| Date | May 2010 | Marks available | 9 | Reference code | 10M.3.sl.TZ2.B2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Deduce, Describe, List, and State | Question number | B2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Proteins are natural polymers.
(a) List four major functions of proteins in the human body.
(b) Deduce the structures of two different tripeptides that can be formed when all three amino acids given below react together.

(c) Deduce the number of tripeptides that could be formed by using all three of the above amino acids to form a tripeptide.
(d) State the type of bonding that is responsible for the primary and secondary structures of proteins.
Primary:
Secondary:
(e) Describe and explain the tertiary structure of proteins. Include in your answer all the bonds and interactions responsible for the tertiary structure.
Markscheme
(a) structure / growth / repair
enzymes
hormones
transport
immunoproteins/antibodies
energy source
Two functions score [1].
(b) 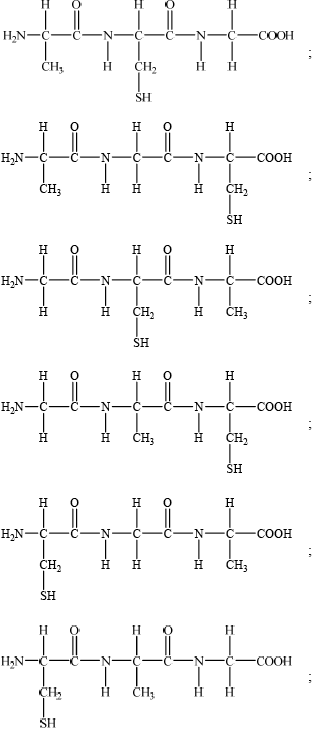
Accept CONH for peptide bond.
Penalize incorrect representation of peptide bond (e.g. COHN) once only.
(c) 6;
(d) 
(e) secondary structure folds to form a (unique) 3-D/dimensional structure of the protein;
Structure stabilized by:
covalent bonds / disulfide bridges
hydrogen/H-bonding
ionic bonds / salt bridges
van der Waals’/dispersion/London forces
Two bond types score [1].
Examiners report
Often quite well done. In part (a), whilst proteins can be used as an energy source, energy storage would not be considered a major function as the body usually stores energy in other forms. In Part (e), few candidates pointed out that the tertiary structure is a folding of the primary and secondary structures that gives the protein its three-dimensional shape.

