| Date | May 2010 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 10M.3.sl.TZ2.G1 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Compare and Describe | Question number | G1 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Addition of hydrogen halides to unsymmetrical alkenes produces a mixture of halogenoalkanes. The latter can be converted into Grignard reagents by reaction with magnesium metal and then used for the preparation of various organic molecules with an increased number of carbon atoms.
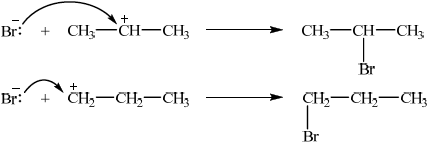
Describe, using equations and curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs, the mechanism of the reaction between propene and hydrogen bromide. Compare the relative stabilities of the two intermediate carbocations which lead to the formation of the major and minor products.
Markscheme
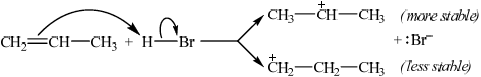
curly arrow showing movement of electron pair from the double bond to hydrogen in HBr;
formation of \({\text{B}}{{\text{r}}^ - }\);
OR
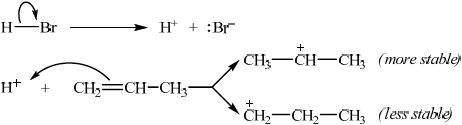
equation for HBr dissociation;
curly arrow showing movement of electron pair from the double bond to \({{\text{H}}^ + }\);
correct structures of both carbocations;
curly arrow showing either C–Br bond formation / mechanism for either product;
Award [3 max] for mechanism.
\({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{)}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}^ + }\) is more stable / \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH}}_2^ + \) is less stable;
Examiners report
A few candidates appeared to have encountered the reactions forming Grignard reagents, but hardly any could give the correct formulas of the products of their reactions.

