Topic 11: Animal physiology HL 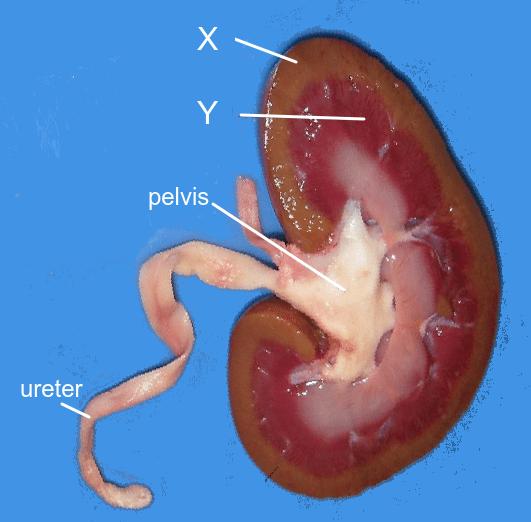
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about HL animal physiology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Animal physiology HL revision resources
This is an introduction to the HL animal physiology topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 11 including antibody production by lymphocytes, vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, muscle fibres, actin and myosin, osmoregulation,...
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The diagram shows the number of deaths per year for children under five. Three diseases are preventable by vaccines, the grey bar shows numbers for diseases not preventable by vaccines.
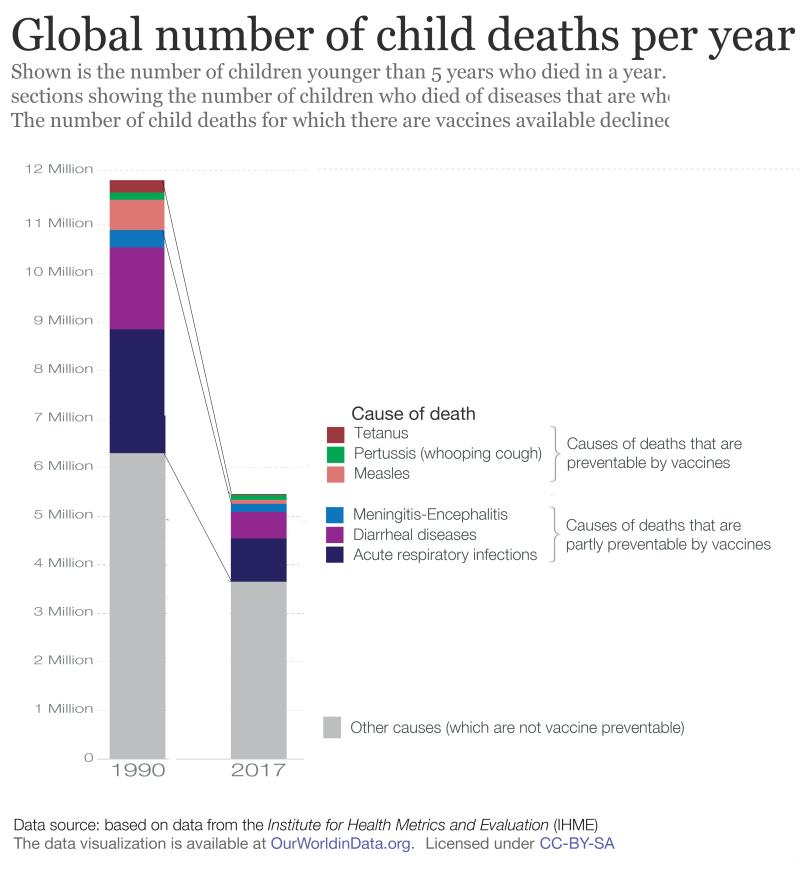
Estimate the percentage decreases in diseases not preventable by vaccines?
In 2017 it had reduced to 3.7 million. This is a decrease of 2.6 million which is 42% of 6.3 million. 2.6 / 6.3 x 100
Which of the following could NOT be used to treat kidney failure?
Treatment of kidney failure can be done by hemodialysis (dialysis of the blood) or kidney transplant.
In an emergency a blood transfusion could help to restore the osmotic potential of the blood temporarily.
Hemoglobin is the protein found in the red blood cells which carries oxygen. So is not helpful in this case.
Which statement describes similarities between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
Similarities in spermatogenesis and oogenesis include mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation.
The diagram below shows cells in a seminal vesicle of a testis.
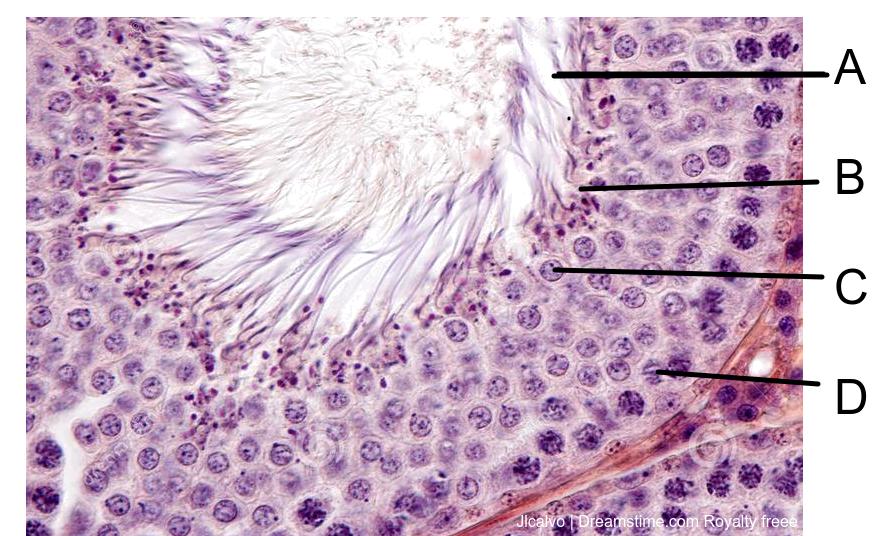
Which of the labels shows a cell most likely to be in the process of differentiation?
Spermatogenesis and oogenesis includes differentiation of haploid cells into sperm cells.
Students need to be able to annotate diagrams of seminiferous tubule to show these details.
The image shows a sperm about to fertilize an egg cell.
Several processes occur during the fertilisation of an egg and sperm cell.
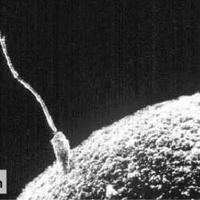
In which order do the three processes given below occur.
Fertilization involves
- attraction of the sperm towards the egg
- binding of the sperm to the egg
- the acrosome reaction
- penetration of the zona pellicuda
- fusion of the plasma membrane of the egg and sperm and
- the cortical reaction. (mechanism that prevents polyspermy)
- fusion of the male and female nuclei
The graph below shows the body mass of a range of animals plotted against their mass at birth.
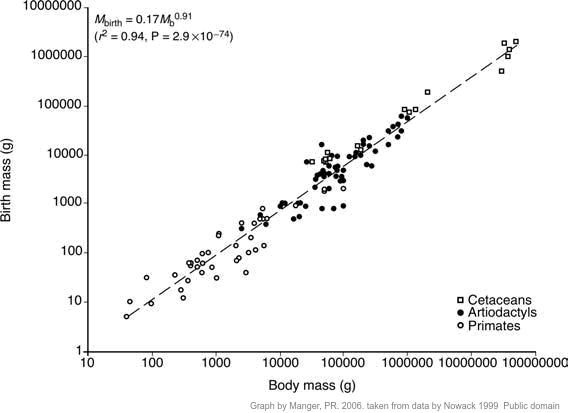
What is the general trend shown in the graph?
To make comparisons of gestation periods it can be assumed that babies grow a a similar rate, and birth size on the graph relates to a longer gestation.
This graph shows a surprisingly good correlation between animal size and the birth size, which could also relate to the more advanced development young at birth in larger mammals.
Note that the scale is logarithmic.
The graph below shows the gestation periods of a range of different animals plotted against their mass at birth.
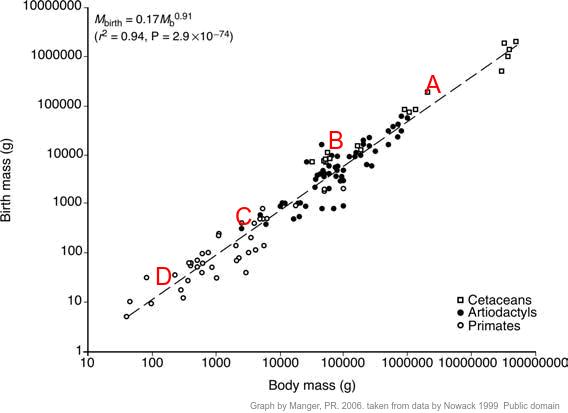
Which of the points A to D on the graph is most likely to represent a human embryo?
You should be able to find the place of the average human (38-week) pregnancy on a graph showing the correlation between animal size and the development of the young at birth in mammals, or birth mass. Humans have a mass of between 50000g and 100000g, and babies are commonly about 3000g at birth. So humans a likely to be in the clusted below the letter B.
In a study by Utrecht University in the Netherlands, a vet was sent to houses to test animals that were living with an owner infected with COVID-19. Six cats out of 154 cats (3.9%) and 7 dogs our of 156 dogs (4.5%) tested positive for COVID-19, while 31 cats (20.1%) and 23 dogs (14.7%) had coronavirus antibodies. The majority of cases in cats and dogs do not have any symptoms of illness.
Which of the folllowing conclusions could be made from the study?
Some pathogens are species specific but this is not the case for the virus COVID-19. This virus can cross the species barrier from one species to another. Some theories suggest that it originated in bats, and may have been transfered to humans through another species, perhaps a pangolin. There is also evidence of zoo animals catching COVID-19 and from the study in this question, domesticated animals like cats and dogs.
The data in the question is inconclusive, in insufficient about whether dogs or cats catch covid more easily.
The disease is most often not a serious illness in these animals, and it is most likely that humans contaminate their pets and ont the pets contaminating humans.
In which way does the body recognise a pathogen causing it to produce an immune response?
Antigens are non-self molecules which initiate the immune response. The immune system does not react to molecules recognised as self (i.e. possessed by the host organism). Macrophages are non-specific phagocytes and are the cells which often first identify non-self antigens.
Why are plasma cells fused with tumour cells to create hybridoma cells in the production of monoclonal antibodies?
I Plasma cells cannot be cultured easily.
II Tumour cells have a very rapid growth rate in cell culture.
III Hybridoma cells cannot produce antibodies.
IV Hybridoma cells produce antigens very rapidly.
Hybridoma cells grow more rapidly than plasma cells in cell culture and produce antibodies (not antigens) much more rapidly.
The image is of the H1N1 virus. There are various strains of this virus which can infect birds, pigs and humans. What is the best explanation of the various strains of the virus and the nature of its infectiousness?
Viruses mutate, a mutant form (strain) may be able to cross the species barrier from one species to another (hence swine flu, bird flu).
Which of the following process involves changes to the ovum membrane preventing polyspermy?
The acrosome reaction allows the sperm to penetrate the ovum membrane and the cortical reaction immediately following causes changes in the membrane that prevent penetration of other sperm.
After fertilisation, what becomes implanted in the endometrium lining?
The fertilised ovum divides in its passage down the oviduct to form a ball of cells, the blastula, which implants itself in the lining of the endometrium.
Diabetics have a blood glucose concentration higher than that of a normal person due to a lack of insulin. One of the signs of diabetes is frequent urination. Which of the following could be an explanation of this symptom?
The high glucose levels of the blood cause high glucose levels in the filtrate, not all of which can be reabsorbed. Some of the glucose is present in the collecting duct so reabsorption by osmosis is less efficient leading to greater urine volumes.
Fish gills are permeable to water, mineral ions and respiratory gases. Marine fish have blood which is hypotonic to sea water, how will gill permeability affect the osmotic balance of their body?
The permeability of the gills mean that water will be lost from the blood by osmosis and salts gained by diffusion. To compensate for this, their urine is highly concentrated.
After an immune response, memory cells are produced. From which cells are these produced?
After antibody production is completed, some plasma cells differentiate into memory cells ready to react if the disease is encountered again.
What is released in response to an allergen?
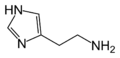
Histamine is released by white cells if they contact an allergen and causes inflammation and swelling.
How is the increase in length of a muscle fibre in the biceps (agonist muscle) achieved during muscular relaxation on the straightening of the forelimb when the triceps (antagonist muscle) contracts?
The contraction of the agonist of a pair of muscles provides the force to lengthen the antagonist muscle which is reflexively relaxed.
The graph below shows global numbers of smallpox cases between 1920 and 2010.
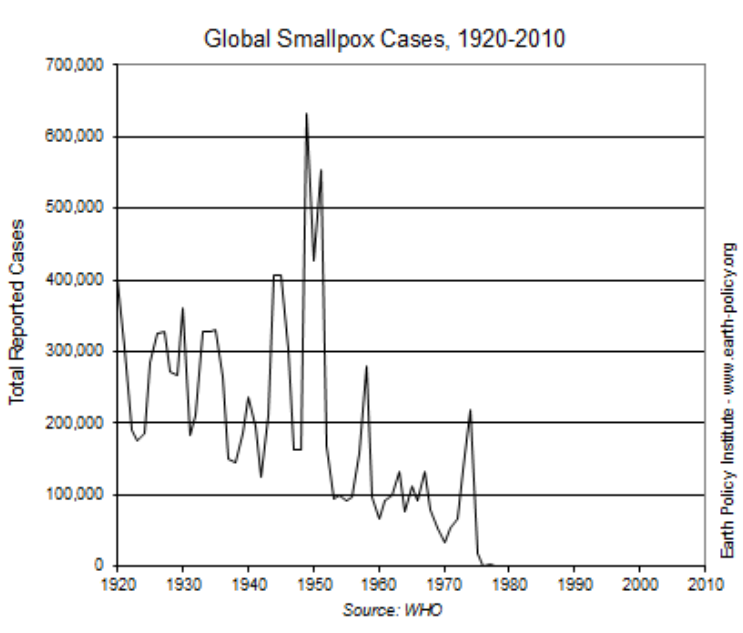
The WHO vaccination and surveillance program began in 1966. Smallpox was declared eradicated in 1980.
What other conclusion could be made using the data from this graph?
The reduction in the number of case was not uniform, outbreaks causes huge increases in cases at several points during this period.
As the number of people vaccinated increased, transmission decreased by herd immunity.
Which events happen during the process of labour immediately before birth? I Oxytocin levels rise II Progesterone levels fall III Dilation of the cervix IV Contraction of uterine smooth muscle.
Progesterone levels fall causing oxytocin levels to rise (positive feedback) and this causes uterine contractions and dilation of the cervix for birth.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 11 Animal physiology HL Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn