| Date | May 2010 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 10M.3.sl.TZ1.B1 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Deduce | Question number | B1 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Individual 2-amino acids have different structures depending on the pH of the solution they are dissolved in. The structures of serine and cysteine are given in Table 19 of the Data Booklet.
Deduce the structure of serine in
(i) a solution with a pH of 2.
(ii) a solution with a pH of 12.
Deduce the structure of serine at the isoelectric point.
Deduce the structures of the two different dipeptides that can be formed when one molecule of serine reacts with one molecule of cysteine.
Markscheme
(i) 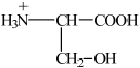 ;
;
If R– used or incorrect amino acid structure chosen from data book apply ECF for subsequent answers.
(ii) 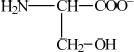 ;
;
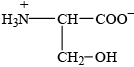 ;
;
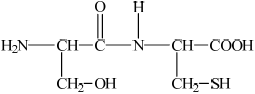 ;
;
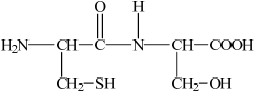 ;
;
Accept –CO–NH–/–CO–HN– for peptide linkage.
Examiners report
Most candidates simply drew the structure of the amino acid from the Data Booklet, and did not indicate the conjugate acid or base of the amino acid in solution in part (a).
Few knew how to draw the structure of the zwitterion in part (b). One G2 respondent commented that deducing the structure of an amino acid at varying pH levels is not on the syllabus. It is, in fact, referred to in B.2.2.
The better candidates were able to draw structures of two dipeptides.
Many weaker candidates were unable to create peptide links, and joined the molecules creatively but incorrectly.

