Assess your score
View Answer
b)
State the type of system in which the total amount of matter present is always constant.
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
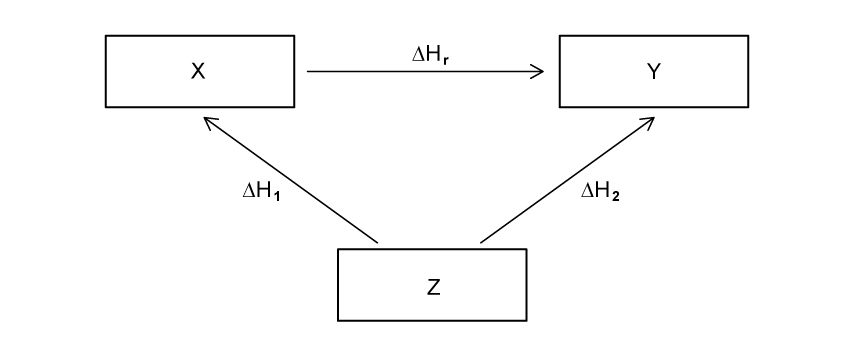
Using the image below, construct an equation that can be used to determine ΔHr from ΔH1 and ΔH2 .
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
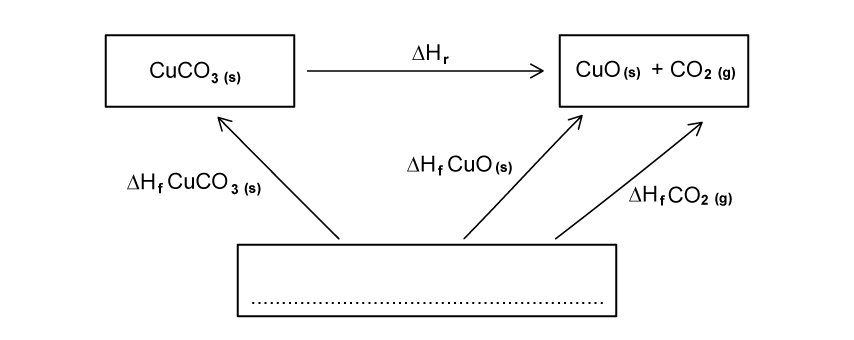
Complete the following Hess’s Law cycle for the decomposition of copper carbonate.
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
Define standard enthalpy of formation, ΔHf .
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Write an equation to show the enthalpy of formation of 1 mole of the following compounds. Include state symbols in your equations.
Methanol, CH3 OH ………………………………..
Carbon dioxide, CO2 ………………………………..
Ethane, C2 H6 ………………………………..
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Using the equations given, construct a Hess’s Law cycle for the following reaction. Include the values for ΔHf in your cycle.
BaCl2 (s) + Zn (s) → Ba (s) + ZnCl2 (s)
Ba (s) + Cl2 (g) → BaCl2 (s) ΔHf = -858.6 kJ mol-1
Zn (s) + Cl2 (g) → ZnCl2 (s) ΔHf = -415.1 kJ mol-1
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Calculate the enthalpy of reaction, ΔHr , for the reaction given in part (c).
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Aluminium oxide reacts with magnesium to form magnesium oxide and aluminium in a displacement reaction via the following reaction.
Construct a Hess’s Law cycle for this reaction
Al2 O3 (s) + 3Mg (s) → 3MgO (s) + 2Al (s)
Enthalpy of formation Enthalpy of formation (kJ mol-1 )
ΔHf (Al2 O3 )
-1675.7
ΔHf (MgO)
-601.7
ΔHf (Mg)
ΔHf (Al)
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Outline why no values are listed for Al (s) and Mg (s) in the table given in part (a).
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Calculate the enthalpy change of reaction, ΔHr , for the reaction in part (a).
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Determine the enthalpy change of reaction, ΔHr , for the following equations if they are reversed.
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl ΔHr = -790 kJ ……………………….
C2 H4 + H2 → C2 H6 ΔHr = -65.6 kJ ………………………
2H 2 O → 2H 2 + O2 ΔHr = +571 kJ ……………………….
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Using the information given in part (a), determine the enthalpy change for the following reaction.
2C2 H4 + 2H2 → 2C2 H6
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Using the information in the table, deduce which equation should be reversed to determine the enthalpy change for the following reaction.
SiO2 + 3C → SiC + 2CO
Equation number Equation Enthalpy change (kJ)
1
Si + O2 → SiO2
-911
2
2C + O2 → 2CO
-211
3
Si + C → SiC
-65.3
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Use the information in part (c) to produce an overall cancelled down equation which can be used to determine the overall enthalpy change for the following reaction.
SiO2 + 3C → SiC + 2CO
Assess your score
View Answer
e)
Deduce the overall enthalpy change, in kJ, using the information in part (c) for the reaction SiO2 + 3C → SiC + 2CO
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
State the equation required to calculate the enthalpy change of reaction, ΔHr , given enthalpy of formation, ΔH f
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Using section 12 in the data booklet and the data in the table calculate the enthalpy change of reaction, ΔHr , for the following reaction.
SO2 (g) + 2H2 S (g) → 3S (s) + 2H2 O (l)
SO2 (g) H2 S (g)
ΔH f (kJ mol-1 ) -297
-20.2
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Show how the equations can be used to produce an alternative route for this reaction .
C2 H4 + H2 → C2 H6
ΔH (kJ mol-1 )
C2 H4 + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 2H2 O
-1411
C2 H6 + 3½O2 → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2 O
-1560
H2 + ½O2 → H2 O
-285.8
Assess your score
View Answer
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question