| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 18M.2.sl.TZ2.3 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Outline | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The emission spectrum of an element can be used to identify it.
Elements show trends in their physical properties across the periodic table.
Draw the first four energy levels of a hydrogen atom on the axis, labelling n = 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Draw the lines, on your diagram, that represent the electron transitions to n = 2 in the emission spectrum.
Outline why atomic radius decreases across period 3, sodium to chlorine.
Outline why the ionic radius of K+ is smaller than that of Cl−.
Copper is widely used as an electrical conductor.
Draw arrows in the boxes to represent the electronic configuration of copper in the 4s and 3d orbitals.
Impure copper can be purified by electrolysis. In the electrolytic cell, impure copper is the anode (positive electrode), pure copper is the cathode (negative electrode) and the electrolyte is copper(II) sulfate solution.
Formulate the half-equation at each electrode.
Outline where and in which direction the electrons flow during electrolysis.
Markscheme
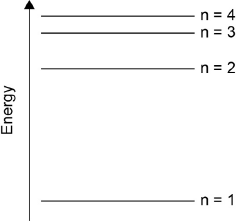
4 levels showing convergence at higher energy
[1 mark]
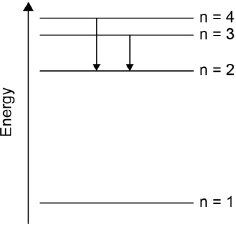
arrows (pointing down) from n = 3 to n = 2 AND n = 4 to n = 2
[1 mark]
same number of shells/«outer» energy level/shielding AND nuclear charge/number of protons/Zeff increases «causing a stronger pull on the outer electrons»
[1 mark]
K+ 19 protons AND Cl– 17 protons
OR
K+ has «two» more protons
same number of electrons/isoelectronic «thus pulled closer together»
[2 marks]
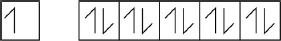
[1 mark]
Anode (positive electrode):
Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e–
Cathode (negative electrode):
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
Accept Cu(s) – 2e– → Cu2+(aq).
Accept \( \rightleftharpoons \) for →
Award [1 max] if the equations are at the wrong electrodes.
[2 marks]
«external» circuit/wire AND from positive/anode to negative/cathode electrode
Accept “through power supply/battery” instead of “circuit”.
[1 mark]
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.6b: Explain why the atomic radius of elements decreases across the period.
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.5b: (i) Predict any changes that may be observed in each...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.7: Which properties decrease down group 1? I. Melting point II. Atomic radius III. ...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.6d: (i) Deduce the order of reactivity of these four metals, from the least to the most...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.6e.i: Compare the properties of the three oxides by completing the table below.
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.7a: State the element that you would expect to have chemical properties most similar to those of...
- 13M.1.hl.TZ1.15: Which process is endothermic? A. ...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.8: Which statement concerning electronegativity is correct? A. Electronegativity increases...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.9: Which statements are correct? I. Fluorine will react with potassium chloride solution to...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.ii: Using Table 7 of the Data Booklet, explain the trends in electronegativity values of the...
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.8: Which properties of the alkali metals decrease going down group 1? A. First ionization...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.4b: (i) Define the term electronegativity. (ii) Compare the relative polarities of the...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.3b: Explain why sulfur, \({{\text{S}}_{\text{8}}}\), has a higher melting point than phosphorus,...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.5b: (i) Define the term first ionization energy of an atom. (ii) Explain the general...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.8b.iv: Sketch and explain the shape of the graph obtained for the successive ionization energies of...
- 09M.1.hl.TZ2.9: Which equation best represents the first ionization energy of magnesium? A. ...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.2a: Describe the acid-base character of the oxides of each of the period 3 elements, Na to Cl.
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.5b.iii: State the equations for the reactions of sodium oxide,...
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.7: Which physical property of elements is represented by y on the graph below? A. First...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.8: Which periodic trend is described correctly?
- 16N.1.hl.TZ0.7: Which property increases down group 17, the halogens? A. Electron affinity B. Boiling...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.8: Which solution forms when phosphorus(V) oxide, P4O10, reacts with water?
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.4e: In addition to magnesium oxide, magnesium forms another compound when burned in air. Suggest...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.5: X, Y and Z represent the successive elements, Ne, Na and Mg, but not necessarily in that...
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.3b: Explain why the melting points of the group 1 metals (Li → Cs) decrease down the group...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.6b: (i) Deduce the order of reactivity of these four metals, from the least to the most...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ1.9: The electronegativities of four elements are given in the table. Which statement is...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.5e.i: \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) does not conduct electricity in the solid...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.7: Which oxides form acidic solutions when added to water? A. ...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.2a: Describe and explain the trend in atomic radius across period 3.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.7a.i: Explain the trend in reactivity of the halogens.
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.9: Which statements about the periodic table are correct? I. The elements Mg, Ca and Sr...
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.10: The electronegativities of four different elements are given below (the letters are not their...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.5b.iii: A graph of atomic radius plotted against atomic number shows that the atomic radius decreases...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.7c: Explain, using diagrams, why CO and \({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) are polar molecules...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.8: Which property increases down group 1? A. First ionization energy B. Melting...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.5d: Samples of sodium oxide and sulfur trioxide are added to separate beakers of water. Deduce...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.7: Which element is a metalloid? A. Co B. As C. Cs D. Es
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.12: Which metal has the strongest metallic bond? A. Li B. Na C. K D. Rb
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.6a: Define the term electronegativity.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.6c.i: State the equations for the reactions of sodium oxide with water and phosphorus(V) oxide with...
- 14N.1.hl.TZ0.6: Which statements are correct for the oxides of period 3 going from Na to Cl? I. The...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.2b: A student formulates the following hypothesis: “If phosphorus were to form a positive ion,...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.2a: Describe and explain the trend in atomic radius across period 3.
- 13M.1.sl.TZ2.9: Which statements are correct for the halogens F to I? I. Melting point increases II. ...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.iii: State the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of potassium bromide, KBr(aq), with...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.iv: Describe the colour change likely to be observed in this reaction.
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.4g: Describe and explain what you will see if chlorine gas is bubbled through a solution of (i) ...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ2.6c: (i) Outline two reasons why a sodium ion has a smaller radius than a sodium atom. (ii) ...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.5a: (i) Identify the property used to arrange the elements in the periodic table. (ii) ...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.3c.ii: State the equation for the reaction of sodium oxide with water.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.3c.i: State the acid-base nature of sodium oxide.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.5b.i: Define the term first ionization energy and state what is meant by the term periodicity.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.5d: Explain, using diagrams, why \({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) is a polar molecule but...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.8: Which statement describes the trends of electronegativity values in the periodic table? A. ...
- 12M.1.sl.TZ2.9: Which series is correctly arranged in order of decreasing radius? A. ...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.3b: State and explain one difference between the reactions of sodium and potassium with water.
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.2d.ii: Suggest why the melting point of vanadium is higher than that of titanium.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.8: Which oxide, when added to water, produces the solution with the highest pH? A. Na2O B....
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.1c.i: Some oxides of period 3, such as Na2O and P4O10, react with water. A spatula measure of each...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.2d.i: Suggest two reasons why solid calcium has a greater density than solid potassium.
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.7: Which statement is correct for the halogens \({\text{(F}} \to {\text{I)}}\)? A. ...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.8: Which combination of properties best describes sodium oxide,...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.8c: (i) Magnesium reacts with oxygen to form an ionic compound, magnesium oxide. Describe how...
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.7: Which properties decrease down both group 1 and group 7? I. Melting point II. First...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.4e: State a balanced equation for the reaction of sodium with water. Include state symbols.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.6b.iv: Explain why the quantitative value for the lattice enthalpy of calcium bromide is larger than...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.10: Which is the best definition of electronegativity? A. Electronegativity is the energy...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.5b.iv: Explain why a sulfide ion, \({{\text{S}}^{2 - }}\), is larger than a chloride ion,...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.5a: Deduce the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between sodium and sulfur. State the...
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.2b: (i) State the equation for the reaction of this oxide of phosphorus with water. (ii) Predict...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.6: What is the order of decreasing ionic radius? A. S2− > Cl− > Al3+ > Mg2+ B. ...
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.2a: Explain the general increasing trend in the first ionization energies of the period...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.7: Which describes the oxide of sodium, Na2O?
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.3b.i: Outline why atomic radius decreases across period 3, sodium to chlorine.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.i: State the equation for the reaction between potassium and chlorine.
- 14M.1.hl.TZ1.7: Which statements about reactivity are correct? I. Potassium reacts more vigorously than...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.8: What is the definition of the term first ionization energy? A. The energy released when...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.5e.iii: State equations for the reactions of \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) and...
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.8: Which period 3 oxide, when added to water, forms an acidic solution? A. ...
- 13M.1.hl.TZ1.8: Each of the following oxides is added to separate equal volumes of distilled water. Which of...
- 13M.1.hl.TZ2.7: Which statements are correct for the alkali metals Li to Cs? I. Melting point...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.i: Define the term electronegativity.
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.4d: (i) State whether aqueous solutions of magnesium oxide and magnesium chloride are acidic,...
- 09N.1.hl.TZ0.8: Which species has the largest radius? A. Cl– B. K C. Na+ D. K+
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.7a.v: The inter-ionic distance between the ions in NaF is very similar to that between the ions in...
- 09N.1.sl.TZ0.8: What happens when sodium is added to water? I. A gas is evolved II. The temperature...
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.8: Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table? A. Melting point B. ...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.3c: Explain why silicon has the highest melting point and argon has the lowest melting point.
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.5b.i: calcium has a higher melting point than potassium.
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.3a: State the equation for the reaction between sodium and water.
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.5b: Describe the acid-base character of the oxides of the period 3 elements, Na to Cl. For the...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.4d: Describe the trend in acid-base properties of the oxides of period 3, sodium to chlorine.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.2d.ii: Explain why an aluminium-titanium alloy is harder than pure aluminium.
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.7: Which trends are correct across period 3 (from Na to Cl)? I. Atomic radius decreasesII. ...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.2f: Calcium carbide reacts with water to form ethyne and calcium hydroxide. CaC2(s) + H2O(l) →...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.2e: Calcium carbide reacts with water to form ethyne and calcium hydroxide. CaC2(s) + H2O(l) →...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.9a.ii: Suggest, giving your reasons, the approximate pH values of the solutions formed by adding...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.5a: (i) State the changes in the acid-base nature of the oxides across period 3 (from...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ1.8: The horizontal axis of the bar chart represents the elements of period 3 from sodium to...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.8: Which pair of elements shows the greatest difference in electronegativity? A. Mg and...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.4a: (i) Describe the colour change that occurs when aqueous chlorine is added to aqueous...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.4b: The colour change in the reaction between aqueous chlorine and aqueous sodium iodide is very...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.2b: A student formulates the following hypothesis: “If phosphorus were to form a positive ion,...
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.8: Which combination is correct for the properties of the alkali metals from Li to Cs?
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.8b.ii: Explain how information from this graph provides evidence for the existence of main energy...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.9: Which statement is correct for all elements in the same period? A. They have the same...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.7: Which property generally decreases across period 3? A. Atomic number B. ...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.12: The number of electrons in the valence shell of elements A and B, are 6 and 7 respectively....
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.1c.i: Suggest why it is necessary for sodium to be removed by this reaction.
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.7: Which equation represents the first electron affinity of chlorine? A. Cl(g)+e-→ Cl-(g)B....
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.1d: Impurities cause phosphine to ignite spontaneously in air to form an oxide of phosphorus and...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.2a: State the equations for the reactions of sodium oxide with water and phosphorus(V) oxide with...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.9b.i: Identify the acid-base character of the oxides of each of the elements from sodium to...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.9b.ii: State the equations for the separate reactions of sodium oxide and phosphorus(V) oxide with...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.6c.ii: State the equations for the separate reactions of sodium oxide and phosphorus(V) oxide with...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ2.8a: Define the term first ionization energy.
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.5d: Explain why the ionic radius of a chloride ion is greater than the atomic radius of a...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.5b: (i) Predict any changes that may be observed in each...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.6: Which series is arranged in order of increasing radius? A. ...
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.9: Which series is arranged in order of increasing radius? A. ...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.7a.ii: Deduce, using equations where appropriate, if bromine reacts with sodium chloride solution...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.21: Which is a characteristic property of sodium oxide? A. It turns moist blue litmus paper...
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.9: Which oxides produce an acidic solution when added to water? I. ...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.12: Which combination of the characteristics of element X, a metal, and element Y, a non metal,...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.9: Which pair of elements has the greatest difference in electronegativity? A. Cs and...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.ii: Explain why an aqueous solution of sodium chloride cannot be used to obtain sodium metal by...
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.2b: Explain why the melting points of the group 1 metals (Li → Cs) decrease down the group.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.8: Which statement is correct? A. Atomic radius decreases down group 17. B. First...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.7: Which increase across a period from left to right?
- 15M.1.hl.TZ2.7: What is the definition of electronegativity? A. The relative measure of the tendency of...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.6c.i: Identify the acid-base character of the oxides of each of the elements from sodium to...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ2.5a: (i) Describe the colour change that occurs when aqueous chlorine is added to aqueous...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.5a: (i) State the equation for the reaction of sodium metal with water. (ii) Describe...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.5e.ii: State the acid-base natures of \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) and...
- 14N.1.hl.TZ0.7: The elements argon, potassium, and calcium are consecutive in the periodic table. Which gives...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.6c: State an equation for the reaction of magnesium oxide with water.
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.9: Which oxides are acidic? I. \({{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{10}}}}\) II. ...
- 10N.1.hl.TZ0.7: The x-axis of the graph below represents the atomic number of the elements in period...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.4f: With reference to electronic arrangements, suggest why the reaction between rubidium and...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.3a: Explain the increase in the melting point from sodium to aluminium.
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.12: What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.5b.ii: State the electron arrangement of argon and explain why the noble gases, helium, neon and...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.5b.v: Explain why the melting points of the Group 1 metals \({\text{(Li}} \to {\text{Cs)}}\)...
- 11M.1.hl.TZ1.8: Which statement about the elements in group 7 is correct? A. ...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.6f.ii: Samples of sodium oxide and solid sulfur trioxide are added to separate beakers of water....
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.5a.ii: Explain why the first ionization energy of magnesium is higher than that of sodium.
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.5a.i: Define the term first ionization energy.
- 16N.1.hl.TZ0.8: Which correctly describes the reaction between potassium and excess water? A. The reaction...
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.8: Which oxide dissolves in water to give a solution with a pH below 7? A. MgO B. Li2O C....
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.2c: State an equation for the reaction of phosphorus (V) oxide, P4O10 (s), with water.
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.2d.i: Suggest two reasons why solid calcium has a greater density than solid potassium.

