| Date | May 2009 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 09M.2.sl.TZ1.7 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Predict | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Three compounds with similar relative molecular masses are butane, propanal and propan-1-ol.
List the three compounds in order of increasing boiling point (lowest first) and explain the differences in their boiling points.
Predict, with an explanation, which of the three compounds is least soluble or miscible in water.
When propan-1-ol is oxidized using a warm acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI) two different organic products can be obtained. Deduce the name and structural formula for each of these two products.
Propan-2-ol is an isomer of propan-1-ol. Draw the structure of propan-2-ol.
Identify the class of alcohols that propan-2-ol belongs to and state the name of the organic product formed when it is oxidized by an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI).
Markscheme
butane \( < \) propanal\( < \) propan-1-ol;
butane has van der Waals/London/dispersion forces;
propanal has dipole-dipole attractive forces;
propan-1-ol has hydrogen bonding;
imf marks are independent of the order.
Treat references to bond breaking as contradictions if the imfs are correct.
butane is least soluble;
it cannot form hydrogen bonds/attractive forces with water molecules;
propanal and propanoic acid;
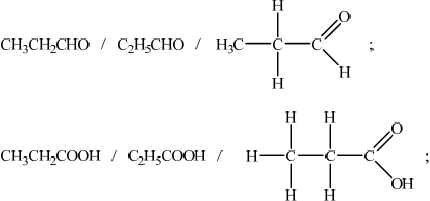
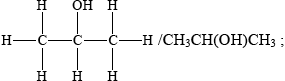
secondary (alcohol);
propanone / acetone;
Examiners report
For (a) (i) of those who attempted this question about half got the order correct. Those with it correct usually gave creditable explanations. With the weaker candidates the most common error was an explanation making reference to the breaking of covalent bonds rather than intermolecular forces.
In (a)(ii) most candidates identified butane as the compound but there were very few sound explanations
The oxidation products of propan-1-ol were generally given correctly by both name and structure.
The structure in (a)(iv) was usually drawn correctly.
Candidates were generally able to identify the class of alcohol and the name of the oxidation product in (a)(v), although this was sometimes referred to as propan-2-one.

