| Date | November 2013 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 13N.3.hl.TZ0.8 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Identify | Question number | 8 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The following products result from the hydrolysis of a triglyceride.
\({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{31}}}}{\text{COOH}}\) \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{13}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{27}}}}{\text{COOH}}\) \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{15}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{29}}}}{\text{COOH}}\)
Draw a possible structure for the triglyceride.
State the other reactant and one essential condition that would favour this hydrolysis reaction in the body.
Identify which product is polyunsaturated, and outline why foods containing this type of fatty acid are important for health.
Markscheme
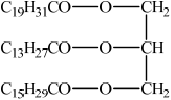 ;
;
Accept alternative orders for the hydrocarbon tails.
water/\({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) and enzyme/biological catalyst/lipase;
Accept acidic/alkaline/basic condition instead of water.
Do not award mark for lipase alone without water/ H2O.
\({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{31}}}}{\text{COOH}}\);
they lower level of LDL cholesterol/low-density lipoproteins / reduce (the risk of) heart disease;
Allow comparison with saturated fats with explanation.
Examiners report
Option B was a very popular, and question 6 was well answered with the exception of not listing alkenyl when identifying two functional groups common to three vitamins (A, C and D). Some students did not read the question on formula of zwitterion carefully and instead have the formula of the amino acid itself without any charges. In the separation of alanine and cysteine, the first mark was well scored by many while the second mark proved to be more demanding and often candidates lost this mark as no reference was made to charges or charges inversely stated. Although the disulfide bridge was correctly identified by even weaker candidates a much few were able to identify this as a covalent bond. Structure of the triglyceride was better answered than in past sessions but drawing the ester linkage correctly was still challenging for many candidates. Although the identification of the other reactant (water) was identified by many, the one essential condition (enzyme/lipase) was done poorly. Identification of the polyunsaturated fatty acid was done well by most but the second mark on its ability to lower LDL cholesterol was missed by most. The question on enzymes and inorganic catalysts was done poorly since comparison was often missing. While some candidates were able to suggest a pair of ions in cytochrome oxidase, only stronger candidates provided both pairs. Competitive and non-competitive inhibition was generally well done; however, the reason why it is more likely that NO, rather than the cyanide ion, acts competitively was not done as well. The redox reaction of the reducing agent \({\text{X}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\) with \({{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) produced a range of possible equations but rarely did candidates scored full marks.
Option B was a very popular, and question 6 was well answered with the exception of not listing alkenyl when identifying two functional groups common to three vitamins (A, C and D). Some students did not read the question on formula of zwitterion carefully and instead have the formula of the amino acid itself without any charges. In the separation of alanine and cysteine, the first mark was well scored by many while the second mark proved to be more demanding and often candidates lost this mark as no reference was made to charges or charges inversely stated. Although the disulfide bridge was correctly identified by even weaker candidates a much few were able to identify this as a covalent bond. Structure of the triglyceride was better answered than in past sessions but drawing the ester linkage correctly was still challenging for many candidates. Although the identification of the other reactant (water) was identified by many, the one essential condition (enzyme/lipase) was done poorly. Identification of the polyunsaturated fatty acid was done well by most but the second mark on its ability to lower LDL cholesterol was missed by most. The question on enzymes and inorganic catalysts was done poorly since comparison was often missing. While some candidates were able to suggest a pair of ions in cytochrome oxidase, only stronger candidates provided both pairs. Competitive and non-competitive inhibition was generally well done; however, the reason why it is more likely that NO, rather than the cyanide ion, acts competitively was not done as well. The redox reaction of the reducing agent \({\text{X}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\) with \({{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) produced a range of possible equations but rarely did candidates scored full marks.
Option B was a very popular, and question 6 was well answered with the exception of not listing alkenyl when identifying two functional groups common to three vitamins (A, C and D). Some students did not read the question on formula of zwitterion carefully and instead have the formula of the amino acid itself without any charges. In the separation of alanine and cysteine, the first mark was well scored by many while the second mark proved to be more demanding and often candidates lost this mark as no reference was made to charges or charges inversely stated. Although the disulfide bridge was correctly identified by even weaker candidates a much few were able to identify this as a covalent bond. Structure of the triglyceride was better answered than in past sessions but drawing the ester linkage correctly was still challenging for many candidates. Although the identification of the other reactant (water) was identified by many, the one essential condition (enzyme/lipase) was done poorly. Identification of the polyunsaturated fatty acid was done well by most but the second mark on its ability to lower LDL cholesterol was missed by most. The question on enzymes and inorganic catalysts was done poorly since comparison was often missing. While some candidates were able to suggest a pair of ions in cytochrome oxidase, only stronger candidates provided both pairs. Competitive and non-competitive inhibition was generally well done; however, the reason why it is more likely that NO, rather than the cyanide ion, acts competitively was not done as well. The redox reaction of the reducing agent \({\text{X}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\) with \({{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) produced a range of possible equations but rarely did candidates scored full marks.

