Hydration of Alkenes
- When alkenes are treated with steam at 300 oC, a pressure of 60 atmospheres and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) or phosphoric acid (H3PO4) catalyst, the water is added across the double bond in a reaction known as hydration
- An alkene is converted into an alcohol
- The reaction processes via an intermediate in which H+ and HSO4- ions are added across the double bond
- The intermediate is quickly hydrolysed by water, reforming the sulfuric acid
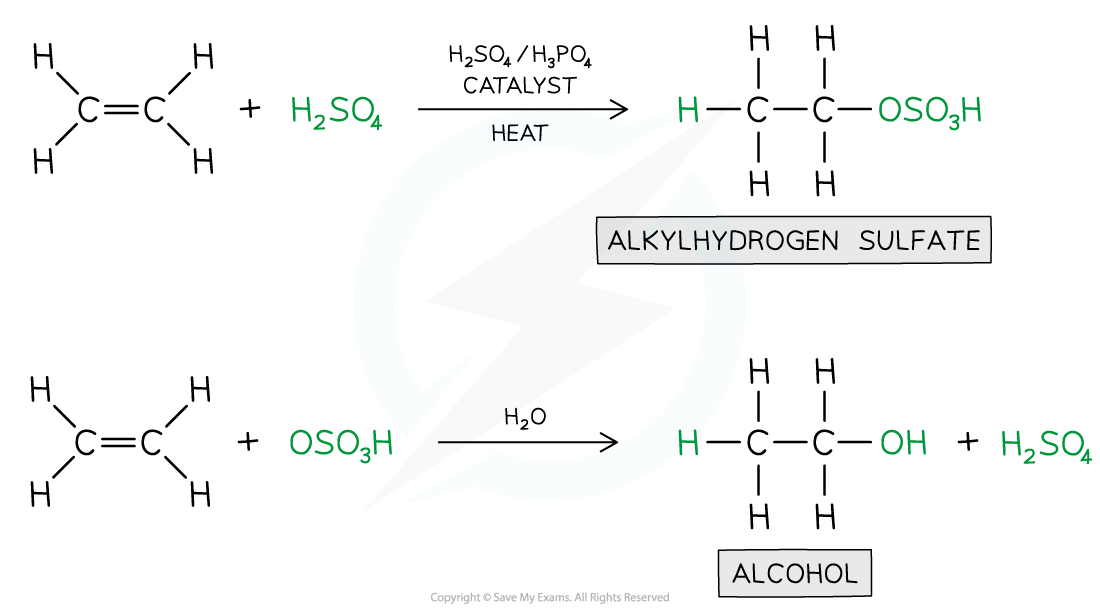
Hydration in Alkenes
- This is a very important industrial reaction for producing large quantities of ethanol, a widely used solvent and fuel
- The process is much faster and higher yielding that producing ethanol by fermentation
