Topic 4: Ecology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about Ecology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Ecology revision resources
This is an introduction to the ecology topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 4 including ecological terminology, species, communities, ecosystems, the nature of energy flow, carbon cycling including carbon reservoirs, carbon...
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Which classification grouping includes all organisms which have the potential to interbreed and produce fertile offspring?
Species are "groups of organisms that can potentially interbreed to produce fertile offspring".
In an experiment in a small garden, quadrat frames were used to sample the number of clover plants growing in the grass lawn.

Why is it important to use random sampling in the placement of the quadrats?
Random quadrat sampling is a standard method used to avoid bias and selection.
In most food webs the transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next is usually about 10%.
What effect is this likely to have on food chains?
The loss of energy and biomass from trophic level to trophic level is considered to limit the length of food chains. Four trophic levels is common, and five uncommon. It is very rare to have a food web made of chains longer than five trophic levels.
In ecology a pyramid of energy is often used to show the flow of energy in an ecosystem.
What does the unit kJ/m2/yr represent in such a diagram?
of ecosystem in a year.
Samples would be taken several times over the year to find the all the organisms in a 1m2 quadrat.
The energy contained in the biomass of these organisms will be measured (or calculated).
Kilojoules are the units of energy.
What is the usual source of energy in ecosystems?
The sun provides energy to ecosystems, continuously, and it is trapped in organic molecules by photosynthesis by autotrphs. Inorganic nutrients are recycled by decomposers but when they are reabsorbed into plants they do not provide energy.
Some chemoautotrophs can use inorganic energy from mineral elements but the great majority of autotrophs use light.
This diagram shows a simple model of energy flow.
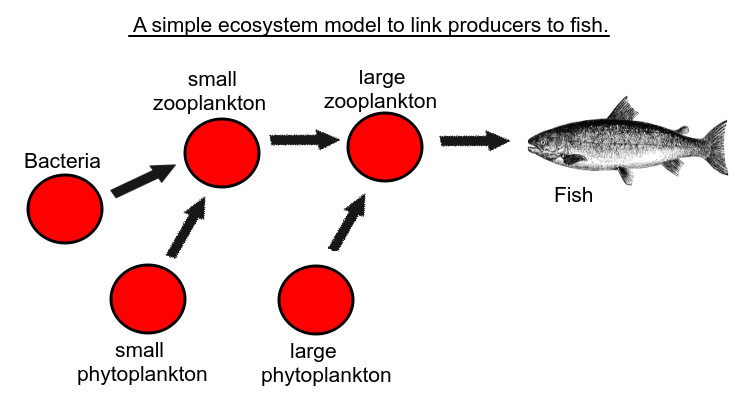
Which of the organisms could be called "secondary consumers"?
Producers are photosynthetic, primary consumers eat producers, and secondary consumers eat primary consumers. The situation is complicated this this model, because the large zooplankton could be described as a primary consumer or a secondary consumer, because it eats large phytoplankton which is a producer and small zooplankton.
In what forms is Carbon present in aquatic ecosystems, and available for autotrophs to use in photosynthesis?
In the syllabus carbon is said to be present as dissolved carbon dioxide and hydrogen carbonate ions.
Methane (CH4) is produced in some situations in ecosystems.
When does this happen?
Methane is produced from decaying organic matter in anaerobic conditions by bacteria.
This is common in the formation of peat, in waterlogged soils.
Why would a Χ2 (chi squared) test be applied to the data for a count of a plant species in the trampled area of a field in comparison to a grazed area?
Statistical tests are applied to ascertain if the difference between two situations are a significant difference. The test applied may or may not support the hypothesis.
Which of the following forms of energy can be the primary energy source for an ecosystem I heat II light III chemical IV electrical?
Most ecosystems depend upon light energy as a primary source but some can use chemical energy (particularly Archaeans living in extreme environments such as thermal vents, deep sea)
What is a definition of the biomass of a population?
Biomass refers to the mass of living tissue in a population.
How could the biomass of a population at the second trophic level be measured?
An estimate is taken from a representative sample. From this an estimate of the size of the population is made and then a measure of the mass or the sample captured.
Recycling of inorganic substances can be on a global or local scale. Which of the following are recycled on a global scale? I Energy II Carbon III Oxygen IV Water.
Carbon dioxide, oxygen and water are recycled, energy cannot be recycled. As the cycles have a gaseous component, the cycle is global rather than local.
In terms of radiation, reflection and absorbtion, which is the best explanantion of the greenhouse effect?
Most of the short wave radiation from the sun that strikes the earth is converted to heat. Some radiation is reflected as long-wave radiation, much of which is trapped in the greenhouse layer causing a heating effect
Why is it difficult to prove a direct link between climate change and human activities increasing carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere?
It is difficult for scientists to demonstrate a direct link as there are many confounding variables which can affect the climate
The graph illustrates global mean annual temperatures between 1880 and 2018 shown in comparison to the overall mean annual temperature during this period.
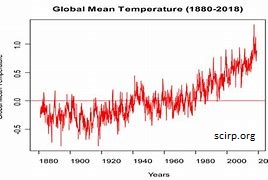
What is the difference between the lowest and the highest mean annual temperature shown on the graph?
The lowest is -0.80C and the highest is 1.40C totalling 2.20C
Which is the best definition of the term, "heterotrophic"
Heterotrophs need to obtain organic material from other organisms. They cannot produce organic material from inorganic molecules. They ingest and internally digest other living organisms.
In an experiment in a small garden, quadrat frames were used to sample the number of clover plants growing in the grass lawn.

Why are quadrats used to estimate population size?
Population size done by counting the whole population is generally too time consuming.
When members of a species are separated by a physical barrier this can lead to populations which are prevented from reproducing, because individuals from each population never meet.
What is the name given to this situation?
Populations of a single species may be reproductively isolated and form separate populations.
What trends in the energy available are seen at successive levels in food chains?
Energy lost at one level of a food chain is not available for the next level so the energy available in the orgainsms at each successive level will decrease.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 4 Ecology Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn