| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 17M.2.hl.TZ1.5 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | 5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
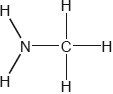
Two hydrides of nitrogen are ammonia and hydrazine, . One derivative of ammonia is methanamine whose molecular structure is shown below.
Hydrazine is used to remove oxygen from water used to generate steam or hot water.
The concentration of dissolved oxygen in a sample of water is .
Estimate the H−N−H bond angle in methanamine using VSEPR theory.
State the electron domain geometry around the nitrogen atom and its hybridization in methanamine.
Ammonia reacts reversibly with water.
Explain the effect of adding ions on the position of the equilibrium.
Hydrazine reacts with water in a similar way to ammonia. (The association of a molecule of hydrazine with a second H+ is so small it can be neglected.)
Calculate the pH of a solution of hydrazine.
Suggest a suitable indicator for the titration of hydrazine solution with dilute sulfuric acid using section 22 of the data booklet.
Outline, using an ionic equation, what is observed when magnesium powder is added to a solution of ammonium chloride.
Determine the enthalpy change of reaction, , in kJ, when 1.00 mol of gaseous hydrazine decomposes to its elements. Use bond enthalpy values in section 11 of the data booklet.
The standard enthalpy of formation of is . Calculate the enthalpy of vaporization, , of hydrazine in . (If you did not get an answer to (f), use but this is not the correct answer.)
Calculate, showing your working, the mass of hydrazine needed to remove all the dissolved oxygen from of the sample.
Calculate the volume, in , of nitrogen formed under SATP conditions. (The volume of 1 mol of gas = at SATP.)
Markscheme
107°
Accept 100° to < 109.5°.
Literature value = 105.8°
[1 mark]
tetrahedral
sp3
No ECF allowed.
[2 marks]
removes/reacts with
moves to the right/products «to replace ions»
Accept ionic equation for M1.
[2 marks]
Kb = 10–5.77 / 1.698 x 10–6
OR
[OH–]2 «= 1.698 × 10–6 × 0.0100» = 1.698 × 10–8
OR
[OH–] «» = 1.303 × 10–4 «mol dm–3»
pH «» = 10.1
Award [3] for correct final answer.
Give appropriate credit for other methods containing errors that do not yield correct final answer.
[3 marks]
methyl red
OR
bromocresol green
OR
bromophenol blue
OR
methyl orange
[1 mark]
bubbles
OR
gas
OR
magnesium disappears
Do not accept “hydrogen” without reference to observed changes.
Accept "smell of ammonia".
Accept 2H+(aq) + Mg(s) Mg2+(aq) + H2(g)
Equation must be ionic.
[2 marks]
bonds broken:
E(N–N) + 4E(N–H)
OR
bonds formed:
E(NN) + 2E(H–H)
OR
Award [3] for correct final answer.
Award [2 max] for +95 «kJ».
[3 marks]
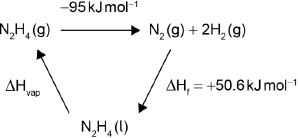
OR
Award [2] for correct final answer. Award [1 max] for –44 «kJ mol–1».
Award [2] for:
ΔHvap = –50.6 kJ mol–1 – (–85 J mol–1) = +34 «kJ mol–1».
Award [1 max] for –34 «kJ mol–1».
[2 marks]
total mass of oxygen
OR
Award [3] for correct final answer.
[3 marks]
Award [1] for correct final answer.
[1 mark]

