Topic 6: Human physiology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about Human Physiology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Human physiology revision resources
This is an introduction to the human physiology topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 6 including digestion, heart and circulation, immune system, lungs and gas exchange, the nervous system, hormones and reproduction....
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
What is the advantage of villi and microvilli increasing the surface area of epithelium in the small intestines?
The larger the surface area of epithelium the faster the rate of absorption is..
What is the fate of cellulose in the human digestive system?
Humans don't make enzymes to digest cellulose. Bacteria can digest cellulose in the human intestines, but much of the cellulose eaten is undigested. It is sometimes called 'Fibre'.
If the skin is broken then a blood clot forms to seal this cut.
What is the role of fibrinogen in the process of blood clotting?
Platelets release clotting factors. first in the process of blood clotting.
There is a cascade of reactions in which fibrinogen is converted into fibrin.
Blood clotting seals cuts in the skin. (skin diagrams are not required.)
When activated some lymphocytes produce antibodies and other lymphocytes act as memory cells.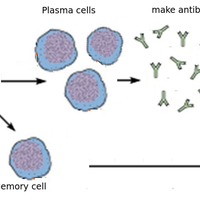
Which of the following best describes the role of memory cells?
Some lymphocytes act as memory cells and can quickly reproduce to form a clone of plasma cells if a pathogen carrying a specific antigen is encountered again.
Note: Subgroups of phagocyte and lymphocyte are not required, except these two types of cells derived from lymphocytes.
Florey and Chain shared a Nobel Prize with Alexander Fleming for their work on penicilin.
Which of the following statements best describes their experiment which tested penecillin on mice?
Describe Florey and Chain’s experiments to test penicillin on bacterial infections in mice.
In March 1940 Chain requested that two mice be injected with a sample of the penicillin.
The mice survived showing that penicillin was not toxic to mice.
Florey then tested the antibacterial properties of penicillin in mice.
Eight mice were injected with hemolytic streptococci (bacteria)
Four of these were subsequently injected with doses of penicillin. Four were untreated.
Less than one day later the four mice that had received penicillin were alive, but the untreated mice were dead.
Further testing involving hundreds of mice was carried out
On August 24, 1940, Florey and Chain reported their findings in the Lancet; as a cure for bacterial disease.
How do nerve impulses travel in the nervous system?
Although neurones release chemical neurotransmitters at their endings they actually transmit electrical impulses along their length. This is caused by movement of charged ions across the membrane, but these ions don't move along the neurone.
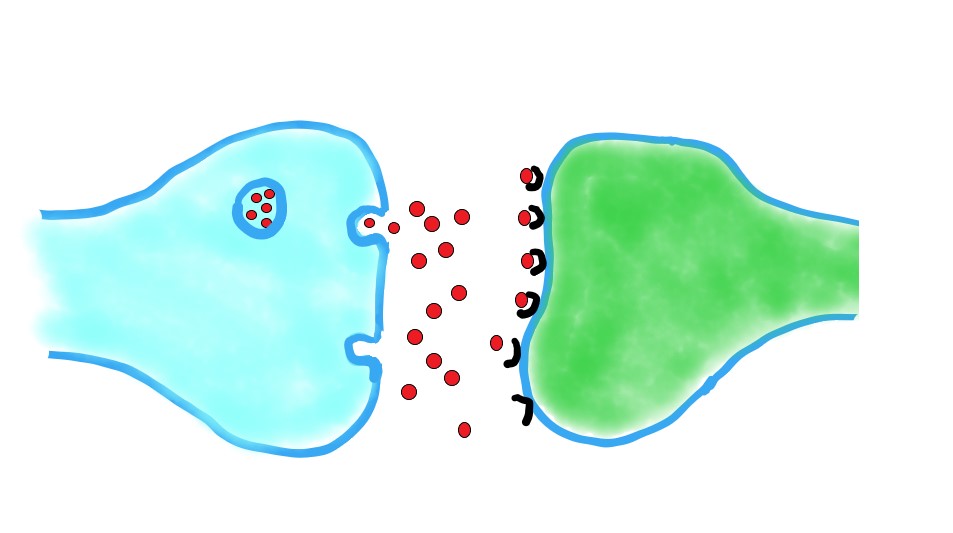 The diagram shows parts of two neurones at a synapse.
The diagram shows parts of two neurones at a synapse.
The red dots show a neurotransmitter being released into the synaptic cleft.
Which of the statements below best describes what usually happens to the neurotransmitter molecules after their release?
Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors in post synaptic neurones.
After this they can be broken down by enzymes before reabsorption by the presynaptic neurone.
What are the main functions of the intestines of the human?
The digestive system moves ingested nutrients by peristalsis, secretes some enzymes and much mucus, digests macromolecules and absorbs nutrients.
While excretion of some chemicals does pass by the digestive system, this is not its main function. Sensitivity is not an important function, nor is storage.
Which of the following is achieved by peristalsis?
.
Peristaltic movements cause mixing of the food contents with enzymes and move the digesting food slowly through the intestines.
Why could the liver considered to be an organ of the digestive system?
The blood leaving the small intestine is transported to the liver where digested nutrients such as glucose can be stored as glycogen, but a more important role of the liver in digestion is the production of bile, which is secreted to emulsify lipids to aid their digestion.
Which of the following are absorbed by villi?
I Haemoglobin molecules
II Vitamin C
III Minerals
IV Amino acids
Villi absorb monomer products of digestion and small soluble molecules such as vitamins and minerals.
Proteins larger than a few peptides long need to be hydrolysed before they can be absorbed.
Which process best describes the action of digestive enzymes on polymers?
Digestive enzymes break the bonds in polymers by adding water - hydrolysis.
Which statement correctly describes an artery?
Arteries are defined by the direction of flow from the heart, they do have muscular walls but so do veins (even though they are thinner), the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood
What is the role of muscle fibres and elastic fibres in the walls of arteries?
The elastic walls of the arteries expand and then contract between contractions of the ventricles, this movement maintains blood pressure between pump cycles.
Which of the following is the main contribution of epidemiological studies to our knowledge of disease?
Epidemiologists study disease to examine causes and consequences which may lead to preventative measures
Why is the rib cage moved upwards and outwards during deep inspiration?
The raising of the rib cage increases thoracic volume, decreasing pressure, causing air to enter because the pressure in the thorax is lower than atmospheric pressure.
The axon of a motor neuron in vertebrates is surrounded by a myelin sheath. How does the myelin sheath affect the transmission of an action potential?
Nodes of Ranvier are found between successive Schwann cells in the myelin sheath. The impulse "jumps" from one node to the next, increasing the speed of transmission.
Why is the somatic (body) circulation separate from the pulmonary (lung) circulation?
.
.
The right side of the heart generates a low pressure and slow flow rate to allow blood to become oxygenated and to not damage the lung alveoli.
Where would the highest pressure be found in the heart?
Systole is contraction of a heart chamber, the left ventricle has the highest pressure to pump blood around the systemic (body) circulation.
Which major blood vessel does not have valves?
The pulmonary vein does not need valves because it is short in length and the pressure of blood from the heart retains the flow. The aorta and pulmonary artery have veins to prevent backflow of blood to the heart. The vena cava is the main vein returning blood to the heart from the body and has valves.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 6 Human Physiology Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn