Alkanes
- Hydrocarbons are compounds containing hydrogen and carbon only
- There are four families of hydrocarbons you should know: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and arenes
- Alkanes have the general molecular formula CnH2n+2. They contain only single bonds and are said to be saturated
- Alkanes are named using the nomenclature rule alk + ane
- The alk depends on the number of carbons as outlined in the previous Section 10.1.2
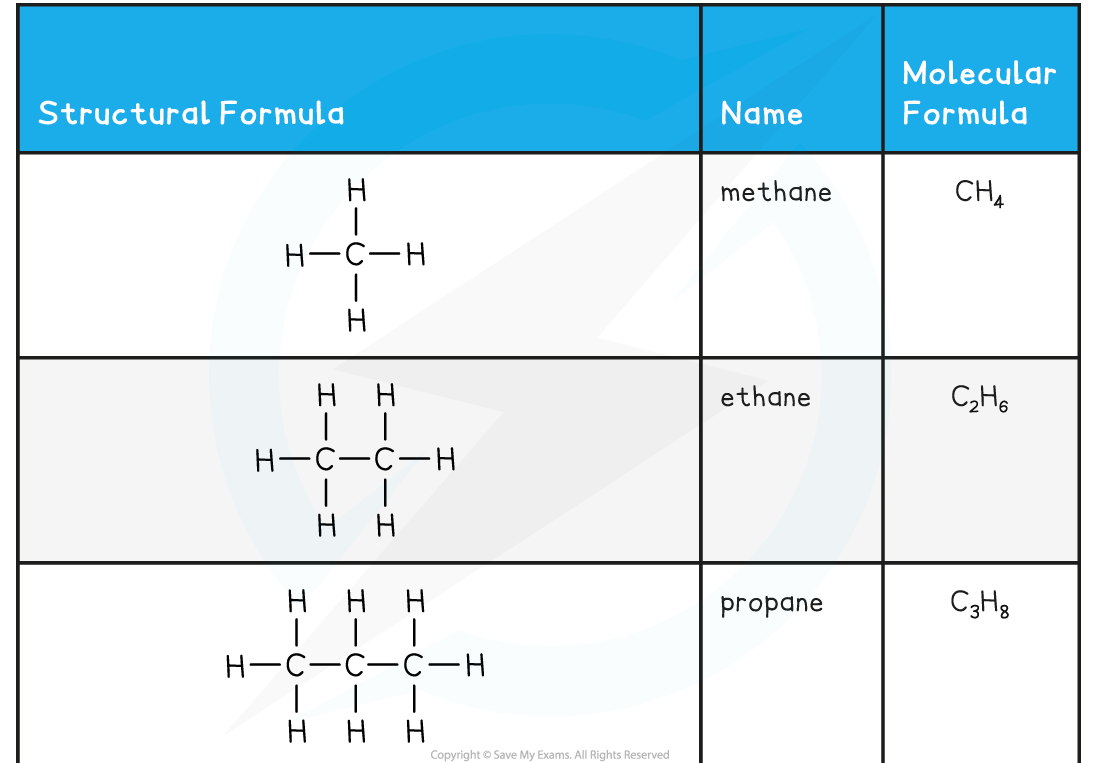
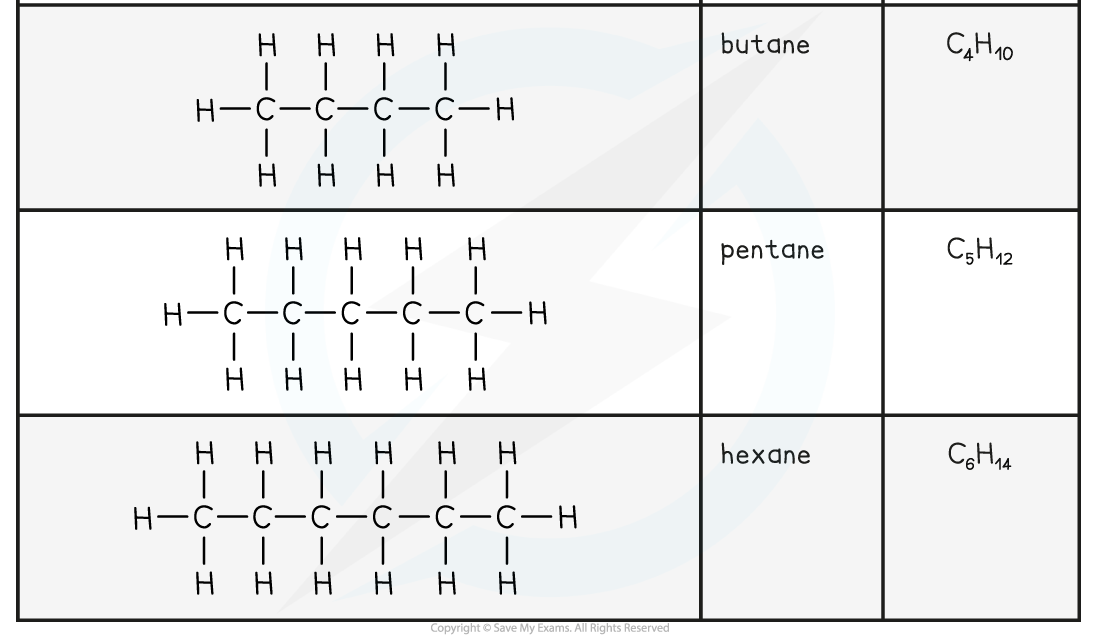
The first six members of the alkane family
Alkenes
- Alkenes have the general molecular formula CnH2n
- They are said to be unsaturated
- Alkenes are named using the nomenclature rule alk + ene
- In molecules with a straight chain of 4 or more carbon atoms, the position of the C=C double bond must be specified
- The carbon atoms on the straight chain must be numbered, starting with the end closest to the double bond
- The lowest-numbered carbon atom participating in the double bond is indicated just before the -ene:
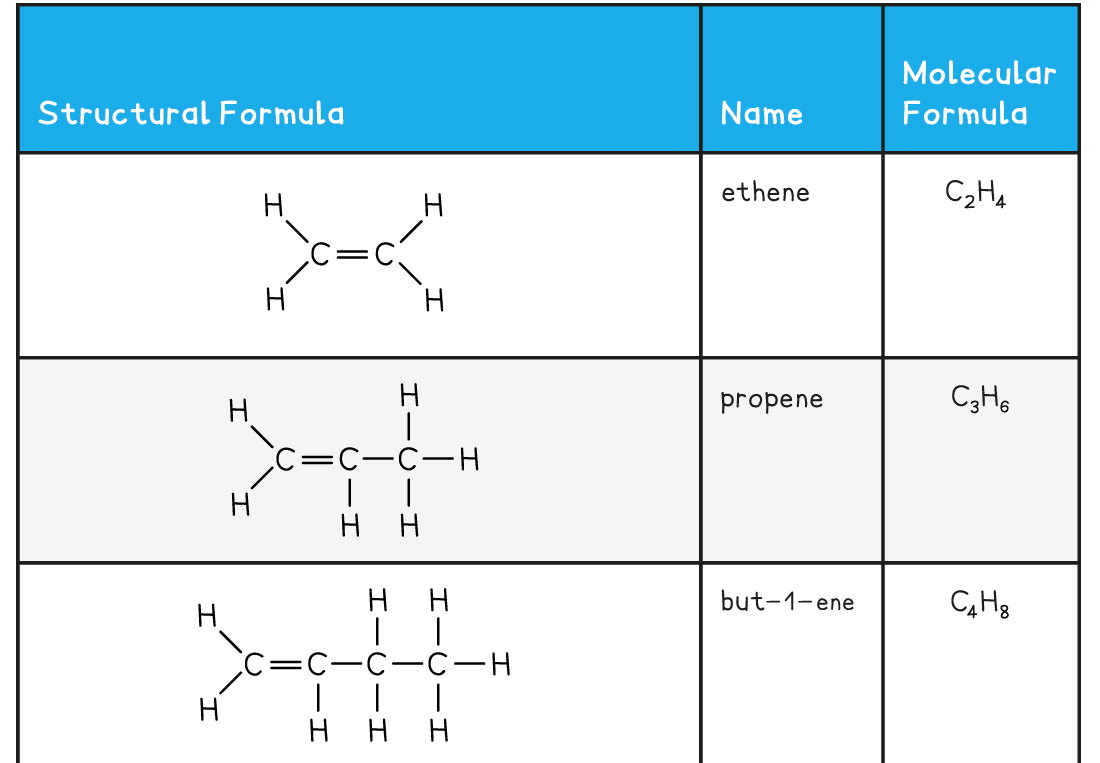
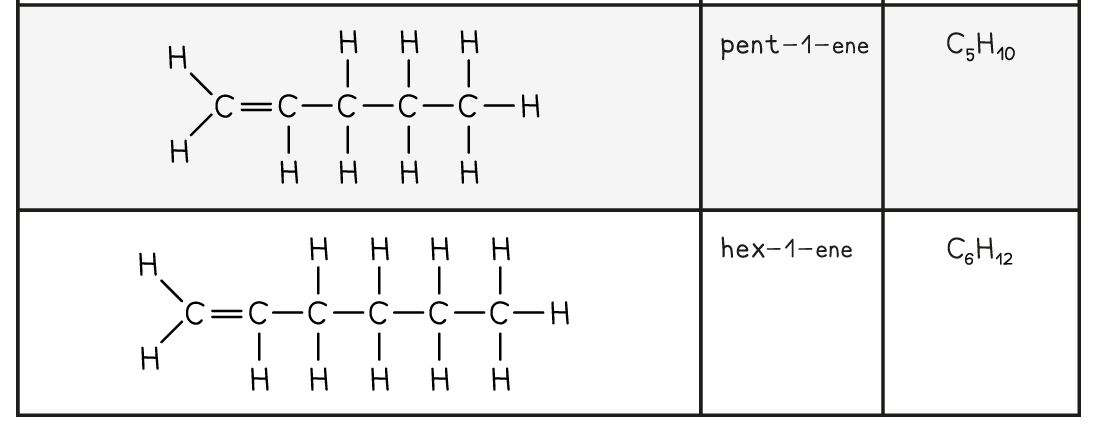
The first five members of the alkene family
- There is a distinction to be made between the name of the functional group and the name of the family
- The name of the family is alkene, but the name of the functional group is alkenyl
Alkynes
- Alkynes have the general molecular formula CnH2n-2
- The triple bond makes them unsaturated molecules
- Alkynes are named using the nomenclature rule alk + yne
- As with alkenes, in molecules with a straight chain of 4 or more carbon atoms, the position of the triple bond must be specified
- The carbon atoms on the straight chain must be numbered, starting with the end closest to the triple bond
- The lowest-numbered carbon atom participating in the triple bond is indicated just before the -yne:
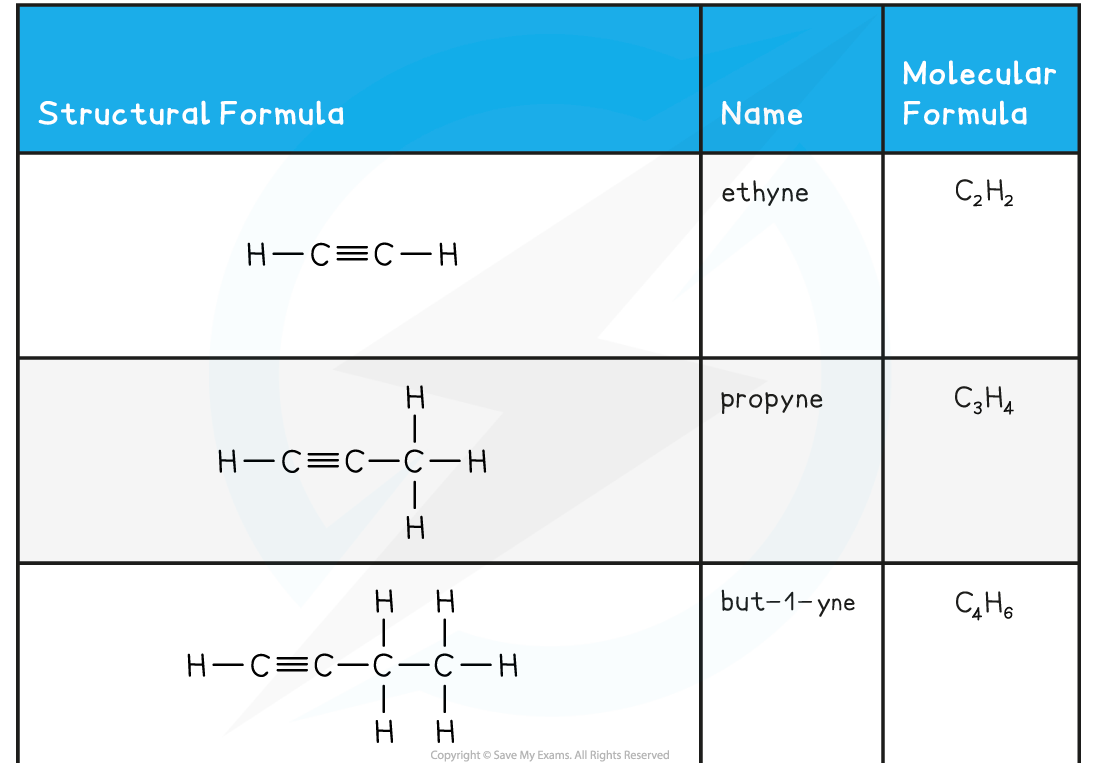
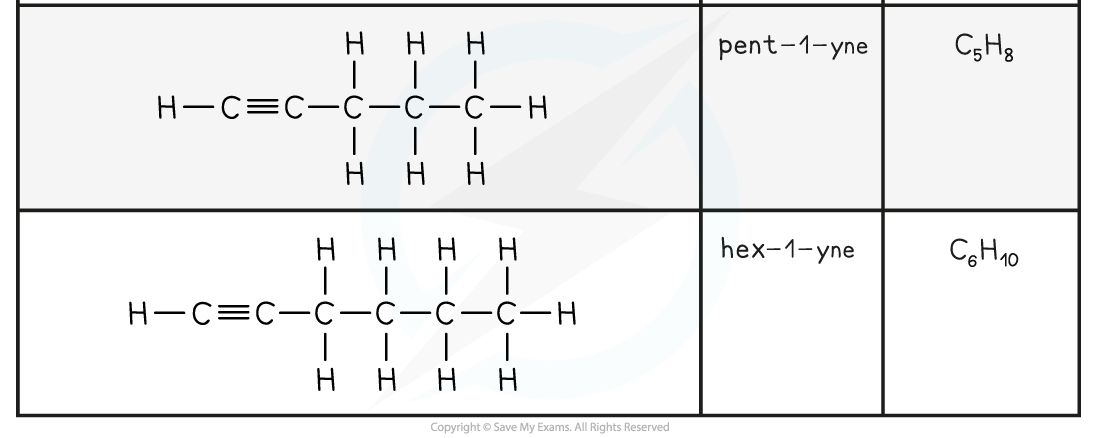
The first five members of the alkyne family
- The name of the functional group is alkynyl
Arenes
- Arene is the collective name given to compounds with one or more rings with pi electrons that are delocalised throughout the ring(s)
- Compounds with this feature are said to be aromatic
- This doesn't mean they are necessarily smelly, although a lot of naturally occurring arenes do have distinctive smells!

Arenes are present in many everyday chemicals and pharmaceuticals
- Benzene, C6H6, is the only aromatic hydrocarbon that is covered in IB Chemistry and is dealt with in Section 10.1.12
- The functional group in benzene is known as a phenyl group when attached to other molecules
