Topic 10: Genetics HL 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about HL Genetics.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
10 Genetics HL revision resources
This is an introduction to the HL genetics and evolution topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 10 including crossing over, chiasmata, recombinant phenotypes, linked genes, polygenic inheritance, polyploidy and gene pools.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
The drawing below shows an image of homologous chromosomes during meiosis and two diagrams drawn by biologists to show chiasmata formed by crossing over.

Which of the diagrams A or B shows the most convincing interpretation and why?
In diagrams of crossing over sister chromatids will be closely aligned, except at the point where crossing over occurs and a chiasma is formed.
In A the chromatids are close together except where one of the sister chromatids from each chromosome crosses over.
What is a feature of unlinked genes?
Unlinked genes show independent assortment in meiosis as they are on different chromosomes (but linked genes do not, hence non-Mendelian ratios of phenotypes)
When would a biologist use a chi-squared test?
Chi-squared tests are used to calculate if differences between observed and expected frequencies are statistically significant
Which of the following would be considered a "recombinant phenotype"?
The skill to identify recombinants in crosses involving two linked genes is important.
The phenotypes are different from the 'grandparents' in recombinant phenotypes.
So greeen peas with a smooth surface are recombinant.
Which of the following is the best definition of a gene pool?
A gene pool consists of all the genes and their different alleles, present in an interbreeding population.
What is the difference between gene pool and genome ?
A gene pool consists of all the genes and their different alleles, present in an interbreeding population.
It is described as a pool because it is potentially available to all offspring, so long as the population is interbreeding.
What do homologous chromosomes have in common?
Homologous chromosomes contain alleles of identical genes, some alleles and therefore DNA and base pairs will be different
A spermatogonium is a cell that divides by meiosis to form four spermatozoa (male gametes).
How many chromatids will a human spermatogonium contain at the beginning of prophase I of meiosis?
The DNA replicates during the S phase of interphase, before prophase I begins, this forms chromosomes with two chromatids each.
The diploid chromosome number of a human is 46 (23 pairs) so there will be 92 chromatids at the beginning of meiosis, as each chromosome has two chromatids.
Which phase of meiosis is shown in the diagram?
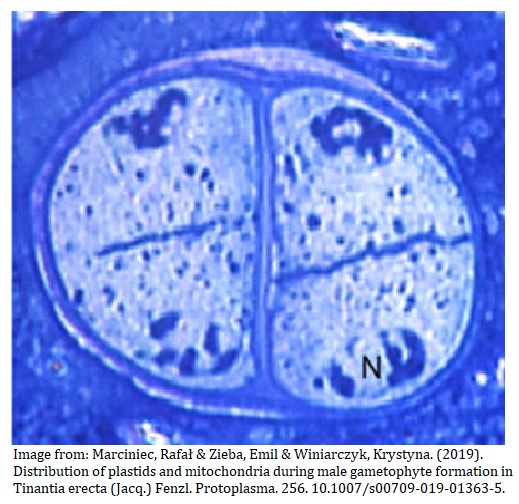
The image shows 4 sets of chromosomes each surrounded by a nuclear membrane. This is Telophase II of meiosis. Four cells will be formed after cytokinesis.
Which of the following contribute to the unique genetic nature of gametes produced by a mammal?
I. Mitosis.
II. Random assortment of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis.
III. Crossing over in meiosis.
IV. DNA replication.
Random assortment of homologous chromosomes and crossing over contribute to variation in gametes, Mitosis produces clones and DNA replication, without any copying errors, only doubles the amount of DNA.
Why does polygenic inheritance appear as continuous variation in phenotypes?
Polygenic inheritance is a type of inheritance where a number of genes, each of which has its own alleles, contribute to a specific phenotype giving a range of phenotypic appearances
Which is the best description of continuous variation?
Continuous variation e.g. human skin colour, varies within extremes, has many intermediate values and may also be influenced by the environment
An investigation was carried out into two genes in bean plants. Each gene had two alleles showing simple dominance. The study concluded that the genes were linked. How could the data collected indicate this?
If the outcome does not correspond to a Mendelian ratio, and the number of recombinant phenotypes is lower than expected, the explanation is that they are linked and not independently assorted. The outcome should be test statistically to be sure that there is a significant difference.
Black hair and long coat in Labradors are dominant traits over cinnamon hair and short coat. If you possessed a black haired long coated female, what mating could be carried out to demonstrate whether she would be true breeding (homozygous for these characteristics?
Breeding true means that the individual is homozygous. The cross that should be carried out to determine whether the individual is homozygous or heterozygous is the backcross with the homozygous recessive traits, this gives the maximum chance of the recessive gene (if present) showing in the phenotype of the offspring
What process causes a change in the gene pool over time?
Gene pools change over time due to the natural selection of phenotypes that favour survival, and some phenotypes become less common. So there are more alleles from the successful phenotypes.
What is the effect of evolution on a gene pool?
Alleles of genes with survival value allow breeding success of the individuals possessing them. By the survival of the fittest to breeding age the frequencies of alleles in the population changes over time. Mutation is a source of variation but it is not affected by evolution, nor is the frequency of the mutation as evolution occurs
Several populations of the Wood frog (Rana sylvatica) were studied in the USA. It was found that although they all inhabit the woods and the same lake frogs from different populations do not interbreed. What could be the cause of this?
The frog populations occupy the same habitat so are not geographically isolated, but they could have different breeding periods (temporal isolation) or different means of recognition of partners of the same species (behavioural isolation)
Which type of selection favours the extreme characteristics in a population over the mean of the characteristic?
In a trait which has extremes (e.g. length of beak), the environmental pressures may favour the extremes (e.g. long and short beak) over the median. This is disruptive selection.
What is punctuated equilibrium in evolution?
Punctuated equilibrium is characterised by periods of stability followed by rapid evolution. The rapid evolution may be due to catastrophic events or die-offs of species.
Which of the following contribute to the unique combinations of alleles in gametes ?
I Independent assortment in mitosis.
II Independent assortment in meiosis.
III Mutation.
IV Segregation.
Mitosis does not contribute to variation in the gamete. Mutations may occur during replication of DNA prior to Meiosis I. Independent assortment and segregation of chromosomes causes variation in the combinations of chromosomes in the gamete
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 10 Genetics HL Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn