| Date | May 2014 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 14M.1.sl.TZ1.28 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Question number | 28 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Which type of halogenoalkane is the substance shown below, and which type of nucleophilic reaction does it undergo with an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution?
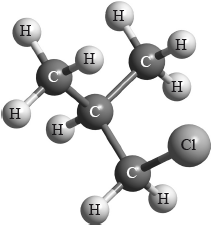
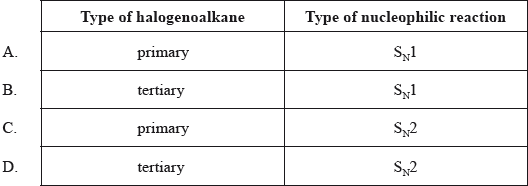
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
[N/A]
Syllabus sections
Show 77 related questions
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.8e: Explain the mechanism of the reaction between 2-bromo-2-methylpropane, (CH3)3CBr, and aqueous...
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.8d: State an equation for the formation of NO2+.
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.8c: State the reagents used in the nitration of benzene.
- 17N.1.hl.TZ0.35: What is the product of the reaction between pentan-2-one and sodium borohydride, NaBH4? A....
- 17N.1.hl.TZ0.33: Propene reacts separately with H2O/H+ and H2/Ni to give products X and Z...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7d: Below are two isomers, A and B, with the molecular formula C4H9Br. Explain the mechanism...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.i: State the reagents and the name of the mechanism for the nitration of benzene.
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.37: In which order should the reagents be used to convert benzene into phenylamine (aniline)?
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.7e: State the reagents used in the two-stage conversion of nitrobenzene to aniline.
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.7d: Explain the mechanism for the nitration of benzene, using curly arrows to show the movement...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.7c: State the reagents used to convert benzene to nitrobenzene and the formula of...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.6c.iii: When the product X is reacted with NaOH in a hot alcoholic solution, C2H3Cl is formed. State...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.36: What is the product of the reduction of 2-methylbutanal? A. 2-methylbutan-1-ol B. ...
- 16N.2.hl.TZ0.6c: Suggest why the rate of alkaline hydrolysis of an enantiomer of iodopropane is greater than...
- 16N.2.hl.TZ0.5d: Construct the mechanism of the formation of 2-bromopropane from hydrogen bromide and propene...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.2b: One important industrial use of phosgene is the production of polyurethanes. Phosgene is...
- 16M.1.hl.TZ0.36: ...
- 16M.1.hl.TZ0.35: ...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ1.36: What should be changed to alter the rate of nucleophilic substitution of tertiary...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ2.21: The hydrolysis of tertiary bromoalkanes with a warm dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide solution...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ2.37: What is the correct order for the increasing rate of hydrolysis of halogenoalkanes by dilute...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.6c: Explain why the rate of the reaction between iodomethane,...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.7b: Ethanol can be made by reacting aqueous sodium hydroxide with bromoethane. Explain the...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10c.i: Compound C, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{OH}}\), can also be formed...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10c.ii: Explain why the hydroxide ion is a better nucleophile than water.
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.29: Which combination best describes the substitution reaction between bromoethane and dilute...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.8d.i: Deduce the mechanism for the reaction using equations and curly arrows to represent the...
- 14M.3.hl.TZ2.27a: (i) Identify the two reagents used to form the electrophile in the nitration of...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.26: In organic reaction mechanisms, what does a curly arrow represent? A. The movement of a...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.7d: (i) Identify the reagent necessary for this reaction to occur. (ii) Deduce the...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6d: (i) State the reagent required. (ii) Explain the mechanism of this reaction,...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.10d: Transition metals and their compounds often catalyse reactions. The catalyzed decomposition...
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.29: Chloroethane, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}\), reacts with...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.7d: Explain the mechanism for the substitution reaction of bromoethane with sodium hydroxide. Use...
- 14N.3.sl.TZ0.26d: Propanone could also be formed from propene by reaction with steam over an acidic catalyst,...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.38: What is the major organic product formed from the reaction of (CH\(_3\))\(_3\)CBr with a...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.8e.i: Explain the mechanism of this reaction using curly arrows to represent the movement of...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.8e.iii: Suggest why, for some other halogenoalkanes, this hydrolysis is much more effective in...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.8g.ii: State the reagent and any catalyst required for both the formation of Y and the conversion of...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.8g.i: Draw the structure of Y.
- 13M.1.hl.TZ1.37: Which factors affect the rate of nucleophilic substitution in halogenoalkanes? I. The...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.9d.iii: Identify the rate-determining step of this mechanism.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.9d.ii: Halogenalkanes can react with NaOH via \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\) and...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8d: Explain the mechanism for the reaction in (c) of...
- 13M.1.hl.TZ2.37: Which halogenoalkane reacts the fastest with hydroxide ions in a nucleophilic substitution...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.vi: Explain one suitable mechanism for the reaction in (v) using curly arrows to represent the...
- 10N.3.hl.TZ0.G1d: Identify the organic product in the following...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.5e: (i) State the meaning of each of the symbols in SN2. (ii) Explain the mechanism of...
- 10N.3.sl.TZ0.G2a: ...
- 09N.1.hl.TZ0.34: Which reaction occurs via a free-radical mechanism? A. ...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.9c.i: State whether this reaction is SN1 or SN2.
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.9c.ii: Explain the mechanism of the reaction using curly arrows to represent the movement of...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.7b.i: Identify the isomer(s) which will react with aqueous sodium hydroxide almost exclusively by...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.7b.ii: Using the formula RBr to represent a bromoalkane, state an equation for the rate determining...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.7b.iii: Identify one isomer that will react with aqueous sodium hydroxide almost exclusively by an...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.7c: State and explain how the rates of the reactions in parts (b) (i) and (b) (iii) are affected...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.7d: State and explain how the rate of reaction of 1-bromobutane with sodium hydroxide compares...
- 10M.3.hl.TZ1.G3b: Methylbenzene reacts when heated with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.6d: (i) Isomer a is formed by reacting 1-bromobutane with aqueous sodium hydroxide. State...
- 10M.3.sl.TZ1.G2c: When but-1-ene reacts with hydrogen bromide, two possible organic products could be formed...
- 10M.3.sl.TZ2.G1b: Describe, using equations and curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs, the...
- 09M.1.hl.TZ1.37: Which statements about substitution reactions are correct? I. The reaction between...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.9a.ii: Identify the type of reaction and explain the mechanism for the preparation of but-1-ene from...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.9a.iii: State the equation (using structural formulas) for the preparation of 1-aminobutane from...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.9a.iv: Explain the mechanism for the preparation of 1-aminobutane from 1-bromobutane using curly...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.9b.iii: Explain why the mechanism of the reaction will be different if 1-bromobutane is replaced by...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.8c: The reagents used in an elimination reaction are shown below. Explain the mechanism of...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.7d.i: 2-chloro-3-methylbutane reacts with sodium hydroxide via an...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.7d.ii: Explain why the hydroxide ion is a better nucleophile than water.
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.27: What is the type of mechanism and an important feature of the reaction between...
- 11M.1.hl.TZ2.37: Propanitrile can be prepared by reacting bromoethane with potassium cyanide. Which statement...
- 11M.1.hl.TZ2.36: Halogenoalkanes can undergo \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\) and...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.i: The reaction with 1-bromopentane proceeds by an \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\)...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.ii: The reaction with 2-bromo-2-methylbutane proceeds by an \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\)...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.iii: Explain why 1-bromopentane reacts by an \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\) mechanism...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.29: Which type of reaction occurs when 2-iodo-2-methylpropane,...
- 11N.1.hl.TZ0.37: Which halogenoalkane reacts fastest with sodium hydroxide? A. 1-iodobutane B. ...

