Comparing Strong & Weak Acids
- Strong and weak acids can be distinguished from each other by their:
- pH value (using a pH meter or universal indicator)
- Electrical conductivity
- Reactivity
pH value
- An acid dissociates into H+ in solution according to:
HA → H+ + A-
- The stronger the acid, the greater the concentration of H+ and therefore the lower the pH
pH value of a Strong Acid & Weak Acid Table

Electrical conductivity
- Since a stronger acid has a higher concentration of H+ it conducts electricity better
- Stronger acids therefore have a greater electrical conductivity
- The electrical conductivity can be determined by using a conductivity meter
- Like the pH meter, the conductivity meter is connected to an electrode
- The conductivity of the solution can be read off the meter
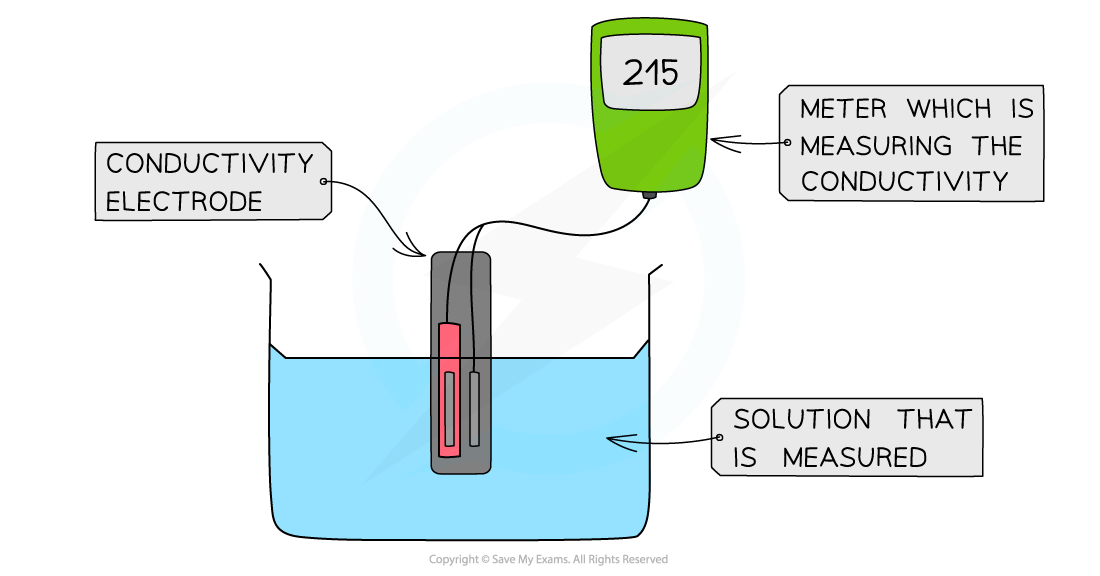
The diagram shows a digital conductivity meter that measures the electrical conductivity of a solution using an electrode
Reactivity
- Strong and weak acids of the same concentrations react differently with reactive metals
- This is because the concentration of H+ is greater in strong acids compared to weak acids
- The greater H+ concentration means that more H2 gas is produced in a shorter time
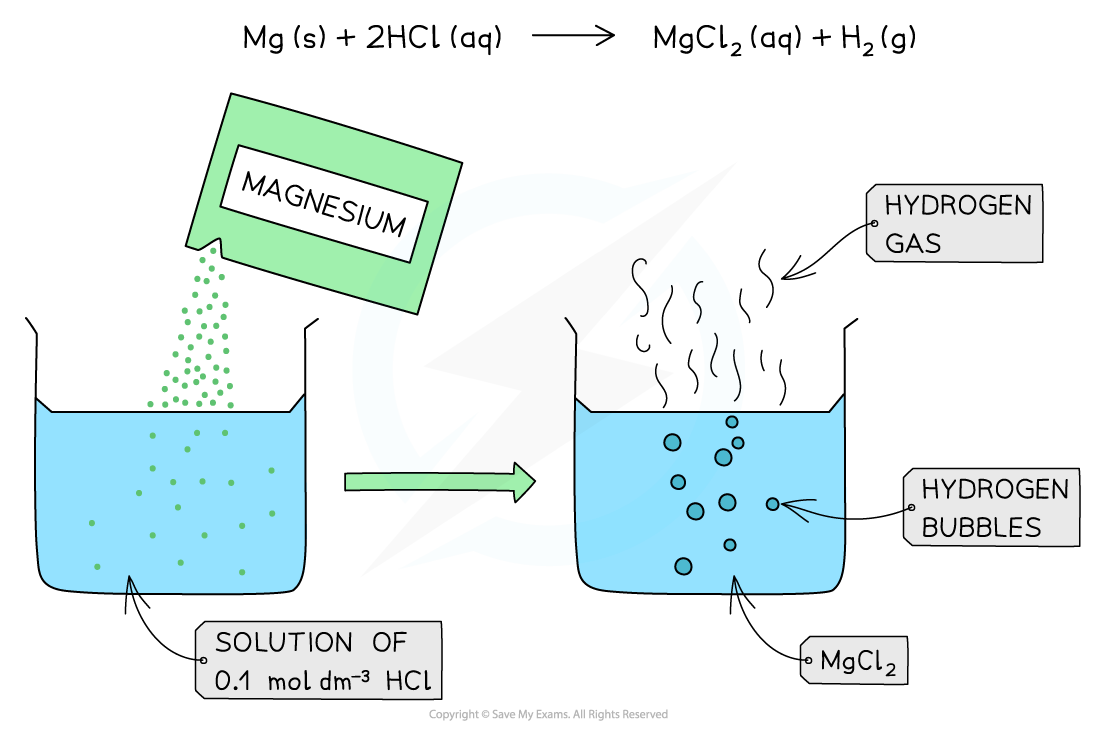
The diagram shows the reaction of 0.1 mol dm-3 of a strong acid (HCl) with Mg. The reaction produces a lot of bubbles and hydrogen gas due to the high concentration of H+ present in solution
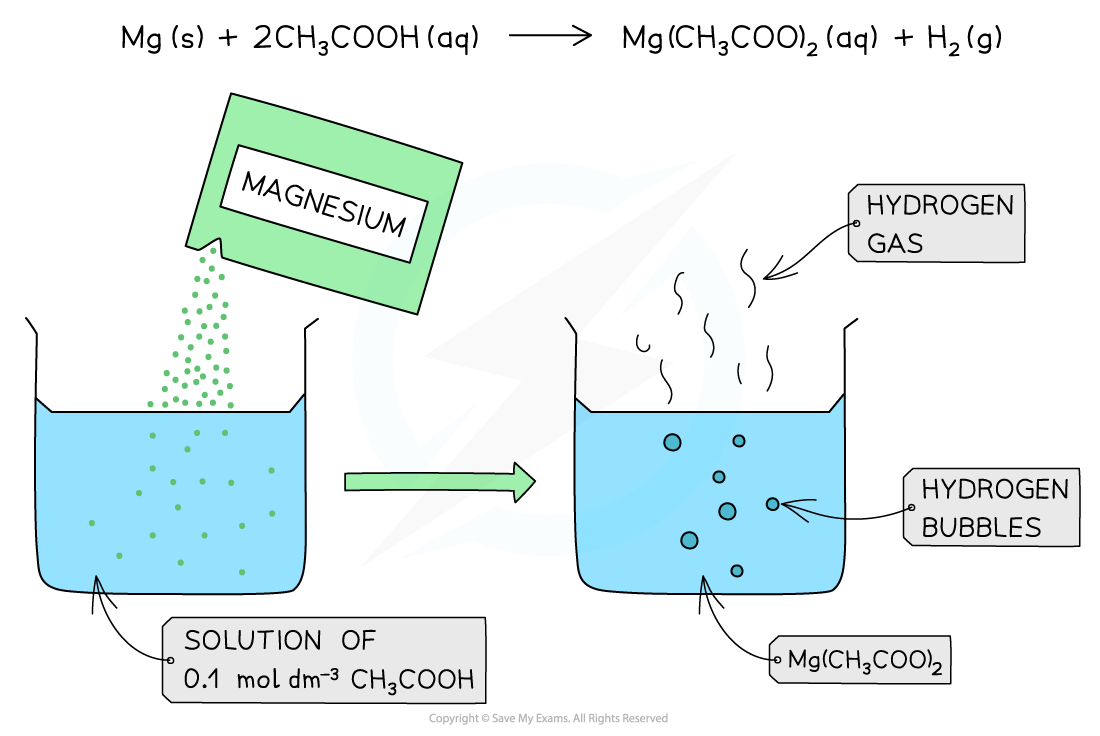
The diagram shows the reaction of 0.1 mol dm-3 of a weak acid (CH3COOH) with Mg. The reaction produces fewer bubbles of hydrogen gas due to the lower concentration of H+ present in solution
- Similar observations would be made in the reaction between strong and weak acids with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates, although the gas given off this time is carbon dioxide
- With oxides and hydroxides, there may not be a lot of visible changes although it is likely that they would dissolve faster in a strong acid than in a weak acid
- These reactions are also likely to produce larger enthalpy changes which could be seen in higher temperature rises
Exam Tip
The above-mentioned properties of strong and weak acids depend on their ability to dissociate and form H+ ions.Stronger acids dissociate more, producing a greater concentration of H+ ions and therefore showing lower pH values, greater electrical conductivity and more vigorous reactions with reactive metals.
