DP Chemistry Questionbank

Topic 11: Measurement and data processing
Description
[N/A]Directly related questions
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.29: What is always correct about the molecular ion, M+, in a mass spectrum of a compound? A. The M+...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.3g: Suggest one reason why the values of rates of reactions obtained at higher temperatures may be...
-
16N.3.sl.TZ0.1b:
CT values are influenced by temperature and by pH. The table below shows the CT values for chlorine needed to achieve 99% inactivation of a specific bacterium at stated values of pH and temperature.
(i) With reference to the temperature data in the table, suggest why it may be more difficult to treat water effectively with chlorine in cold climates.
(ii) Sketch a graph on the axes below to show how the CT value (at any temperature) varies with pH.
(iii) Comment on the relative CT values at pH 6.0 and pH 9.0 at each temperature.
(iv) Chlorine reacts with water as follows:
Cl2 (g) + H2O (l) HOCl (aq) + HCl (aq)
HOCl (aq) OCl− (aq) + H+ (aq)
Predict how the concentrations of each of the species HOCl (aq) and OCl− (aq) will change if the pH of the disinfected water increases.
-
16N.1.sl.TZ0.30:
A student measured the change in mass on heating a sample of calcium carbonate, CaCO3(s). What is the mass loss?
Mass before heating: 2.347 g ± 0.001
Mass after heating: 2.001 g ± 0.001A. 0.346g ± 0.001
B. 0.346g ± 0.002
C. 0.35g ± 0.002
D. 0.35g ± 0.001
-
16N.1.sl.TZ0.28:
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) for this molecule?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
-
20N.1.sl.TZ0.28:
A student obtained the following data to calculate , using .
What is the percentage uncertainty in the calculated value of ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.sl.TZ0.29:
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) in cyclohexanol?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.sl.TZ0.1d(vi):
Deduce the number of signals and their chemical shifts in the spectrum of ethoxyethane. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
-
20N.2.sl.TZ0.2b:
The IR spectrum of one of the compounds is shown:
COBLENTZ SOCIETY. Collection © 2018 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved.
Deduce, giving a reason, the compound producing this spectrum. -
20N.2.hl.TZ0.2d:
The IR spectrum of one of the compounds is shown:
COBLENTZ SOCIETY. Collection © 2018 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved.
Deduce, giving a reason, the compound producing this spectrum.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.5f(ii):
Potassium hydroxide solutions can react with carbon dioxide from the air. The solution was made one day prior to using it in the titration.
Predict, giving a reason, the effect of this error on the calculated concentration of ethanoic acid in 5(e).
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.1d(v):
Deduce the number of signals and chemical shifts with splitting patterns in the 1H NMR spectrum of ethoxyethane. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
- 20N.2.hl.TZ0.5f(i): Potassium hydroxide solutions can react with carbon dioxide from the air. The solution was made...
- 20N.3.sl.TZ0.1d: Suggest one source of error in the experiment, excluding faulty apparatus and human error, that...
-
20N.3.sl.TZ0.2e:
Calculate the percentage uncertainty and percentage error in the experimentally determined value of for methanol.
- 20N.1.sl.TZ0.30: Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum is used to identify hydrogen environments in a...
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.28:
What can be determined about a molecule from the number of signals in its 1HNMR spectrum?
A. Bonds present
B. Molecular formula
C. Molecular mass
D. Number of hydrogen environments
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.29:
What is the density, in gcm−3, of a 34.79 g sample with a volume of 12.5 cm3?
A. 0.359
B. 0.36
C. 2.783
D. 2.78
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
What is the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) for 1,3,5-hexatriene (C6H8)?
A. 1
B. 3
C. 5
D. 6
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.23: The graph shows values of ΔG for a reaction at different temperatures. Which statement is...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.38: The molar mass of a gas, determined experimentally, is 32 g mol−1. Its literature molar mass is...
-
17M.1.hl.TZ1.40:
Which technique is used to determine the bond lengths and bond angles of a molecule?
A. X-ray crystallography
B. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy
C. Mass spectroscopy
D. 1H NMR spectroscopy
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.1a.ii:
A student produced these results with [H+] = 0.15 moldm−3. Propanone and acid were in excess and iodine was the limiting reagent.
Determine the relative rate of reaction when [H+] = 0.15 moldm−3.
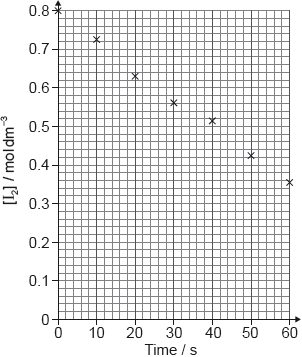
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.5c.ii:
The mass and 1HNMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its structural formula and hence the name of the compound.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.6c.ii:
The mass and 1H NMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its structural formula and hence the name of the compound.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.1a:
Calculate the percentage uncertainty of the volume of the aqueous sodium hydroxide.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.1b:
Suggest how the precision of this measurement could be improved.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.3:
Suggest how the end point of the titration might be estimated from the graph.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.4:
State and explain how the graph would differ if 1 moldm−3 sulfuric acid had been used instead of 1 moldm−3 hydrochloric acid.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.5b:
Heat losses would make this method less accurate than the pH probe method. Outline why the thermometric method would always give a lower, not a higher, concentration.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.5f:
Outline why the thermochemical method would not be appropriate for 0.001 moldm−3 hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide of a similar concentration.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.10a:
Below are the IR spectra of two plastics (A and B); one is PETE, the other is low density polyethene (LDPE).
Deduce, giving your reasons, the identity and resin identification code (RIC) of A and B using sections 26 and 30 of the data booklet.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.18a:
Dose response curves are determined for each drug.
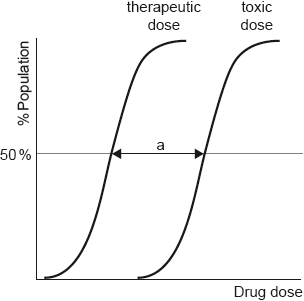
Outline the significance of range “a”.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.19d:
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16a:
Explain the shape of the curve at low oxygen partial pressure up to about 5 kPa.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16b.i:
Sketch a graph on the axes above to show the effect of decreasing pH on the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin (the Bohr Effect).
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16b.ii:
Outline the effect of decreasing pH on the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin.
-
17M.1.sl.TZ2.28:
Which information can be gained from an infrared (IR) spectrum?
A. Ionization energy of the most abundant element
B. Number of different elements in the compound
C. Bonds present in a molecule
D. Molecular formula of the compound
-
17M.1.sl.TZ2.29:
What can be deduced from the following 1HNMR spectrum?
A. There is only one hydrogen atom in the molecule.
B. There is only one hydrogen environment in the molecule.
C. The molecule is a hydrocarbon.
D. There is only one isotope in the element.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.30: What is the graphical relationship between n and T in the ideal gas equation, pV = nRT, all other...
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.1a.ii:
Suggest why the final mass of solid obtained by heating 3.760 g of AgxOy may be greater than 3.275 g giving one design improvement for your proposed suggestion. Ignore any possible errors in the weighing procedure.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.2b.i:
Calculate the percentage uncertainty for the mass of K2Cr2O7(s) from the given data.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.8b:
Identify the species responsible for the peak at m/z = 110 in the mass spectrum of hydroquinone.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.8c:
Identify the highest m/z value in the mass spectrum of quinone.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.i:
Deduce what information can be obtained from the 1H NMR spectrum.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.ii:
Identify the functional group that shows stretching at 1710 cm–1 in the infrared spectrum of this compound using section 26 of the data booklet and the 1H NMR.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.1a:
The following graph represents world energy consumption by type for the years 1988–2013.
Estimate the percentage of energy consumption which did not directly produce CO2 in 2013.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.1b:
O2 is consumed in producing CO2 for electricity generation. The graph shows the relationship between the world’s electricity generation and CO2 production between 1994 and 2013.
Calculate the mass, in million tonnes, of oxygen gas ultimately found in CO2 which is consumed in generating 18000 terawatts of electricity using the equation given for the best fit line. Give your answer to 2 significant figures.
Assume coal is the only energy source.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.1c.iii:
The change in APO O2/N2 ratio, per meg, is measured relative to an O2/N2 reference.
Calculate the APO Δ(O2/N2) value for an oxygen concentration of 209400 ppm assuming that any change in N2 concentration is negligible. Reference values for O2 and N2 are 209 460 and 790 190 ppm respectively.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.2b.ii:
Suggest one improvement to the investigation.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.4:
Infrared (IR) spectra can be used to distinguish between various types of plastics. Some simplified IR spectra are given here.
Explain, with a reference to molecular structure, which two of the plastics can not be distinguished by IR spectroscopy.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.18a.ii:
Deduce the wavenumber of one absorbance seen in the IR spectrum of only one of the compounds, using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.20a.iii:
Suggest two absorbances, other than the absorbances due to the ring structure and C–H bonds, that would be present in the infrared (IR) spectrum of aspirin.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.21c.i:
Predict the number of different hydrogen environments in the molecule ignoring the benzene rings.
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.1a: Using the graph, estimate the initial temperature of the solutions.
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.1b: Determine the maximum temperature reached in each experiment by analysing the graph.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.iii: Deduce the number of signals and the ratio of areas under the signals in the 1H NMR spectra of...
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.1b.ii: State the equation of the straight line obtained using the data.
-
17N.1.sl.TZ0.29:
What information is provided by 1H NMR, MS and IR for an organic compound?
I. 1H NMR: chemical environment(s) of protons
II. MS: fragmentation pattern
III. IR: types of functional groupA. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
17N.3.sl.TZ0.7b.ii:
One of the two infrared (IR) spectra is that of polyethene and the other of polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE).
Deduce, with a reason, which spectrum is that of PTFE. Infrared data is given in section 26 of the data booklet.
- 17N.3.hl.TZ0.22a.i: Both spectra show a peak at wavenumber 1700 cm–1. Identify the bond responsible for this peak.
-
17N.3.hl.TZ0.22a.ii:
Deduce which spectrum belongs to paracetamol, giving two reasons for your choice. Use section 26 of the data booklet.
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.30: A student performs an acid-base titration using a pH meter, but forgets to calibrate it. Which...
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.1a: Using the graph, estimate the initial temperature of the solution.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.1b: Determine the maximum temperature reached in the experiment by analysing the graph.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.1b.i: Suggest what the correlation coefficient of −0.9999 indicates.
-
17N.3.sl.TZ0.3c:
Calculate the percentage of water by mass in the NaCl•2H2O crystals. Use the data from section 6 of the data booklet and give your answer to two decimal places.
-
17N.3.sl.TZ0.2c:
Calculate the uncertainty in the change in pH.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.3a: Estimate the lowest freezing point of water that can be reached by adding sodium chloride.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.3b: Estimate the percentage by mass of NaCl dissolved in a saturated sodium chloride solution at +10 ºC.
- 21M.1.sl.TZ1.29: Burette readings for a titration are shown. What is the mean titre? A. 11.1 cm3 ±...
-
21M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
Determine the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) of paracetamol.
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
- 21M.1.sl.TZ1.28: The enthalpy of combustion of a fuel was determined using the calorimeter shown. The final result...
- 21M.1.sl.TZ2.30: A liquid was added to a graduated cylinder. What can be deduced from the graph?
- 21M.1.sl.TZ2.29: How should the difference between 27.0 ± 0.3 and 9.0 ± 0.2 be shown? A. 18.0 ± 0.1 B. 18.0 ±...
-
21M.1.sl.TZ2.28:
Which spectra would show the difference between propan-2-ol, CH3CH(OH)CH3, and propanal, CH3CH2CHO?
I. mass
II. infrared
III. 1H NMRA. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
21M.2.sl.TZ1.6b(ii):
Deduce the relationship between the concentration of N2O5 and the rate of reaction.
- 21M.2.sl.TZ1.5b: Justify why ethene has only a single signal in its 1H NMR spectrum.
- 21M.2.hl.TZ1.5b(i): Justify why ethene has only a single signal in its 1H NMR spectrum.
- 21M.2.sl.TZ2.4e(i): Deduce two features of this molecule that can be obtained from the mass spectrum. Use section 28...
- 21M.2.sl.TZ2.4e(ii): Identify the bond responsible for the absorption at A in the infrared spectrum. Use section 26 of...
-
21M.2.sl.TZ2.4e(iii):
Deduce the identity of the unknown compound using the previous information, the 1H NMR spectrum and section 27 of the data booklet.
SDBS, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST).
- 21M.2.hl.TZ2.4g(i): Deduce two features of this molecule that can be obtained from the mass spectrum. Use section 28...
- 21M.2.hl.TZ2.4g(ii): Identify the bond responsible for the absorption at A in the infrared spectrum. Use section 26 of...
-
21M.2.hl.TZ2.4g(iii):
Deduce the identity of the unknown compound using the previous information, the 1H NMR spectrum and section 27 of the data booklet.
SDBS, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST).
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.4c:
Predict from your line of best fit the rate of reaction when the concentration of HCl is 1.00 mol dm−3.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1k:
The IR spectrum of urea is shown below.
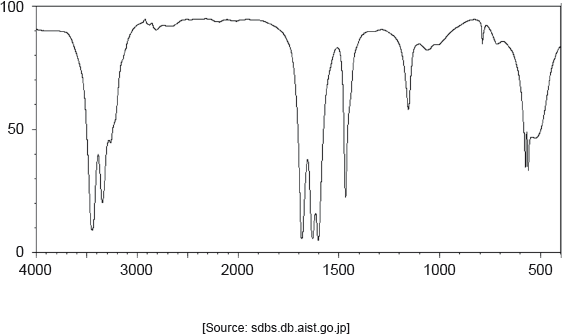
Identify the bonds causing the absorptions at 3450 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1j:
The mass spectrum of urea is shown below.
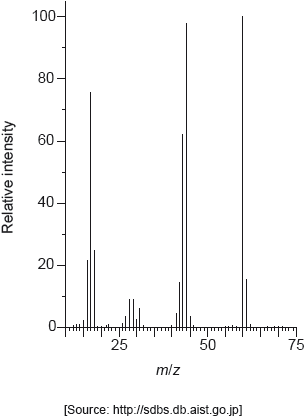
Identify the species responsible for the peaks at m/z = 60 and 44.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1l.i:
Predict the number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.4b.ii:
Draw the best fit line for the reaction excluding point D.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ1.1h:
The IR spectrum of urea is shown below.
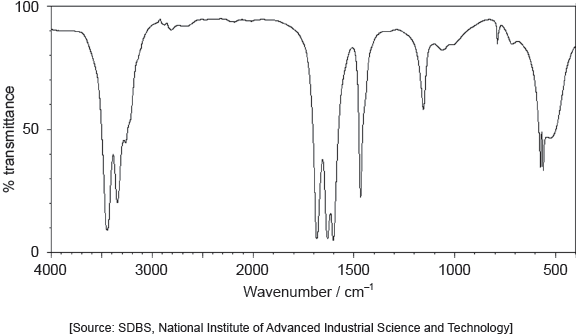
Identify the bonds causing the absorptions at 3450 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 using section 26 of the data booklet.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.13: The enthalpy of combustion of ethanol is determined by heating a known mass of tap water in a...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.29: What is the index of hydrogen deficiency, IHD, of 3-methylcyclohexene? A. 0 B. 1 C. ...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.28: Which value of q, in J, has the correct number of significant figures? q = mcΔT where m = 2.500...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.30: What is the ratio of the areas of the signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of pentan-3-ol? A. ...
-
18M.2.sl.TZ1.1g:
The mass spectrum of urea is shown below.
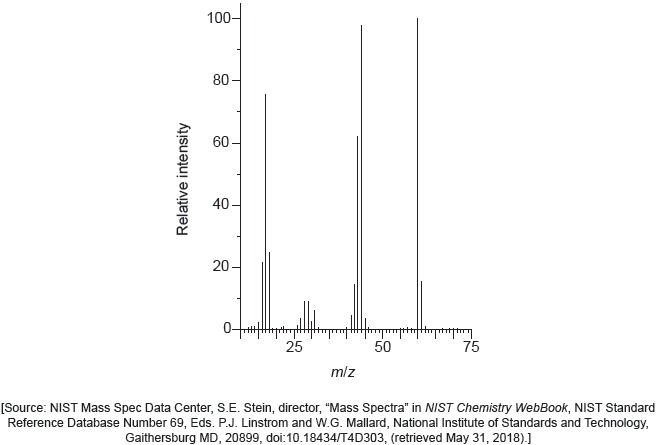
Identify the species responsible for the peaks at m/z = 60 and 44.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ1.1i:
Predict the number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
-
18M.3.sl.TZ1.2d.i:
Justify why it is inappropriate to record the uncertainty of the mean as ±0.01 s.
-
18M.3.sl.TZ1.2d.ii:
If doubling the concentration doubles the reaction rate, suggest the mean time you would expect for the reaction with 2.00 mol dm−3 hydrochloric acid.
-
18M.3.sl.TZ1.2d.iii:
Another student, working alone, always dropped the marble chips into the acid and then picked up the stopwatch to start it. State, giving a reason, whether this introduced a random or systematic error.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.28: Which feature of a molecule does infrared spectrometry detect? A. molecular mass B. ...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.29: How are the uncertainties of two quantities combined when the quantities are multiplied...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.30: The rate of a reaction is studied at different temperatures. Which is the best way to plot the...
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.i:
Deduce the molecular formula of the compound.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.ii:
Identify the bonds causing peaks A and B in the IR spectrum of the unknown compound using section 26 of the data booklet.
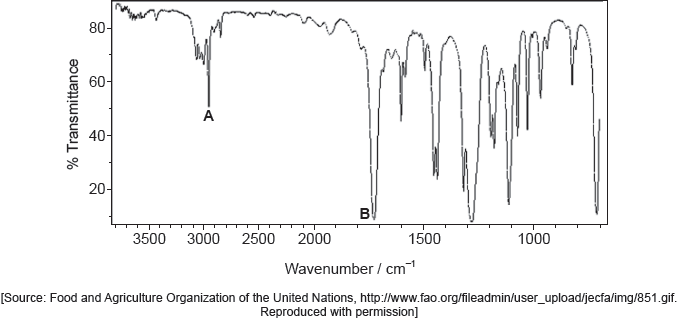
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.iii:
Deduce full structural formulas of two possible isomers of the unknown compound, both of which are esters.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.iv:
Deduce the formula of the unknown compound based on its 1H NMR spectrum using section 27 of the data booklet.
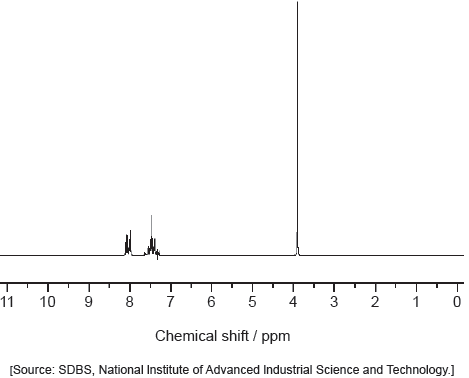
-
18M.3.sl.TZ2.7b:
Deduce the number of 1H NMR signals produced by the zwitterion form of alanine.
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.5: Consider the mass spectrum of an element: What is the relative atomic mass of this...
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.29: Which graph shows the relationship between the pressure and volume of a sample of gas at constant...
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.28: What is the slope of the graph? A. −0.0025 mol dm−3 s−1 B. −0.0025 mol dm−3 s C. ...
-
21N.1.sl.TZ0.30:
What can be deduced from the mass spectrum of CH3COCH2CH2CH3?
NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection (C) 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved. 2-Pentanone Mass Spectrum, MS Number 291264. [graph] Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C107879&Units=SI&Mask=200#Mass-Spec2-pentanone [Accessed 4 May 2020]. source adapted.
A. The molar mass is 43 g mol−1.B. The atoms have many isotopes.
C. The most likely bond to break is C–C between carbons 2 and 3.
D. The signal with the largest mass is due to the oxidation of the ketone in the spectrometer.
-
21N.1.hl.TZ0.23:
The graph shows Gibbs free energy of a mixture of N2O4 (g) and NO2 (g) in different proportions.
N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
Which point shows the system at equilibrium?
-
21N.2.sl.TZ0.1c:
Identify each compound from the spectra given, use absorptions from the range of 1700 cm−1 to 3500 cm−1. Explain the reason for your choice, referring to section 26 of the data booklet.
-
21N.2.sl.TZ0.6b:
A student dissolved 0.1240 ± 0.0001 g of Na2S2O3 to make 1000.0 ± 0.4 cm3 of solution to use in the Winkler Method.
Determine the percentage uncertainty in the molar concentration.
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.1c:
Identify each compound from the spectra given, use absorptions from the range of 1700 cm−1 to 3500 cm−1. Explain the reason for your choice, referring to section 26 of the data booklet.
- 21N.2.hl.TZ0.1e: Predict the fragment that is responsible for a m/z of 31 in the mass spectrum of propan‑1‑ol. Use...
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.6b:
A student dissolved 0.1240 ± 0.0001 g of Na2S2O3 to make 1000.0 ± 0.4 cm3 of solution to use in the Winkler Method.
Determine the percentage uncertainty in the molar concentration.
-
18N.3.hl.TZ0.1b:
Deduce the equation for the relationship between absorbance and concentration.
-
18N.2.sl.TZ0.1b.iii:
The only significant uncertainty is in the temperature measurement.
Determine the absolute uncertainty in the calculated value of ΔH if the uncertainty in the temperature rise was ±0.2 °C.
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.6c:
Sketch the pH curve for the titration of 25.0 cm3 of ethylamine aqueous solution with 50.0 cm3 of butanoic acid aqueous solution of equal concentration. No calculations are required.
-
18N.2.sl.TZ0.1c.i:
Sketch a graph of the concentration of iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4, against time as the reaction proceeds.
-
18N.3.sl.TZ0.1d.ii:
Deduce the appropriate number of significant figures for your answer in (d)(i).
- 18N.2.hl.TZ0.2c: The mass spectrum of the compound is shown. Deduce the relative molecular mass of the compound.
-
18N.3.sl.TZ0.1d.i:
The original piece of brass weighed 0.200 g. The absorbance was 0.32.
Calculate, showing your working, the percentage of copper by mass in the brass.
-
18N.3.hl.TZ0.1e.ii:
Deduce the appropriate number of significant figures for your answer in (e)(i).
- 18N.2.hl.TZ0.2b: The infrared spectrum of the compound is shown. Deduce the functional group of the compound.
- 18N.1.sl.TZ0.29: What is the ratio of areas under each signal in the 1H NMR spectrum of 2-methylbutane? A. 6...
- 18N.1.sl.TZ0.30: What are the absolute and percentage uncertainties for the change in mass? Initial mass: 22.35...
-
18N.2.sl.TZ0.1c.ii:
Outline how the initial rate of reaction can be determined from the graph in part (c)(i).
-
18N.3.hl.TZ0.1e.i:
The original piece of brass weighed 0.200 g. The absorbance was 0.32.
Calculate, showing your working, the percentage of copper by mass in the brass.
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.1b.iii:
The only significant uncertainty is in the temperature measurement.
Determine the absolute uncertainty in the calculated value of ΔH if the uncertainty in the temperature rise was ±0.2 °C.
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.1c.i:
Sketch a graph of the concentration of iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4, against time as the reaction proceeds.
- 18N.1.sl.TZ0.28: Which is correct for the spectra of organic compounds? A. Mass spectroscopy provides...
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.1c.ii:
Outline how the initial rate of reaction can be determined from the graph in part (c)(i).
-
18N.3.sl.TZ0.1b:
Deduce the equation for the relationship between absorbance and concentration.
-
22M.1.sl.TZ1.28:
A student performed an experiment to find the melting point of sulfur, obtaining 118.0 °C. The literature value is 115.2 °C. What was the percentage error?
A.B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.sl.TZ1.29:
Which compound produces this mass spectrum?
[Spectral Database for Organic Compounds, SDBS. SDBS Compounds and Spectral Search. [graph] Available at:
https://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp [Accessed 3 January 2019].] -
22M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) of this molecule?
Paracetamol (acetaminophen)
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.25c:
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.3: Which graph represents the relationship between the amount of gas, n, and the absolute...
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.28: How many signals are observed in the 1H NMR spectrum of this compound?A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
-
22M.1.sl.TZ2.30:
20 cm3 of 1 mol dm−3 sulfuric acid was added dropwise to 20 cm3 of 1 mol dm−3 barium hydroxide producing a precipitate of barium sulfate.
H2SO4 (aq) + Ba(OH)2 (aq) → 2H2O (l) + BaSO4 (s)
Which graph represents a plot of conductivity against volume of acid added?
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.17: A reaction has an activation energy of 40 kJ mol−1 and an enthalpy change of −60 kJ mol−1. Which...
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.29: What is the uncertainty, in cm3, of this measurement?A. ±0.01 B. ±0.1 C. ±0.15 D. ±1
- 22M.1.hl.TZ2.20: Which energy profile diagram represents an exothermic SN1 reaction?
-
22M.1.hl.TZ2.40:
Given equimolar concentrations, which substance would produce the strongest signal in a 1H NMR spectrum?
A. (CH3)3CHB. C6H6
C. C8H18
D. Si(CH3)4
-
22M.2.sl.TZ1.1b(ii):
Determine the percentage uncertainty of the mass of product after heating.
-
22M.2.sl.TZ1.1c(ii):
Suggest an explanation, other than product being lost from the crucible or reacting with nitrogen, that could explain the yield found in (b)(iii).
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.1b(ii):
Determine the percentage uncertainty of the mass of product after heating.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.1c(ii):
Suggest an explanation, other than product being lost from the crucible or reacting with nitrogen, that could explain the yield found in (b)(iii).
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.2c(iii):
Carbonates also react with HCl and the rate can be determined by graphing the mass loss. Suggest why this method is less suitable for the reaction of Mg with HCl.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.2c(i):
Use the graph to deduce the dependence of the reaction rate on the amount of Mg.
-
22M.2.sl.TZ2.4d(iv):
Suggest two differences in the 1H NMR of but-2-ene and the organic product from (d)(ii).
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.8d(iv):
Suggest two differences in the 1H NMR of but-2-ene and the organic product from (d)(ii).
-
22M.2.sl.TZ2.1b(iii):
Suggest a reason why the volume of hydrogen gas collected was smaller than predicted.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.1a:
State the number of 1H NMR signals for this isomer of xylene and the ratio in which they appear.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.4b(i):
In a laboratory experiment solutions of potassium iodide and hydrogen peroxide were mixed and the volume of oxygen generated was recorded. The volume was adjusted to 0 at t = 0.
The data for the first trial is given below.
Plot a graph on the axes below and from it determine the average rate of
formation of oxygen gas in cm3 O2 (g) s−1.Average rate of reaction:
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.2e:
The experiment gave an error in the rate because the pressure gauge was inaccurate.
Outline whether repeating the experiment, using the same apparatus, and averaging the results would reduce the error.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.1b(i):
Describe the density trend across periods 4 and 5 of the periodic table.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.5d(iv):
The uncertainty of the 100.0cm3 volumetric flask used to make the solution was ±0.6cm3.
Calculate the maximum percentage uncertainty in the mass of NaHCO3 so that the concentration of the solution is correct to ±1.0 %.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.1b(iii):
Compare the ease of oxidation of s-block and d-block metals to their melting points and densities. Use section 25 of the data booklet.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.2c(i):
Describe one systematic error associated with the use of the gas syringe, and how the error affects the calculated rate.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.2c(ii):
Identify one error associated with the use of an accurate stopwatch.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.5b:
The infrared (IR) spectrum of polyethene is given.
Suggest how the IR spectrum of polychloroethene would diff er, using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
19M.1.hl.TZ1.39:
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O2 (g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 (aq).
Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
- 19M.1.hl.TZ1.38: How should a measurement of 5.00 g from a balance be recorded? A. 5.00 ± 0.1 g B. 5.00 ± 0.01...
- 19M.1.hl.TZ2.38: The following data were recorded for determining the density of three samples of silicon,...
-
19M.1.hl.TZ2.39:
What can be deduced from the infrared (IR) spectrum of a compound?
A. Number of hydrogens
B. Number of hydrogen environments
C. Bonds present
D. Molar mass
-
19M.1.hl.TZ2.40:
Which technique involves breaking covalent bonds when carried out on an organic compound?
A. infrared spectroscopy
B. nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
C. X-ray crystallography
D. mass spectrometry
-
19M.2.sl.TZ1.1a:
State the number of 1H NMR signals for this isomer of xylene and the ratio in which they appear.
Number of signals:
Ratio:
-
19M.2.sl.TZ1.4b(i):
In a laboratory experiment solutions of potassium iodide and hydrogen peroxide were mixed and the volume of oxygen generated was recorded. The volume was adjusted to 0 at t = 0.
The data for the first trial is given below.
Plot a graph on the axes below and from it determine the average rate of formation of oxygen gas in cm3 O2 (g) s−1.
Average rate of reaction:
-
19M.2.sl.TZ2.1c(v):
The IR spectrum and low resolution 1H NMR spectrum of the actual product formed are shown.
Deduce whether the product is A or B, using evidence from these spectra together with sections 26 and 27 of the data booklet.
Identity of product:
One piece of evidence from IR:
One piece of evidence from 1H NMR:
-
19M.2.sl.TZ2.2d:
The experiment gave an error in the rate because the pressure gauge was inaccurate. Outline whether repeating the experiment, using the same apparatus, and averaging the results would reduce the error.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ1.1b(iii):
Compare the ease of oxidation of s-block and d-block metals to their melting points and densities. Use section 25 of the data booklet.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ1.1b(i):
Describe the density trend across periods 4 and 5 of the periodic table.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ2.2c(i):
Describe one systematic error associated with the use of the gas syringe, and how the error affects the calculated rate.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ2.2c(ii):
Identify one error associated with the use of an accurate stopwatch.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ2.5b:
The infrared (IR) spectrum of polyethene is given.
Suggest how the IR spectrum of polychloroethene would differ, using section 26 of the data booklet.
- 19M.1.sl.TZ1.28: How should a measurement of 5.00 g from a balance be recorded? A. 5.00 ± 0.1 g B. 5.00 ± 0.01...
-
19M.1.sl.TZ2.29:
Data collected from a larger number of silicon samples could also be plotted to determine the density using the following axes.
Which statements are correct?
I. The density is the slope of the graph.
II. The data will show that mass is proportional to volume.
III. The best-fit line should pass through the origin.A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
19M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
What is the degree of unsaturation (index of hydrogen deficiency) for the molecule?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 5
-
19M.1.sl.TZ1.29:
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O2(g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 (aq).
Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
- 19M.1.sl.TZ2.27: What is the name of this compound using IUPAC rules? A. 2,3-diethylbutane B....
- 19M.1.sl.TZ2.28: The following data were recorded for determining the density of three samples of silicon,...
-
19M.1.sl.TZ2.30:
What can be deduced from the infrared (IR) spectrum of a compound?
A. Number of hydrogens
B. Number of hydrogen environments
C. Bonds present
D. Molar mass
-
19N.2.sl.TZ0.2b(i):
Calculate the percentage uncertainty of the day 5 titre.
-
19N.2.hl.TZ0.3d(iii):
Explain why the 1H NMR spectrum of C3H6O, produced in (d)(i), shows only one signal.
- 19N.2.sl.TZ0.2b(ii): Suggest a modification to the procedure that would make the results more reliable.
- 19N.1.hl.TZ0.5: Which shows the first ionization energies of successive elements across period 2, from left to...
- 19N.1.sl.TZ0.29: What is the value of the temperature change? Initial temperature: 2.0 ± 0.1 °C Final...
- 19N.3.hl.TZ0.14a: The graph shows the change in oxygen partial pressure in blood, measured at different pH...
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.12b(ii): The 1H NMR spectrum of one of the products has four signals. The integration trace shows a ratio...
-
19N.3.sl.TZ0.1b(i):
Determine the initial rate of reaction of limestone with nitric acid from the graph.
Show your working on the graph and include the units of the initial rate.
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.1b(iii): Suggest a source of error in the procedure, assuming no human errors occurred and the balance was...
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.1a: Draw a best-fit line on the graph.
- 19N.1.sl.TZ0.14: Which quantity is likely to be the most inaccurate due to the sources of error in this...
Sub sections and their related questions
11.1 Uncertainties and errors in measurement and results
-
16N.1.sl.TZ0.30:
A student measured the change in mass on heating a sample of calcium carbonate, CaCO3(s). What is the mass loss?
Mass before heating: 2.347 g ± 0.001
Mass after heating: 2.001 g ± 0.001A. 0.346g ± 0.001
B. 0.346g ± 0.002
C. 0.35g ± 0.002
D. 0.35g ± 0.001
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.3g: Suggest one reason why the values of rates of reactions obtained at higher temperatures may be...
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.29:
What is the density, in gcm−3, of a 34.79 g sample with a volume of 12.5 cm3?
A. 0.359
B. 0.36
C. 2.783
D. 2.78
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.38: The molar mass of a gas, determined experimentally, is 32 g mol−1. Its literature molar mass is...
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.1b:
Suggest how the precision of this measurement could be improved.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.5b:
Heat losses would make this method less accurate than the pH probe method. Outline why the thermometric method would always give a lower, not a higher, concentration.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.5f:
Outline why the thermochemical method would not be appropriate for 0.001 moldm−3 hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide of a similar concentration.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.1a.ii:
Suggest why the final mass of solid obtained by heating 3.760 g of AgxOy may be greater than 3.275 g giving one design improvement for your proposed suggestion. Ignore any possible errors in the weighing procedure.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.2b.i:
Calculate the percentage uncertainty for the mass of K2Cr2O7(s) from the given data.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.1b:
O2 is consumed in producing CO2 for electricity generation. The graph shows the relationship between the world’s electricity generation and CO2 production between 1994 and 2013.
Calculate the mass, in million tonnes, of oxygen gas ultimately found in CO2 which is consumed in generating 18000 terawatts of electricity using the equation given for the best fit line. Give your answer to 2 significant figures.
Assume coal is the only energy source.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.1c.iii:
The change in APO O2/N2 ratio, per meg, is measured relative to an O2/N2 reference.
Calculate the APO Δ(O2/N2) value for an oxygen concentration of 209400 ppm assuming that any change in N2 concentration is negligible. Reference values for O2 and N2 are 209 460 and 790 190 ppm respectively.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.2b.ii:
Suggest one improvement to the investigation.
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.30: A student performs an acid-base titration using a pH meter, but forgets to calibrate it. Which...
-
17N.3.sl.TZ0.2c:
Calculate the uncertainty in the change in pH.
-
17N.3.sl.TZ0.3c:
Calculate the percentage of water by mass in the NaCl•2H2O crystals. Use the data from section 6 of the data booklet and give your answer to two decimal places.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.13: The enthalpy of combustion of ethanol is determined by heating a known mass of tap water in a...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.28: Which value of q, in J, has the correct number of significant figures? q = mcΔT where m = 2.500...
-
18M.3.sl.TZ1.2d.i:
Justify why it is inappropriate to record the uncertainty of the mean as ±0.01 s.
-
18M.3.sl.TZ1.2d.ii:
If doubling the concentration doubles the reaction rate, suggest the mean time you would expect for the reaction with 2.00 mol dm−3 hydrochloric acid.
-
18M.3.sl.TZ1.2d.iii:
Another student, working alone, always dropped the marble chips into the acid and then picked up the stopwatch to start it. State, giving a reason, whether this introduced a random or systematic error.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.29: How are the uncertainties of two quantities combined when the quantities are multiplied...
- 18N.1.sl.TZ0.30: What are the absolute and percentage uncertainties for the change in mass? Initial mass: 22.35...
-
18N.2.sl.TZ0.1b.iii:
The only significant uncertainty is in the temperature measurement.
Determine the absolute uncertainty in the calculated value of ΔH if the uncertainty in the temperature rise was ±0.2 °C.
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.1b.iii:
The only significant uncertainty is in the temperature measurement.
Determine the absolute uncertainty in the calculated value of ΔH if the uncertainty in the temperature rise was ±0.2 °C.
-
18N.3.sl.TZ0.1d.ii:
Deduce the appropriate number of significant figures for your answer in (d)(i).
-
18N.3.hl.TZ0.1e.ii:
Deduce the appropriate number of significant figures for your answer in (e)(i).
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.2e:
The experiment gave an error in the rate because the pressure gauge was inaccurate.
Outline whether repeating the experiment, using the same apparatus, and averaging the results would reduce the error.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.5d(iv):
The uncertainty of the 100.0cm3 volumetric flask used to make the solution was ±0.6cm3.
Calculate the maximum percentage uncertainty in the mass of NaHCO3 so that the concentration of the solution is correct to ±1.0 %.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.2c(i):
Describe one systematic error associated with the use of the gas syringe, and how the error affects the calculated rate.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.2c(ii):
Identify one error associated with the use of an accurate stopwatch.
- 19M.1.hl.TZ1.38: How should a measurement of 5.00 g from a balance be recorded? A. 5.00 ± 0.1 g B. 5.00 ± 0.01...
- 19M.1.hl.TZ2.38: The following data were recorded for determining the density of three samples of silicon,...
-
19M.2.sl.TZ2.2d:
The experiment gave an error in the rate because the pressure gauge was inaccurate. Outline whether repeating the experiment, using the same apparatus, and averaging the results would reduce the error.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ2.2c(i):
Describe one systematic error associated with the use of the gas syringe, and how the error affects the calculated rate.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ2.2c(ii):
Identify one error associated with the use of an accurate stopwatch.
- 19M.1.sl.TZ1.28: How should a measurement of 5.00 g from a balance be recorded? A. 5.00 ± 0.1 g B. 5.00 ± 0.01...
- 19M.1.sl.TZ2.27: What is the name of this compound using IUPAC rules? A. 2,3-diethylbutane B....
- 19M.1.sl.TZ2.28: The following data were recorded for determining the density of three samples of silicon,...
-
19N.2.sl.TZ0.2b(i):
Calculate the percentage uncertainty of the day 5 titre.
- 19N.2.sl.TZ0.2b(ii): Suggest a modification to the procedure that would make the results more reliable.
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.1b(iii): Suggest a source of error in the procedure, assuming no human errors occurred and the balance was...
- 19N.1.sl.TZ0.29: What is the value of the temperature change? Initial temperature: 2.0 ± 0.1 °C Final...
- 19N.1.sl.TZ0.14: Which quantity is likely to be the most inaccurate due to the sources of error in this...
-
20N.1.sl.TZ0.28:
A student obtained the following data to calculate , using .
What is the percentage uncertainty in the calculated value of ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 20N.2.hl.TZ0.5f(i): Potassium hydroxide solutions can react with carbon dioxide from the air. The solution was made...
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.5f(ii):
Potassium hydroxide solutions can react with carbon dioxide from the air. The solution was made one day prior to using it in the titration.
Predict, giving a reason, the effect of this error on the calculated concentration of ethanoic acid in 5(e).
- 20N.3.sl.TZ0.1d: Suggest one source of error in the experiment, excluding faulty apparatus and human error, that...
-
20N.3.sl.TZ0.2e:
Calculate the percentage uncertainty and percentage error in the experimentally determined value of for methanol.
- 21M.1.sl.TZ1.28: The enthalpy of combustion of a fuel was determined using the calorimeter shown. The final result...
- 21M.1.sl.TZ1.29: Burette readings for a titration are shown. What is the mean titre? A. 11.1 cm3 ±...
- 21M.1.sl.TZ2.29: How should the difference between 27.0 ± 0.3 and 9.0 ± 0.2 be shown? A. 18.0 ± 0.1 B. 18.0 ±...
-
21N.2.sl.TZ0.6b:
A student dissolved 0.1240 ± 0.0001 g of Na2S2O3 to make 1000.0 ± 0.4 cm3 of solution to use in the Winkler Method.
Determine the percentage uncertainty in the molar concentration.
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.6b:
A student dissolved 0.1240 ± 0.0001 g of Na2S2O3 to make 1000.0 ± 0.4 cm3 of solution to use in the Winkler Method.
Determine the percentage uncertainty in the molar concentration.
-
22M.1.sl.TZ1.28:
A student performed an experiment to find the melting point of sulfur, obtaining 118.0 °C. The literature value is 115.2 °C. What was the percentage error?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.29: What is the uncertainty, in cm3, of this measurement?A. ±0.01 B. ±0.1 C. ±0.15 D. ±1
-
22M.2.sl.TZ1.1b(ii):
Determine the percentage uncertainty of the mass of product after heating.
-
22M.2.sl.TZ1.1c(ii):
Suggest an explanation, other than product being lost from the crucible or reacting with nitrogen, that could explain the yield found in (b)(iii).
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.1b(ii):
Determine the percentage uncertainty of the mass of product after heating.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.1c(ii):
Suggest an explanation, other than product being lost from the crucible or reacting with nitrogen, that could explain the yield found in (b)(iii).
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.2c(iii):
Carbonates also react with HCl and the rate can be determined by graphing the mass loss. Suggest why this method is less suitable for the reaction of Mg with HCl.
-
22M.2.sl.TZ2.1b(iii):
Suggest a reason why the volume of hydrogen gas collected was smaller than predicted.
11.2 Graphical techniques
-
16N.3.sl.TZ0.1b:
CT values are influenced by temperature and by pH. The table below shows the CT values for chlorine needed to achieve 99% inactivation of a specific bacterium at stated values of pH and temperature.
(i) With reference to the temperature data in the table, suggest why it may be more difficult to treat water effectively with chlorine in cold climates.
(ii) Sketch a graph on the axes below to show how the CT value (at any temperature) varies with pH.
(iii) Comment on the relative CT values at pH 6.0 and pH 9.0 at each temperature.
(iv) Chlorine reacts with water as follows:
Cl2 (g) + H2O (l) HOCl (aq) + HCl (aq)
HOCl (aq) OCl− (aq) + H+ (aq)
Predict how the concentrations of each of the species HOCl (aq) and OCl− (aq) will change if the pH of the disinfected water increases.
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.23: The graph shows values of ΔG for a reaction at different temperatures. Which statement is...
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.1a.ii:
A student produced these results with [H+] = 0.15 moldm−3. Propanone and acid were in excess and iodine was the limiting reagent.
Determine the relative rate of reaction when [H+] = 0.15 moldm−3.

-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.1a:
Calculate the percentage uncertainty of the volume of the aqueous sodium hydroxide.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.3:
Suggest how the end point of the titration might be estimated from the graph.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.4:
State and explain how the graph would differ if 1 moldm−3 sulfuric acid had been used instead of 1 moldm−3 hydrochloric acid.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.18a:
Dose response curves are determined for each drug.

Outline the significance of range “a”.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16a:
Explain the shape of the curve at low oxygen partial pressure up to about 5 kPa.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16b.i:
Sketch a graph on the axes above to show the effect of decreasing pH on the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin (the Bohr Effect).
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.16b.ii:
Outline the effect of decreasing pH on the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.30: What is the graphical relationship between n and T in the ideal gas equation, pV = nRT, all other...
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.1a:
The following graph represents world energy consumption by type for the years 1988–2013.
Estimate the percentage of energy consumption which did not directly produce CO2 in 2013.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.1a: Using the graph, estimate the initial temperature of the solution.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.1b: Determine the maximum temperature reached in the experiment by analysing the graph.
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.1a: Using the graph, estimate the initial temperature of the solutions.
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.1b: Determine the maximum temperature reached in each experiment by analysing the graph.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.1b.i: Suggest what the correlation coefficient of −0.9999 indicates.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.1b.ii: State the equation of the straight line obtained using the data.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.3a: Estimate the lowest freezing point of water that can be reached by adding sodium chloride.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.3b: Estimate the percentage by mass of NaCl dissolved in a saturated sodium chloride solution at +10 ºC.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.4b.ii:
Draw the best fit line for the reaction excluding point D.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.4c:
Predict from your line of best fit the rate of reaction when the concentration of HCl is 1.00 mol dm−3.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.30: The rate of a reaction is studied at different temperatures. Which is the best way to plot the...
-
18N.2.sl.TZ0.1c.i:
Sketch a graph of the concentration of iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4, against time as the reaction proceeds.
-
18N.2.sl.TZ0.1c.ii:
Outline how the initial rate of reaction can be determined from the graph in part (c)(i).
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.1c.i:
Sketch a graph of the concentration of iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4, against time as the reaction proceeds.
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.1c.ii:
Outline how the initial rate of reaction can be determined from the graph in part (c)(i).
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.6c:
Sketch the pH curve for the titration of 25.0 cm3 of ethylamine aqueous solution with 50.0 cm3 of butanoic acid aqueous solution of equal concentration. No calculations are required.
-
18N.3.sl.TZ0.1b:
Deduce the equation for the relationship between absorbance and concentration.
-
18N.3.sl.TZ0.1d.i:
The original piece of brass weighed 0.200 g. The absorbance was 0.32.
Calculate, showing your working, the percentage of copper by mass in the brass.
-
18N.3.hl.TZ0.1b:
Deduce the equation for the relationship between absorbance and concentration.
-
18N.3.hl.TZ0.1e.i:
The original piece of brass weighed 0.200 g. The absorbance was 0.32.
Calculate, showing your working, the percentage of copper by mass in the brass.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.4b(i):
In a laboratory experiment solutions of potassium iodide and hydrogen peroxide were mixed and the volume of oxygen generated was recorded. The volume was adjusted to 0 at t = 0.
The data for the first trial is given below.
Plot a graph on the axes below and from it determine the average rate of
formation of oxygen gas in cm3 O2 (g) s−1.Average rate of reaction:
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.1b(i):
Describe the density trend across periods 4 and 5 of the periodic table.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ1.1b(iii):
Compare the ease of oxidation of s-block and d-block metals to their melting points and densities. Use section 25 of the data booklet.
-
19M.1.hl.TZ1.39:
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O2 (g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 (aq).
Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
-
19M.2.sl.TZ1.4b(i):
In a laboratory experiment solutions of potassium iodide and hydrogen peroxide were mixed and the volume of oxygen generated was recorded. The volume was adjusted to 0 at t = 0.
The data for the first trial is given below.
Plot a graph on the axes below and from it determine the average rate of formation of oxygen gas in cm3 O2 (g) s−1.
Average rate of reaction:
-
19M.3.sl.TZ1.1b(i):
Describe the density trend across periods 4 and 5 of the periodic table.
-
19M.3.sl.TZ1.1b(iii):
Compare the ease of oxidation of s-block and d-block metals to their melting points and densities. Use section 25 of the data booklet.
-
19M.1.sl.TZ1.29:
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O2(g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 (aq).
Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
-
19M.1.sl.TZ2.29:
Data collected from a larger number of silicon samples could also be plotted to determine the density using the following axes.
Which statements are correct?
I. The density is the slope of the graph.
II. The data will show that mass is proportional to volume.
III. The best-fit line should pass through the origin.A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.1a: Draw a best-fit line on the graph.
-
19N.3.sl.TZ0.1b(i):
Determine the initial rate of reaction of limestone with nitric acid from the graph.
Show your working on the graph and include the units of the initial rate.
- 19N.3.hl.TZ0.14a: The graph shows the change in oxygen partial pressure in blood, measured at different pH...
- 19N.1.hl.TZ0.5: Which shows the first ionization energies of successive elements across period 2, from left to...
- 21M.1.sl.TZ2.30: A liquid was added to a graduated cylinder. What can be deduced from the graph?
-
21M.2.sl.TZ1.6b(ii):
Deduce the relationship between the concentration of N2O5 and the rate of reaction.
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.28: What is the slope of the graph? A. −0.0025 mol dm−3 s−1 B. −0.0025 mol dm−3 s C. ...
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.29: Which graph shows the relationship between the pressure and volume of a sample of gas at constant...
-
21N.1.hl.TZ0.23:
The graph shows Gibbs free energy of a mixture of N2O4 (g) and NO2 (g) in different proportions.
N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
Which point shows the system at equilibrium?
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.3: Which graph represents the relationship between the amount of gas, n, and the absolute...
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.17: A reaction has an activation energy of 40 kJ mol−1 and an enthalpy change of −60 kJ mol−1. Which...
-
22M.1.sl.TZ2.30:
20 cm3 of 1 mol dm−3 sulfuric acid was added dropwise to 20 cm3 of 1 mol dm−3 barium hydroxide producing a precipitate of barium sulfate.
H2SO4 (aq) + Ba(OH)2 (aq) → 2H2O (l) + BaSO4 (s)
Which graph represents a plot of conductivity against volume of acid added?
- 22M.1.hl.TZ2.20: Which energy profile diagram represents an exothermic SN1 reaction?
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.2c(i):
Use the graph to deduce the dependence of the reaction rate on the amount of Mg.
11.3 Spectroscopic identification of organic compounds
-
16N.1.sl.TZ0.28:
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) for this molecule?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.29: What is always correct about the molecular ion, M+, in a mass spectrum of a compound? A. The M+...
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.28:
What can be determined about a molecule from the number of signals in its 1HNMR spectrum?
A. Bonds present
B. Molecular formula
C. Molecular mass
D. Number of hydrogen environments
-
17M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
What is the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) for 1,3,5-hexatriene (C6H8)?
A. 1
B. 3
C. 5
D. 6
-
17M.1.hl.TZ1.40:
Which technique is used to determine the bond lengths and bond angles of a molecule?
A. X-ray crystallography
B. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy
C. Mass spectroscopy
D. 1H NMR spectroscopy
-
17M.2.sl.TZ1.5c.ii:
The mass and 1HNMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its structural formula and hence the name of the compound.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.6c.ii:
The mass and 1H NMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its structural formula and hence the name of the compound.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.10a:
Below are the IR spectra of two plastics (A and B); one is PETE, the other is low density polyethene (LDPE).
Deduce, giving your reasons, the identity and resin identification code (RIC) of A and B using sections 26 and 30 of the data booklet.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ1.19d:
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
17M.1.sl.TZ2.28:
Which information can be gained from an infrared (IR) spectrum?
A. Ionization energy of the most abundant element
B. Number of different elements in the compound
C. Bonds present in a molecule
D. Molecular formula of the compound
-
17M.1.sl.TZ2.29:
What can be deduced from the following 1HNMR spectrum?
A. There is only one hydrogen atom in the molecule.
B. There is only one hydrogen environment in the molecule.
C. The molecule is a hydrocarbon.
D. There is only one isotope in the element.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.8b:
Identify the species responsible for the peak at m/z = 110 in the mass spectrum of hydroquinone.
-
17M.2.sl.TZ2.8c:
Identify the highest m/z value in the mass spectrum of quinone.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.i:
Deduce what information can be obtained from the 1H NMR spectrum.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.ii:
Identify the functional group that shows stretching at 1710 cm–1 in the infrared spectrum of this compound using section 26 of the data booklet and the 1H NMR.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.4:
Infrared (IR) spectra can be used to distinguish between various types of plastics. Some simplified IR spectra are given here.
Explain, with a reference to molecular structure, which two of the plastics can not be distinguished by IR spectroscopy.
-
17M.3.sl.TZ2.18a.ii:
Deduce the wavenumber of one absorbance seen in the IR spectrum of only one of the compounds, using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.20a.iii:
Suggest two absorbances, other than the absorbances due to the ring structure and C–H bonds, that would be present in the infrared (IR) spectrum of aspirin.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.21c.i:
Predict the number of different hydrogen environments in the molecule ignoring the benzene rings.
-
17N.1.sl.TZ0.29:
What information is provided by 1H NMR, MS and IR for an organic compound?
I. 1H NMR: chemical environment(s) of protons
II. MS: fragmentation pattern
III. IR: types of functional groupA. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.iii: Deduce the number of signals and the ratio of areas under the signals in the 1H NMR spectra of...
-
17N.3.sl.TZ0.7b.ii:
One of the two infrared (IR) spectra is that of polyethene and the other of polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE).
Deduce, with a reason, which spectrum is that of PTFE. Infrared data is given in section 26 of the data booklet.
- 17N.3.hl.TZ0.22a.i: Both spectra show a peak at wavenumber 1700 cm–1. Identify the bond responsible for this peak.
-
17N.3.hl.TZ0.22a.ii:
Deduce which spectrum belongs to paracetamol, giving two reasons for your choice. Use section 26 of the data booklet.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1j:
The mass spectrum of urea is shown below.

Identify the species responsible for the peaks at m/z = 60 and 44.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1k:
The IR spectrum of urea is shown below.

Identify the bonds causing the absorptions at 3450 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1l.i:
Predict the number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.29: What is the index of hydrogen deficiency, IHD, of 3-methylcyclohexene? A. 0 B. 1 C. ...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.30: What is the ratio of the areas of the signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of pentan-3-ol? A. ...
-
18M.2.sl.TZ1.1g:
The mass spectrum of urea is shown below.

Identify the species responsible for the peaks at m/z = 60 and 44.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ1.1h:
The IR spectrum of urea is shown below.

Identify the bonds causing the absorptions at 3450 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ1.1i:
Predict the number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.28: Which feature of a molecule does infrared spectrometry detect? A. molecular mass B. ...
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.i:
Deduce the molecular formula of the compound.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.ii:
Identify the bonds causing peaks A and B in the IR spectrum of the unknown compound using section 26 of the data booklet.

-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.iii:
Deduce full structural formulas of two possible isomers of the unknown compound, both of which are esters.
-
18M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.iv:
Deduce the formula of the unknown compound based on its 1H NMR spectrum using section 27 of the data booklet.

-
18M.3.sl.TZ2.7b:
Deduce the number of 1H NMR signals produced by the zwitterion form of alanine.
- 18N.1.sl.TZ0.28: Which is correct for the spectra of organic compounds? A. Mass spectroscopy provides...
- 18N.1.sl.TZ0.29: What is the ratio of areas under each signal in the 1H NMR spectrum of 2-methylbutane? A. 6...
- 18N.2.hl.TZ0.2b: The infrared spectrum of the compound is shown. Deduce the functional group of the compound.
- 18N.2.hl.TZ0.2c: The mass spectrum of the compound is shown. Deduce the relative molecular mass of the compound.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ1.25c:
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.1a:
State the number of 1H NMR signals for this isomer of xylene and the ratio in which they appear.
-
19M.3.hl.TZ2.5b:
The infrared (IR) spectrum of polyethene is given.
Suggest how the IR spectrum of polychloroethene would diff er, using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
19M.1.hl.TZ2.39:
What can be deduced from the infrared (IR) spectrum of a compound?
A. Number of hydrogens
B. Number of hydrogen environments
C. Bonds present
D. Molar mass
-
19M.1.hl.TZ2.40:
Which technique involves breaking covalent bonds when carried out on an organic compound?
A. infrared spectroscopy
B. nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
C. X-ray crystallography
D. mass spectrometry
-
19M.2.sl.TZ1.1a:
State the number of 1H NMR signals for this isomer of xylene and the ratio in which they appear.
Number of signals:
Ratio:
-
19M.2.sl.TZ2.1c(v):
The IR spectrum and low resolution 1H NMR spectrum of the actual product formed are shown.
Deduce whether the product is A or B, using evidence from these spectra together with sections 26 and 27 of the data booklet.
Identity of product:
One piece of evidence from IR:
One piece of evidence from 1H NMR:
-
19M.3.sl.TZ2.5b:
The infrared (IR) spectrum of polyethene is given.
Suggest how the IR spectrum of polychloroethene would differ, using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
19M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
What is the degree of unsaturation (index of hydrogen deficiency) for the molecule?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 5
-
19M.1.sl.TZ2.30:
What can be deduced from the infrared (IR) spectrum of a compound?
A. Number of hydrogens
B. Number of hydrogen environments
C. Bonds present
D. Molar mass
-
19N.2.hl.TZ0.3d(iii):
Explain why the 1H NMR spectrum of C3H6O, produced in (d)(i), shows only one signal.
- 19N.3.sl.TZ0.12b(ii): The 1H NMR spectrum of one of the products has four signals. The integration trace shows a ratio...
-
20N.1.sl.TZ0.29:
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) in cyclohexanol?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 20N.1.sl.TZ0.30: Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum is used to identify hydrogen environments in a...
-
20N.2.sl.TZ0.1d(vi):
Deduce the number of signals and their chemical shifts in the spectrum of ethoxyethane. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
-
20N.2.sl.TZ0.2b:
The IR spectrum of one of the compounds is shown:
COBLENTZ SOCIETY. Collection © 2018 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved.
Deduce, giving a reason, the compound producing this spectrum. -
20N.2.hl.TZ0.1d(v):
Deduce the number of signals and chemical shifts with splitting patterns in the 1H NMR spectrum of ethoxyethane. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.2d:
The IR spectrum of one of the compounds is shown:
COBLENTZ SOCIETY. Collection © 2018 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved.
Deduce, giving a reason, the compound producing this spectrum.
-
21M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
Determine the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) of paracetamol.
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
-
21M.1.sl.TZ2.28:
Which spectra would show the difference between propan-2-ol, CH3CH(OH)CH3, and propanal, CH3CH2CHO?
I. mass
II. infrared
III. 1H NMRA. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
- 21M.2.sl.TZ1.5b: Justify why ethene has only a single signal in its 1H NMR spectrum.
- 21M.2.hl.TZ1.5b(i): Justify why ethene has only a single signal in its 1H NMR spectrum.
- 21M.2.sl.TZ2.4e(i): Deduce two features of this molecule that can be obtained from the mass spectrum. Use section 28...
- 21M.2.sl.TZ2.4e(ii): Identify the bond responsible for the absorption at A in the infrared spectrum. Use section 26 of...
-
21M.2.sl.TZ2.4e(iii):
Deduce the identity of the unknown compound using the previous information, the 1H NMR spectrum and section 27 of the data booklet.
SDBS, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST).
- 21M.2.hl.TZ2.4g(i): Deduce two features of this molecule that can be obtained from the mass spectrum. Use section 28...
- 21M.2.hl.TZ2.4g(ii): Identify the bond responsible for the absorption at A in the infrared spectrum. Use section 26 of...
-
21M.2.hl.TZ2.4g(iii):
Deduce the identity of the unknown compound using the previous information, the 1H NMR spectrum and section 27 of the data booklet.
SDBS, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST).
- 21N.1.sl.TZ0.5: Consider the mass spectrum of an element: What is the relative atomic mass of this...
-
21N.1.sl.TZ0.30:
What can be deduced from the mass spectrum of CH3COCH2CH2CH3?
NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection (C) 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved. 2-Pentanone Mass Spectrum, MS Number 291264. [graph] Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C107879&Units=SI&Mask=200#Mass-Spec2-pentanone [Accessed 4 May 2020]. source adapted.
A. The molar mass is 43 g mol−1.B. The atoms have many isotopes.
C. The most likely bond to break is C–C between carbons 2 and 3.
D. The signal with the largest mass is due to the oxidation of the ketone in the spectrometer.
-
21N.2.sl.TZ0.1c:
Identify each compound from the spectra given, use absorptions from the range of 1700 cm−1 to 3500 cm−1. Explain the reason for your choice, referring to section 26 of the data booklet.
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.1c:
Identify each compound from the spectra given, use absorptions from the range of 1700 cm−1 to 3500 cm−1. Explain the reason for your choice, referring to section 26 of the data booklet.
- 21N.2.hl.TZ0.1e: Predict the fragment that is responsible for a m/z of 31 in the mass spectrum of propan‑1‑ol. Use...
-
22M.1.sl.TZ1.29:
Which compound produces this mass spectrum?
[Spectral Database for Organic Compounds, SDBS. SDBS Compounds and Spectral Search. [graph] Available at:
https://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp [Accessed 3 January 2019].] -
22M.1.sl.TZ1.30:
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) of this molecule?
Paracetamol (acetaminophen)
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
- 22M.1.sl.TZ2.28: How many signals are observed in the 1H NMR spectrum of this compound?A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
-
22M.1.hl.TZ2.40:
Given equimolar concentrations, which substance would produce the strongest signal in a 1H NMR spectrum?
A. (CH3)3CHB. C6H6
C. C8H18
D. Si(CH3)4
-
22M.2.sl.TZ2.4d(iv):
Suggest two differences in the 1H NMR of but-2-ene and the organic product from (d)(ii).
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.8d(iv):
Suggest two differences in the 1H NMR of but-2-ene and the organic product from (d)(ii).
