| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 17M.2.sl.TZ2.5 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Calculate | Question number | 5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Magnesium reacts with sulfuric acid:
Mg(s) + H2SO4(aq) → MgSO4(aq) + H2(g)
The graph shows the results of an experiment using excess magnesium ribbon and dilute sulfuric acid.
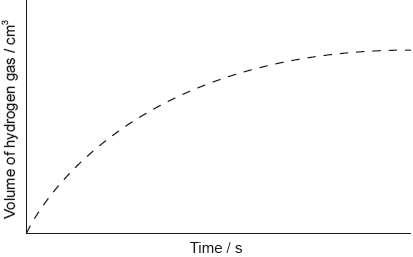
Outline why the rate of the reaction decreases with time.
Sketch, on the same graph, the expected results if the experiment were repeated using powdered magnesium, keeping its mass and all other variables unchanged.
Nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide react according to the following equation:
NO2(g) + CO(g) \( \rightleftharpoons \) NO(g) + CO2(g) ΔH = –226 kJ
Calculate the activation energy for the reverse reaction.
State the equation for the reaction of NO2 in the atmosphere to produce acid deposition.
Markscheme
concentration of acid decreases
OR
surface area of magnesium decreases
Accept “less frequency/chance/rate/probability/likelihood of collisions”.
Do not accept just “less acid” or “less magnesium”.
Do not accept “concentrations of reagents decrease”.
[1 mark]
curve starting from origin with steeper gradient AND reaching same maximum volume
[1 mark]
«Ea(rev) = 226 + 132 =» 358 «kJ»
Do not accept –358.
[1 mark]
2NO2(g) + H2O(l) → HNO3(aq) + HNO2(aq)
OR
2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) → 4HNO3(aq)
Accept ionised forms of the acids.
[1 mark]

