| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.sl.TZ1.1 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Suggest | Question number | 1 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Urea, (H2N)2CO, is excreted by mammals and can be used as a fertilizer.
Calculate the percentage by mass of nitrogen in urea to two decimal places using section 6 of the data booklet.
Suggest how the percentage of nitrogen affects the cost of transport of fertilizers giving a reason.
The structural formula of urea is shown.
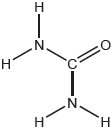
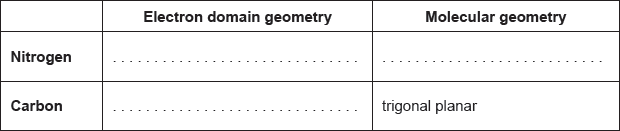
Predict the electron domain and molecular geometries at the nitrogen and carbon atoms, applying the VSEPR theory.
Urea can be made by reacting potassium cyanate, KNCO, with ammonium chloride, NH4Cl.
KNCO(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) → (H2N)2CO(aq) + KCl(aq)
Determine the maximum mass of urea that could be formed from 50.0 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 potassium cyanate solution.
Urea can also be made by the direct combination of ammonia and carbon dioxide gases.
2NH3(g) + CO2(g) \( \rightleftharpoons \) (H2N)2CO(g) + H2O(g) ΔH < 0
Predict, with a reason, the effect on the equilibrium constant, Kc, when the temperature is increased.
Suggest one reason why urea is a solid and ammonia a gas at room temperature.
Sketch two different hydrogen bonding interactions between ammonia and water.
The combustion of urea produces water, carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
Formulate a balanced equation for the reaction.
The mass spectrum of urea is shown below.
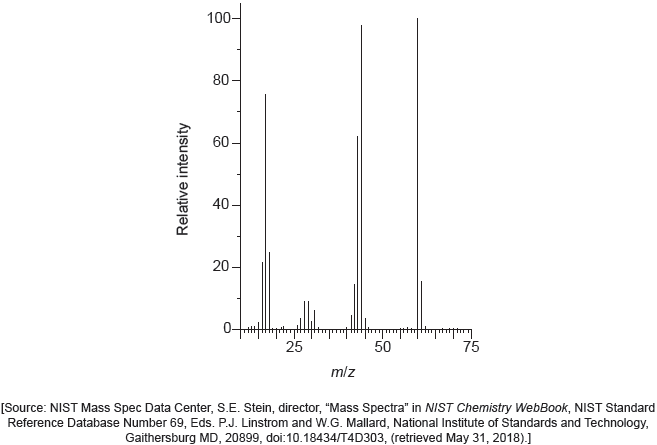
Identify the species responsible for the peaks at m/z = 60 and 44.
The IR spectrum of urea is shown below.
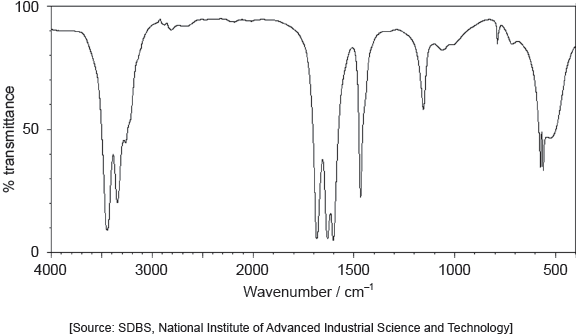
Identify the bonds causing the absorptions at 3450 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 using section 26 of the data booklet.
Predict the number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
Markscheme
molar mass of urea «= 4 × 1.01 + 2 × 14.01 + 12.01 + 16.00» = 60.07 «g mol–1»
«% nitrogen = \(\frac{{2 \times 14.01}}{{60.07}}\) × 100 =» 46.65 «%»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for final answer not to two decimal places.
[2 marks]
«cost» increases AND lower N% «means higher cost of transportation per unit of nitrogen»
OR
«cost» increases AND inefficient/too much/about half mass not nitrogen
Accept other reasonable explanations.
Do not accept answers referring to safety/explosions.
[1 mark]
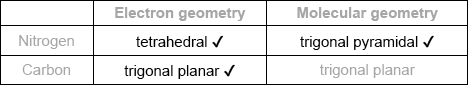
Note: Urea’s structure is more complex than that predicted from VSEPR theory.
[3 marks]
n(KNCO) «= 0.0500 dm3 × 0.100 mol dm–3» = 5.00 × 10–3 «mol»
«mass of urea = 5.00 × 10–3 mol × 60.07 g mol–1» = 0.300 «g»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
[2 marks]
«Kc» decreases AND reaction is exothermic
OR
«Kc» decreases AND ΔH is negative
OR
«Kc» decreases AND reverse/endothermic reaction is favoured
[1 mark]
Any one of:
urea has greater molar mass
urea has greater electron density/greater London/dispersion
urea has more hydrogen bonding
urea is more polar/has greater dipole moment
Accept “urea has larger size/greater van der Waals forces”.
Do not accept “urea has greater intermolecular forces/IMF”.
[1 mark]
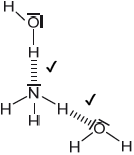
Award [1] for each correct interaction.
If lone pairs are shown on N or O, then the lone pair on N or one of the lone pairs on O MUST be involved in the H-bond.
Penalize solid line to represent H-bonding only once.
[2 marks]
2(H2N)2CO(s) + 3O2(g) → 4H2O(l) + 2CO2(g) + 2N2(g)
correct coefficients on LHS
correct coefficients on RHS
Accept (H2N)2CO(s) + \(\frac{3}{2}\)O2(g) → 2H2O(l) + CO2(g) + N2(g).
Accept any correct ratio.
[2 marks]
60: CON2H4+
44: CONH2+
Accept “molecular ion”.
[2 marks]
3450 cm–1: N–H
1700 cm–1: C=O
Do not accept “O–H” for 3450 cm–1.
[2 marks]
1
[1 mark]

