Question 1a
a)
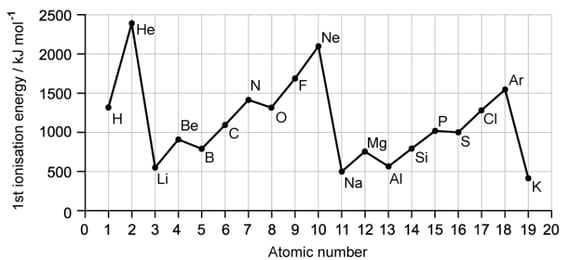
This question refers to the elements in the first three periods of the Periodic Table.
Select an element from the first three periods that fits each of the following descriptions.
i)
The element with the highest first ionisation energy
[1]
ii)
The element that forms a 1− ion with the same electron configuration as helium
[1]
iii)
An element which forms a compound with hydrogen in which the element has an oxidation number of −4
[1]
Question 1b
b)
This question is about the elements which have atomic numbers 33 to 37.
The first ionisation energies of these elements are shown in the table below.
|
Element |
As |
Se |
Br |
Kr |
Rb |
|
Ionisation energy value in kJ /mol-1 |
947 |
941 |
1340 |
1351 |
403 |
i)
Suggest the formulae of the hydrides of arsenic and selenium
[2]
ii)
Explain why the first ionisation energy of rubidium is lower than that of krypton
[2]
iii)
State which of the elements, arsenic to rubidium, has atoms with the smallest atomic radius
[1]
Question 1c
c)
The first 3 elements of Period 3 show a general increase in melting point.
Explain this trend in melting point across these Period 3 elements.
Question 1d
d)
This question is about hydrogen, the element with the atomic number Z = 1.
Hydrogen can be placed in several different positions in periodic tables. One is immediately above lithium in Group 1 as shown in section 6 of the data booklet. Another is in the centre of the first row.
Evaluate the position of hydrogen when it is placed immediately above lithium and state one reason in favour and two against.
[3]