Halogenoalkanes
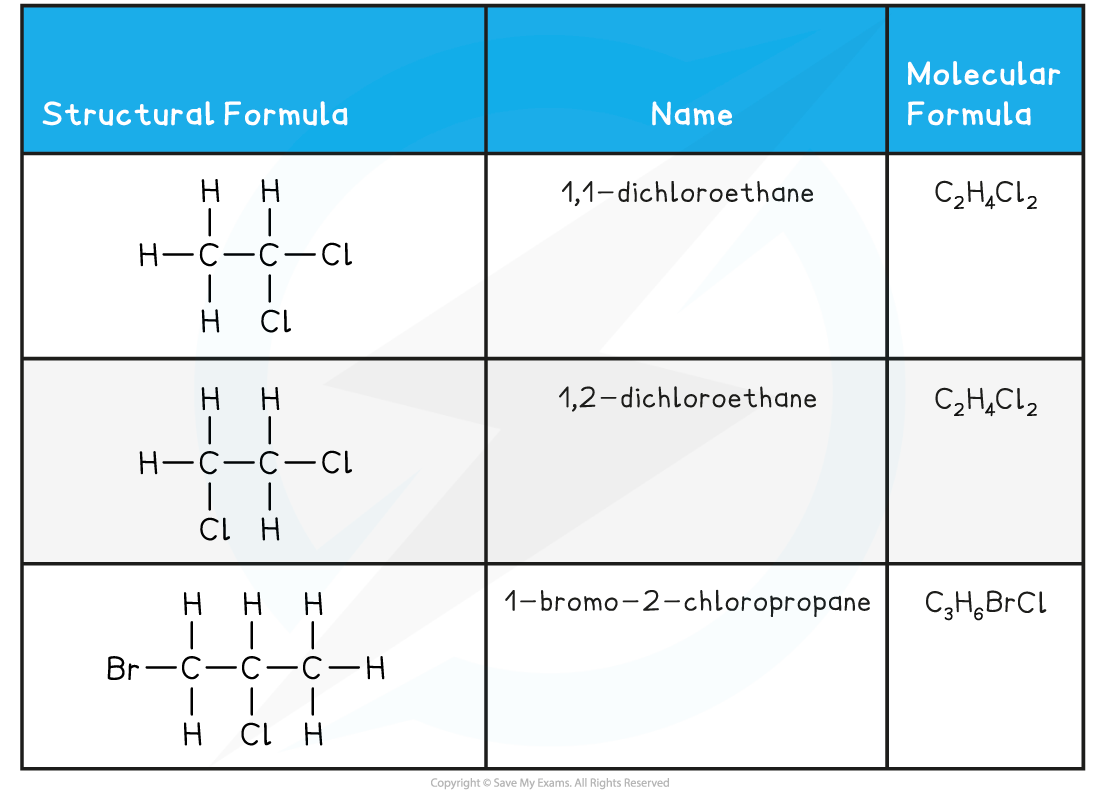
- Halogenoalkanes or Haloalkanes have the general molecular formula, CnH2n+1X, where X represents a halogen
- Haloalkanes are named using the prefix chloro-, bromo- or iodo-, with the ending -ane
- In molecules with a straight chain of three or more carbon atoms, the position of the halogen atom must also be specified
- The carbon atoms on the straight chain must be numbered, starting with the end closest to the halogen atom
- The number of the carbon atom attached to the halogen is indicated before the prefix:
Haloalkanes Examples Table
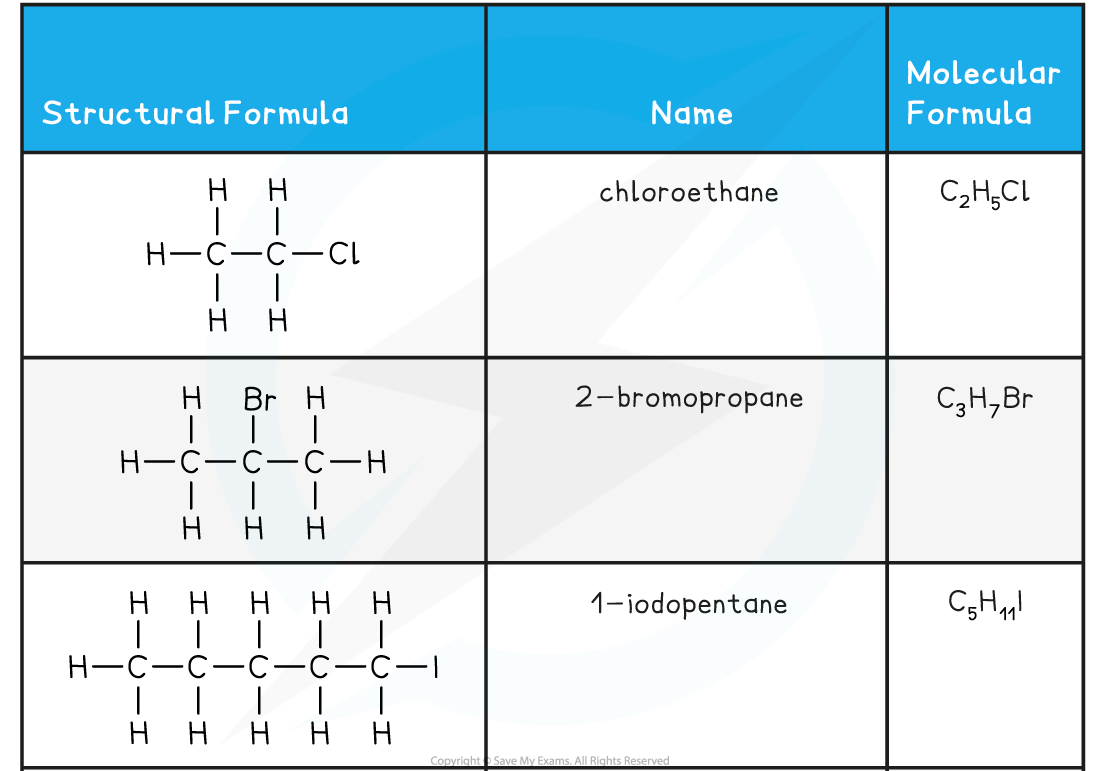
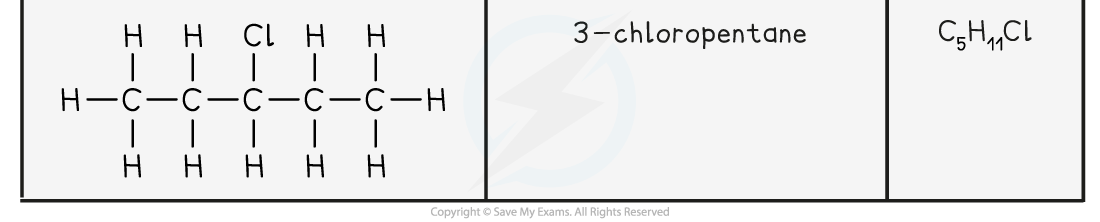
- The position of all halogens in dihaloalkanes except those with one carbon atom must be specified.
- If there is more than one of the same type of halogen atom on the molecule, the di (two), tri (three) or tetra (four) prefixes must also be used
Dihaloalkanes Examples Table