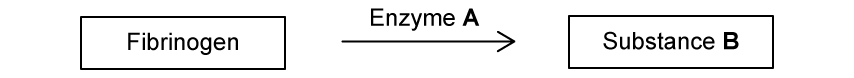a)
The diagram below shows the production and role of antibodies in the body.
Antibodies are produced by cell X .
Identify cell X .
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Antibodies are produced in response to the antigens present on pathogens.
Define the term 'antigen'.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Antibodies aid the body in fighting pathogens in a number of different ways.
State one way in which they achieve this.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Antibodies are short-lived, but memory cells remain to provide long term immunity against a second infection by the same type of pathogen.
Describe the secondary response of the memory cells during an infection by the same type of pathogen.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
The diagram below shows the action of penicillin on the bacterial cell wall.
Penicillin is an example of an antibiotic.
Define the term 'antibiotic'.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Penicillin is an example of a commonly used antibiotic. It is produced naturally by a fungus (penicillium ) to kill competing bacteria in their environment.
Based on the information in the diagram in part a), state the way in which penicillin kills bacteria.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Other than the process stated at part b), list two processes in prokaryotic cells that antibiotics may target.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Antibiotics are not effective against viruses since they lack the structure and mechanisms of prokaryotic cells. Certain viral diseases are treated with substances known as antivirals.
State the way in which an antiviral works.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Skin is the largest organ of the body and forms part of the primary defence against pathogens.
List two ways in which the skin defends the body against pathogens.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Platelets are very important in maintaining the integrity of broken skin as a barrier.
Define the term 'platelet'.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Platelets are essential in the process of blood clotting.
State the role of platelets in response to blood vessel damage.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question