| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.hl.TZ2.9 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 9 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Organic compounds often have isomers.
A straight chain molecule of formula C5H10O contains a carbonyl group. The compound cannot be oxidized by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution.
A tertiary halogenoalkane with three different alkyl groups, (R1R2R3)C−X, undergoes a SN1 reaction and forms two isomers.
Deduce the structural formulas of the two possible isomers.
Mass spectra A and B of the two isomers are given.
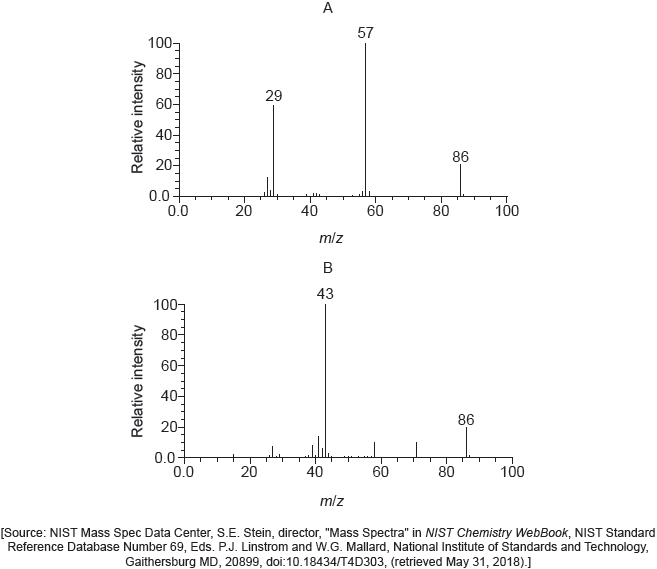
Explain which spectrum is produced by each compound using section 28 of the data booklet.
State the type of bond fission that takes place in a SN1 reaction.
State the type of solvent most suitable for the reaction.
Draw the structure of the intermediate formed stating its shape.
Suggest, giving a reason, the percentage of each isomer from the SN1 reaction.
Nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2, can be converted to phenylamine via a two-stage reaction.
In the first stage, nitrobenzene is reduced with tin in an acidic solution to form an intermediate ion and tin(II) ions. In the second stage, the intermediate ion is converted to phenylamine in the presence of hydroxide ions.
Formulate the equation for each stage of the reaction.
Markscheme
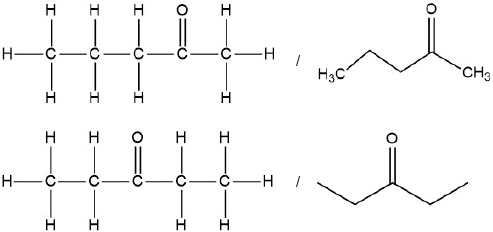
Accept condensed formulas.
[2 marks]
A:
CH3CH2COCH2CH3 AND «peak at» 29 due to
(CH3CH2)+/(C2H5)+/(M – CH3CH2CO)+
OR
CH3CH2COCH2CH3 AND «peak at» 57 due to
(CH3CH2CO)+/(M – CH3CH2)+/(M – C2H5)+
B:
CH3COCH2CH2CH3 AND «peak at» 43 due to
(CH3CH2CH2)+/(CH3CO)+/(C2H3O)+/(M – CH3CO)+
Penalize missing “+” sign once only.
Accept “CH3COCH2CH2CH3 by elimination since fragment CH3CO is not listed” for M2.
[2 marks]
heterolytic/heterolysis
[1 mark]
polar protic
[1 mark]
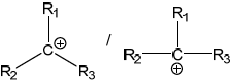
Shape: triangular/trigonal planar
[2 marks]
«around» 50% «each»
OR
similar/equal percentages
nucleophile can attack from either side «of the planar carbocation»
Accept “racemic mixture/racemate” for M1.
[2 marks]
Stage one:
C6H5NO2(l) + 3Sn(s) + 7H+(aq) → C6H5NH3+(aq) + 3Sn2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Stage two:
C6H5NH3+(aq) + OH–(aq) → C6H5NH2(l) + H2O(l)
[2 marks]

