| Date | May 2011 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 11M.3.sl.TZ2.B2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Describe | Question number | B2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A mixture of the amino acids serine (Ser), glutamic acid (Glu) and lysine (Lys) was separated using electrophoresis and a buffer of pH 5.7. A drop containing the mixture was placed in the centre of the paper and a potential difference was applied. The amino acids were developed and the following results were obtained.
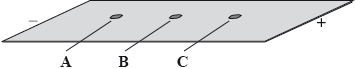
Describe how the amino acid spots may have been developed.
Predict which amino acid is present at spot C. Explain your answer.
The amino acid at spot B is at its isoelectric point. Describe one characteristic of an amino acid at its isoelectric point.
Explain, using equations, how the amino acid glycine (Gly) can act as a buffer
Markscheme
organic dye / ninhydrin;
glutamic acid/Glu;
isoelectric point is below pH of buffer / acts as an acid / loses \({{\text{H}}^ + }\);
becomes negatively charged;
balanced (positive and negative) charges / no overall charge / zwitterion;
amphoteric / buffer solution;
\({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{NC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}} + {{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{N}}^ + }{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}/{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{N}}^ + }{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}^ + } \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{N}}^ + }{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}\);
\({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{NC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{NC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}/\)
\({{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{N}}^ + }{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{NC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\)
Accept \( \to \) instead of \( \rightleftharpoons \)
Examiners report
Many candidates described electrophoresis instead of stating that ninhydrin was used to develop the amino acid spots. The process of electrophoresis was detailed in the stem of the question, so candidates should have been able to determine what was required if the question had been read carefully.
Predicting which amino acid was closer to the positive electrode was challenging, although many candidates scored some marks for their reasoning.
The majority of candidates correctly described one characteristic of an amino acid at its isoelectric point.
In (b) very few could write equations to explain how glycine can act as a buffer. Most candidates answered in words only, even though equations were specifically requested. A G2 comment suggested that SL candidates did not need to know about buffers. This is clearly stated as a requirement in B.2.2.

