| Date | May 2014 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 14M.2.sl.TZ2.1 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Suggest | Question number | 1 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A class studied the equilibrium established when ethanoic acid and ethanol react together in the presence of a strong acid, using propanone as an inert solvent. The equation is given below.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}} + {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
One group made the following initial mixture:
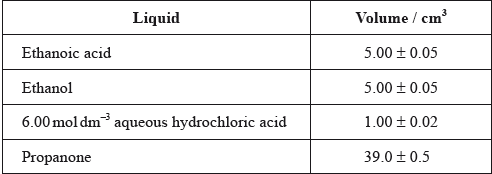
After one week, a \(5.00 \pm 0.05{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) sample of the final equilibrium mixture was pipetted out and titrated with \({\text{0.200 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 2}}\) aqueous sodium hydroxide to determine the amount of ethanoic acid remaining. The following titration results were obtained:
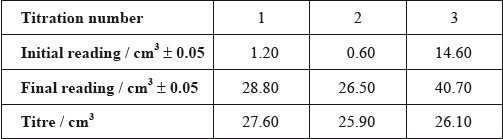
The density of ethanoic acid is \({\text{1.05 g}}\,{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\). Determine the amount, in mol, of ethanoic acid present in the initial mixture.
The hydrochloric acid does not appear in the balanced equation for the reaction. State its function.
Identify the liquid whose volume has the greatest percentage uncertainty.
(i) Calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre for Titration 1 (\({\text{27.60 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\)).
(ii) Suggest the average volume of alkali, required to neutralize the \({\text{5.00 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) sample, that the student should use.
(iii) \({\text{23.00 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of this \({\text{0.200 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) aqueous sodium hydroxide reacted with the ethanoic acid in the \({\text{5.00 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) sample. Determine the amount, in mol, of ethanoic acid present in the \({\text{50.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of final equilibrium mixture.
Referring back to your answer for part (a), calculate the percentage of ethanoic acid converted to ethyl ethanoate.
Deduce the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction.
Outline how you could establish that the system had reached equilibrium at the end of one week.
Outline why changing the temperature has only a very small effect on the value of the equilibrium constant for this equilibrium.
Outline how adding some ethyl ethanoate to the initial mixture would affect the amount of ethanoic acid converted to product.
Propanone is used as the solvent because one compound involved in the equilibrium is insoluble in water. Identify this compound and explain why it is insoluble in water.
Suggest one other reason why using water as a solvent would make the experiment less successful.
Markscheme
\({\text{M(C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH)}}\left( { = (4 \times 1.01) + (2 \times 12.01) + (2 \times 16.00)} \right) = 60.06{\text{ (g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}{\text{)}}\);
Accept 60 (g mol–1).
\({\text{mass (C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH)}}( = 5.00 \times 1.05) = 5.25{\text{ (g)}}\);
\(\frac{{5.25}}{{{\text{60.06}}}} = 0.0874{\text{ (mol)}}\);
Award [3] for correct final answer.
Accept 0.0875 (comes from using Mr = 60 g mol–1).
catalyst / OWTTE;
hydrochloric acid/HCl;
(i) \( \pm 0.1/0.10{\text{ (c}}{{\text{m}}^3}{\text{)}}\);
Do not accept without ±.
(ii) \({\text{26.00 (c}}{{\text{m}}^3}{\text{)}}\);
(iii) \(0.200 \times \frac{{23.00}}{{1000}} = 0.0046\);
\({\text{0.0046}} \times \frac{{{\text{50.0}}}}{{{\text{5.00}}}} = {\text{0.0460 (mol)}}\);
\(\frac{{0.0874 - 0.0460}}{{0.0874}} \times 100 = 47.4\% \);
\({\text{(}}{K_{\text{c}}} = {\text{)}}\frac{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{][}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O]}}}}{{{\text{[}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH][C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH]}}}}\);
Do not penalize minor errors in formulas.
Accept \({\text{(}}{K_{\text{c}}} = {\text{)}}\frac{{{\text{[}}ester{\text{][}}water{\text{]}}}}{{{\text{[}}ethanol / alcohol{\text{][(}}ethanoic{\text{)}} acid{\text{]}}}}\).
repeat the titration a day/week later (and result should be the same) / OWTTE;
Accept “concentrations/physical properties/macroscopic properties of the system do not change”.
enthalpy change/\(\Delta H\) for the reaction is (very) small / OWTTE;
decreases (the amount of ethanoic acid converted);
Accept “increases amount of ethanoic acid present at equilibrium” / OWTTE.
(adding product) shifts position of equilibrium towards reactants/LHS / increases the rate of the reverse reaction / OWTTE;
ethyl ethanoate/\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\);
forms only weak hydrogen bonds (to water);
Allow “does not hydrogen bond to water” / “hydrocarbon sections too long” / OWTTE.
M2 can only be given only if M1 correct.
(large excess of) water will shift the position of equilibrium (far to the left) / OWTTE;
Accept any other chemically sound response, such as “dissociation of ethanoic acid would affect equilibrium”.
Examiners report
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).
Generally candidates found some elements of this question quite challenging but there were accessible marks of even the weakest candidates. The majority of students were able to determine the molar mass of ethanoic acid but some struggled to calculate the mass from the volume. Most candidates were able to identify the role of hydrochloric acid as a catalyst but some struggled to identify the liquid whose volume had the greatest uncertainty. Most candidates were able to calculate the absolute uncertainty of the titre but some lost a mark by omitting the \( + \)/\( - \) sign. Candidates did not identify the first titre as incongruent and simply averaged the three values which perhaps suggests limited experimental experience. Most students could determine an equilibrium constant expression, but many did not answer the question in (g) and did not suggest how the equilibrium could be established experimentally with many referring to the equal rate of the forward and backward reaction. Many candidates were aware of Le Chatelier effects on the position of equilibrium, but a significant number failed to use this information to answer the question asked and could not explain the small effect of temperature changes. Whilst most students managed to identify the ester as the component of the mixture that was insoluble in water, many did not refer to its inability to form strong hydrogen bonds to water which was necessary for the mark. Quite a number of students came up with a valid reason why water would not be a suitable though some students appeared to have overlooked that the question asked for “one other reason” than that implied in (j).

