Question 1
Which row correctly labels this diagram of a cell surface membrane?
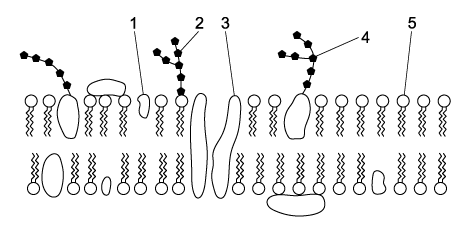
| Cholesterol | Glycoprotein | Glycolipid | Protein | Phospholipid | |
| A. | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| B. | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| C. | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| D. | 5 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
Which row correctly labels this diagram of a cell surface membrane?

| Cholesterol | Glycoprotein | Glycolipid | Protein | Phospholipid | |
| A. | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| B. | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| C. | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| D. | 5 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
What is the main function of cholesterol in the cell surface membrane?
To provide hydrophilic channels.
To regulate membrane fluidity.
To assist active transport.
To assist cell adhesion.
Which of the following correctly describes the model of membrane structure that is now widely accepted?
A phospholipid bilayer with a series of proteins that are free to move around within the membrane.
A phospholipid bilayer.
A phospholipid bilayer with a layer of protein on either side.
A phospholipid bilayer with a series of proteins in fixed positions throughout.
Which of the statements about membrane fluidity is correct?
The higher the proportion of unsaturated fatty acid tails in a membrane, the higher the membrane fluidity.
Cholesterol can restrict the motion of the molecules in a membrane, increasing membrane fluidity.
Cells do not need to regulate membrane fluidity.
The lower the proportion of unsaturated fatty acid tails in a membrane, the higher the membrane fluidity.
Which of the following modes of transport is not an example of active or bulk transport?
Water moving through a partially permeable membrane.
Phagocytosis of a pathogen.
Exocytosis.
Endocytosis.