| Date | May 2013 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 13M.2.sl.TZ1.6 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Compare | Question number | 6 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The element boron has two naturally occurring isotopes, \(^{{\text{10}}}{\text{B}}\) and \(^{{\text{11}}}{\text{B}}\).
Define the term isotopes of an element.
Calculate the percentage abundance of each isotope, given that the relative atomic mass of B is 10.81.
Deduce the Lewis structures of \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) and \({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\).
\[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\]
Describe how covalent bonds are formed.
Compare the shapes of the two molecules and explain the difference using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
Predict and explain whether the molecules \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) and \({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\) are polar molecules.
Markscheme
atoms of the same element/with the same number of protons/with same atomic
number but different number of neutrons/mass number/mass;
\(10x + 11(1 - x) = 10.81,{\text{ }}x = 0.19\);
Accept similar method.
10B: 19% and 11B: 81%;
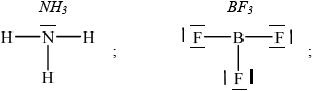
Accept any combination of lines, dots or crosses to represent electron pairs.
sharing of electrons between atoms;
\({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\): (trigonal/triangular) pyramidal;
\({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\): trigonal/triangular planar;
\({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) has 4 negative centres of charge/three bonding pairs and one lone pair and \({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\) has 3 negative centres of charge/three bonding pairs / OWTTE;
(bond angles) 107° in \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) and 120° in \({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\);
Accept 107.5° for NH3.
\({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\) not polar as no net dipole moment / BF bond polarities cancel each other out / symmetrical distribution of charge;
\({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) polar as net dipole moment present / NH bond polarities do not cancel each other out / unsymmetrical distribution of charge;
Accept suitable diagram showing dipole moments.
Do not accept electronegativities cancel out.
Examiners report
Few candidates defined isotopes in terms of atoms.
The percentage abundance was generally done well.
The Lewis structure of \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) was well answered, though many forgot the non-bonding electron pairs of fluorine.
The covalent bond was often just described as electron sharing between non-metals.
Shapes of molecules and angles were often well known, but the explanation using the VSEPR theory was very weak, with many students not being able to describe the bonding and lone pairs in terms of negative charge centres.
Polarity was very poorly understood, with almost no candidates actually talking about polarity of bonds or showing an understanding of the impact of symmetry on the overall dipole moment.

