| Date | November 2011 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 11N.3.sl.TZ0.B2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | B2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Proteins are macromolecules formed from 2-amino acids. Once a protein has been hydrolysed, chromatography and electrophoresis can be used to identify the amino acids present.
State the name of the linkage that is broken during the hydrolysis of a protein and draw its structure.
Explain how electrophoresis is used to analyse a protein.
Markscheme
peptide/amide;
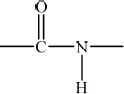 ;
;
Continuation bonds are needed for the mark.
add HCl/NaOH/enzyme (to hydrolyse the protein into amino acids);
mixture of amino acids is placed on the centre of a gel/PAGE/polyacrylamide/paper in buffer solution;
voltage/potential difference applied across gel;
Do not accept electric current.
different amino acids move to different distances according to their charge/isoelectric point / move at different rates towards oppositely charged electrodes;
gel/paper developed by spraying with ninhydrin/organic dye/can be detected by a stain/made to fluoresce under ultra-violet light;
distances moved/isoelectric points are compared with literature values;
Examiners report
It was surprising to see that quite a few candidates did not know the name of the linkage broken during the hydrolysis of a protein and only about half of the candidates, who stated the name could draw the structure of the peptide bond correctly. In some cases glycosidic or ester linkage appeared.
The explanation of how electrophoresis is used to analyse a protein was generally answered very well.

