| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.3.sl.TZ2.1 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Show | Question number | 1 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The table summarizes some properties of graphite and graphene.
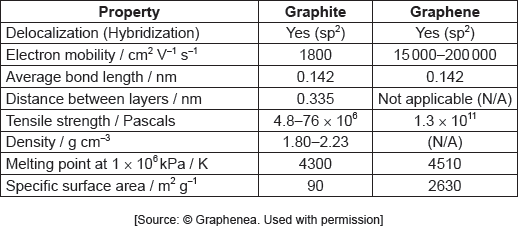
Graphene is two-dimensional, rather than three-dimensional, material.
Justify this by using the structure of graphene and information from the table.
Show that graphene is over 1600 times stronger than graphite.
Identify a value from the table which can be used to support the information about graphene given below.
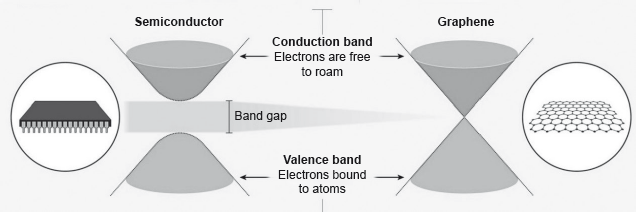
Electrons in a solid are restricted to certain ranges, or bands, of energy (vertical axis). In an insulator or semiconductor, an electron bound to an atom can break free only if it gets enough energy from heat or a passing photon to jump the “band gap”, but in graphene the gap is infinitely small.

Diamond, graphene, and graphite are all network solids.
Suggest, giving a reason, the electron mobility of diamond compared to graphene.
The melting point of diamond at 1 × 106 kPa is 4200 K (in the absence of oxygen).
Suggest, based on molecular structure, why graphene has a higher melting point under these conditions.
Markscheme
consists of single/one sheet/layer «of carbon atoms»
graphene has no density measurement
OR
graphene has no distance between layers data
OR
graphene has large specific surface area «compared to graphite»
Do not accept “sp2” alone without reference to single/one sheet/layer.
Accept “thickness of one atom” OR “consists of a plane” for M1.
[2 marks]
Any one of these alternatives:
ALTERNATIVE 1
«»
1.7 × 103/1711
ALTERNATIVE 2
1600 × 76 × 106 = 1.2 × 1011 «is less than tensile strength of graphene»
ALTERNATIVE 3
= 8.1 × 107 «is greater than upper end of tensile strength for graphite»
Accept any value in the range 1700–27 083. Answer may be expressed in scientific notation or otherwise.
Accept any value calculated which is less than the graphene tensile strength based on a value chosen from within the 4.8–76 × 106 range.
[1 mark]
«graphene has a high electron mobility of» 15 000–200 000 «cm2 V–1 s–1»
A specific value or range of values must be given.
Accept any value in the 15 000–200 000 «cm2 V–1 s–1» range.
[1 mark]
smaller/zero
no delocalized electrons/electrons are bound/electrons not free to move/electrons not free to roam
OR
localized electrons «in sigma bonds»
OR
large band gap
Accept “diamond is a dielectric” OR “diamond does not conduct electricity” for M2.
Award [1 max] for just “immobile/less mobile”.
Award [2] for “electrons immobile «in diamond» due to the large band gap” OR "electrons «in diamond» immobile
since electrons are localized «in the sigma bonds»”.
[2 marks]
shorter bonds in graphene
OR
bonds in graphene intermediate between single and double
OR
bond order in graphene is 1.33
OR
delocalization creates stronger bonds
OR
shorter bonds are stronger
stronger/shorter bonds require higher temperature/faster thermal motion to be altered
OR
stronger/shorter bonds require greater energy to be broken
[2 marks]