing the temperature also decreases the time required for the colour to...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.3a: Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\).
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.18: Which statement best describes and explains the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.17: Which graph best represents the relationship between the average kinetic energy of molecules...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8c.i: Deduce the effect of the concentration of...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8c.ii: Suggest why warm sodium hydroxide solution is used.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.2a: A catalyst provides an alternative pathway for a reaction, lowering the activation energy,...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ2.18: Which statements explain the increase in the rate of a reaction when the temperature is...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.2b: A catalyst provides an alternative pathway for a reaction, lowering the activation energy,...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.2c: Sketch two Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curves for a fixed amount of gas at two...
- 12N.2.hl.TZ0.6a: (i) Define the term rate of reaction. (ii) Temperature and the addition of a...
- 12N.2.hl.TZ0.6f.ii: Deduce the rate expression for each step. Step 1: Step 2:
- 12N.2.hl.TZ0.6b: (i) Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\). (ii) Sketch the two...
- 12N.2.hl.TZ0.6e.ii: Describe qualitatively the relationship between the rate constant, k, and temperature, T.
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.17: Which piece of equipment could not be used in an experiment to measure the rate of this...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.3c: (i) Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\). (ii) Sketch the two...
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.18: In which flask will the reaction between 2.0 g of magnesium carbonate and 25 cm3 1.0 mol...
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.6a: (i) Use the graph to deduce whether the forward reaction is exothermic or endothermic and...
- 10N.3.hl.TZ0.E4: (a) (i) Explain the dependence of the dissociation of diatomic oxygen, O2, and ozone,...
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.18: Which changes increase the rate of the reaction...
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.17: A piece of zinc was added to aqueous nitric acid and the volume of hydrogen gas produced was...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.6a: (i) Use the graph to deduce whether the forward reaction is exothermic or endothermic and...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.6e.v: Suggest, stating a reason, how the addition of a catalyst at constant pressure and...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.6a.ii: Predict the effect on the rate of the forward reaction and on the rate constant if the...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.6c: State two situations when the rate of a chemical reaction is equal to the rate constant.
- 09N.1.sl.TZ0.18: Hydrochloric acid is reacted with large pieces of calcium carbonate, the reaction is then...
- 09N.1.sl.TZ0.19: Which statement is true about using sulfuric acid as a catalyst in the following...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.5c.i: The concentration of \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) is increased at...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.5a.iv: Suggest, stating a reason, how the addition of a catalyst at constant pressure and...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.5b: Graphing is an important method in the study of the rates of chemical reaction. Sketch a...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.5c.ii: The solution of NaI is prepared from a fine powder instead of large crystals.
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.5d: Explain why the rate of a reaction increases when the temperature of the system increases.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.5a.ii: Sketch, on the same graph, the expected results if the experiment were repeated using...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.5a.i: Outline why the rate of the reaction decreases with time.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.17: Which methods can be used to monitor the progress of this...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.16: Which change does not increase the initial rate of reaction when CaCO3(s) is added to excess...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.1b: The student then carried out the experiment at other acid concentrations with all...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.2a: Explain why they added water to the mixtures.
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.2d: (i) This reaction uses a catalyst. Sketch and annotate the Maxwell-Boltzmann energy...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.2: (a) Discuss whether either Alex’s or Hannah’s hypothesis is correct. (b) Explain why...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.6c: (i) Explain the shape of the curve. (ii) Copy the above graph on your answer sheet...
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.18: Which unit could be used for the rate of a chemical reaction? A. mol B. ...
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.19: Which of the following can increase the rate of a chemical reaction? I. Increasing the...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.18: What is the best definition of rate of reaction? A. The time it takes to use up all the...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.19: Which factors can affect reaction rate? I. The state of the reactants II. The...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.20: Equal masses of powdered calcium carbonate were added to separate solutions of hydrochloric...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.1d: The reactants had to be stirred vigorously because they formed two distinct layers in the...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.1c.iv: State and explain the effect that the addition of the sodium hydroxide catalyst will have on...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.iii: The rate of this reaction in (a) (ii), can be studied by measuring the volume of gas...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.i: Define the term rate of reaction.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.iv: The experiment is repeated using a sample of hydrochloric acid with double the volume, but...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.ii: Construct the enthalpy level diagram and label the activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\), the...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.iii: Describe qualitatively the relationship between the rate constant, \(k\), and the...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.i: Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\).
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.17: Consider the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Which factors will affect the...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.5a.iv: State and explain the effect of a catalyst on the position of equilibrium.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.4a: Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\).
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.4b: State two conditions necessary for a reaction to take place between two reactant particles.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.5a.iii: State the effect of a catalyst on the value of \({K_{\text{c}}}\).
- 11M.1.hl.TZ1.20: Curve X on the graph below shows the volume of oxygen formed during the catalytic...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.18: Consider the reaction between gaseous iodine and gaseous...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.17: Which statements describe the action of a catalyst? I. It does not alter the...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.3d: A catalyst of copper mixed with zinc oxide and alumina is used in industry for this...
- 11M.1.hl.TZ2.20: Sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid react according to the equation...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.19: The reaction below represents the Haber process for the industrial production of...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6a.v: The reaction can be catalysed by adding platinum metal. State and explain what effect the...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.ii: List the three characteristic properties of reactant particles which affect the rate of...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.iv: Explain why coal dust burns much faster than a large piece of coal with the same mass.
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.iii: On the axes below sketch two Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curves for the same sample...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.i: Define the term rate of a chemical reaction.
- 12M.1.sl.TZ2.18: The following enthalpy level diagram shows the effect of the addition of a catalyst on a...
- 12M.1.sl.TZ2.17: Which are appropriate units for the rate of a reaction? A. ...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.1c: (i) Draw a curve on the graph opposite to show how the height of the bubble layer changes...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.1a: Explain why the curve reaches a maximum.
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.1b: Use the graph to calculate the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at 120 s.
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.17: A student added 0.20 g of calcium carbonate powder to...
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.18: Which statement about the kinetic theory is not correct? A. The particles in ice vibrate...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.1d.i: It takes just 0.0400 seconds to produce nitrogen gas in the simulation. Calculate the average...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.1d.ii: The students also discovered that a small increase in temperature (e.g. 10 °C) causes a large...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.6e.i: Define the term rate of reaction.
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.6b: Define the term activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\).
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.6d.ii: Sketch the Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curve for a reaction with and without a...

