| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.1.sl.TZ2.13 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Identify | Question number | 13 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Which describes the reaction shown in the potential energy profile?
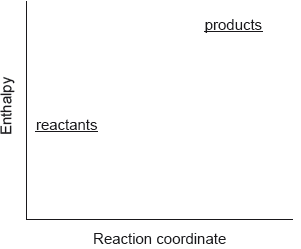
A. The reaction is endothermic and the products have greater enthalpy than the reactants.
B. The reaction is endothermic and the reactants have greater enthalpy than the products.
C. The reaction is exothermic and the products have greater enthalpy than the reactants.
D. The reaction is exothermic and the reactants have greater enthalpy than the products.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
[N/A]
Syllabus sections
Show 73 related questions
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.15: What is the enthalpy change, in kJ, of the following reaction? 3H2 (g) + N2 (g)...
- 17N.2.hl.TZ0.1e: Suggest why the enthalpy change of neutralization of CH3COOH is less negative than that of HCl.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.5b: Nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide react according to the following equation: NO2(g) +...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.15: What can be deduced from the facts that ozone absorbs UV radiation in the region of 340 nm...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.13: What can be deduced from this reaction profile? A. The reactants are less stable than...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.15: In which order does the oxygen–oxygen bond enthalpy increase? A. H2O2 < O2 <...
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.6c: (i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in...
- 16N.2.hl.TZ0.1b: (i) Calculate ΔHθ, in kJ, for this similar reaction below using \(\Delta H_{\rm{f}}^\theta \)...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.1a: Ethane-1,2-diol can be formed according to the following reaction. 2CO (g) +...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.14: In which reaction do the reactants have a lower potential energy than the products? A....
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.10: The C=N bond has a bond length of 130 pm and an average bond enthalpy of 615kJmol-1. Which...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.3b: The enthalpy change for the reaction between nitrogen monoxide and hydrogen is −664 kJ and...
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.3b: (i) Sketch the potential energy profile for the synthesis of phosgene, using the axes given,...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.15: Which equation represents the average bond...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.5b.i: Define the term average bond enthalpy.
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.16: Which equation corresponds to the bond enthalpy of the H–I bond? A. ...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.16: Which enthalpy changes can be calculated using only bond enthalpy data? I. ...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.5b.i: Define the term average bond enthalpy.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7g.i: Define the term average bond enthalpy.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.1b.ii: Calculate the enthalpy change, in \({\text{kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\), for the...
- 14M.3.hl.TZ1.16d: Explain, with the aid of Lewis (electron-dot) structures, the difference between oxygen and...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.2c: Comment on which of the values obtained in (a) and (b)(ii) is more accurate, giving a reason.
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.15: Which processes are exothermic? I. ...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.5c: Calculate the enthalpy change, in \({\text{kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\), when one...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ2.5a: Hydrogen gas can be formed industrially by the reaction of natural gas with steam. ...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.4b.iii: Outline why the value of enthalpy of reaction calculated from bond enthalpies is less accurate.
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.4a: Hydrogen gas can be formed industrially by the reaction of natural gas with steam. ...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.3b.iii: Explain, giving two reasons, the difference in the values for (b)(i) and (ii). If you did not...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.3b.i: Under certain conditions, ethyne can be converted to benzene. Determine the standard...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.15: Which statement is correct? A. In an exothermic reaction, the products have more energy...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.3c.iii: Explain, giving two reasons, the difference in the values for (c)(i) and (ii). If you did not...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.3c.i: Under certain conditions, ethyne can be converted to benzene. Determine the standard...
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.15: Which processes are exothermic? I. ...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.4c: Calculate the enthalpy change, in \({\text{kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\), when one...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.4g.iii: Predict, with an explanation, how the result obtained would compare with the value in Table...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.15: Which statement is correct for the enthalpy level diagram shown? A. The reaction is...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.16: Which combination is correct about the energy changes during bond breaking and bond formation?
- 13M.1.sl.TZ2.17: The reaction between methane and oxygen is...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.6c.ii: Determine the enthalpy change, \(\Delta H\), in...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.2a: Define the term average bond enthalpy.
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.2b: (i) Determine \(\Delta H\), the enthalpy change of the reaction, in...
- 10N.3.hl.TZ0.E4: (a) (i) Explain the dependence of the dissociation of diatomic oxygen, O2, and ozone,...
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.16: Which equation best represents the bond enthalpy of HCl? A. ...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.4d: Hydrazine is a valuable rocket fuel. The equation for the reaction between hydrazine and...
- 10N.3.sl.TZ0.B1a: Glucose, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\), is a...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.7b.iv: Using bond enthalpy values, calculate \(\Delta {H^\Theta }\) for the following...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.7b.v: Suggest with a reason, why the values obtained in parts (b) (i) and (b) (iv) are different.
- 09N.1.sl.TZ0.17: Use the average bond enthalpies below to calculate the enthalpy change, in kJ, for the...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ2.4e: Comment on the environmental safety of the products of the reaction of...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.3c: Suggest one reason why John’s answer is slightly less accurate than Marit’s answer and...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.3b: Determine the value for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of ethene using the values for the...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.16: Which process represents the C–Cl bond enthalpy in tetrachloromethane? A. ...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.2a: Calculate the value for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of ethene obtained using the average...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.2c: Suggest one reason why John’s answer is slightly less accurate than Marit’s answer.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.2d.i: Use the average bond enthalpies to deduce a value for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.2d.ii: The percentage difference between these two methods (average bond enthalpies and enthalpies...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.4a: The standard enthalpy change of formation for...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.6a.ii: Use the information from Table 10 of the Data Booklet to determine the standard enthalpy...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.4c: Sketch an enthalpy level diagram to describe the effect of a catalyst on an exothermic reaction.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.6a.i: Define the term average bond enthalpy.
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.15: Which statement about bonding is correct? A. Bond breaking is endothermic and requires...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.1a: Using the information from Table 10 of the Data Booklet, determine the theoretical enthalpy...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.1c.i: Part (a)
- 11M.1.hl.TZ2.17: Which equation represents the bond enthalpy for the H–Br bond in hydrogen bromide? A. ...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.iv: Explain why the enthalpy of hydrogenation of propene is an exothermic process.
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.iii: Determine a value for the hydrogenation of propene using information from Table 10 of the...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.ii: Enthalpy changes can be determined using average bond enthalpies. Define the term average...
- 12M.3.hl.TZ1.E1a: Oxygen absorbs much of the ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, but ozone is important...
- 12M.3.sl.TZ1.B1a: (i) Calculate the heat required, in kJ, to raise the temperature of the water, using data...
- 12M.3.hl.TZ2.E3a: Explain, in terms of their bonding, how the presence of oxygen and ozone in the ozone layer...
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.14: A student measured the temperature of a reaction mixture over time using a temperature probe....
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.4a: Define the term average bond enthalpy.
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.4c: Determine the standard enthalpy change, in \({\text{kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\),...

