Topic 2: Molecular biology 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about molecular biology.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Molecular biology revision resources
This is an introduction to the molecular biology topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 2 including water, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, DNA, RNA, protein synthesis, respiration and photosynthesis. Detailed revision notes, activities and questions can be found on each of the sub-topic pages.
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
There are about 20 different amino acids found in living organisms and each has a different molecular structure in the R-group.
This can be a simple -H atom, in alanine, or a more complicated structure.
What are the functions of the molecules cellulose and starch in plants?
Plant cells walls are built mainly of cellulose.
Starch in the cell is found in the chloroplast and in the cytoplasm. It is used to store energy.
Which of the following molecules are monosaccharides?
- Lactose
- Galactose
- Sucrose
- Fructose
- Glucose
Monosacharides are Galactose, Fructose and Glucose.
The three disaccharides named in the syllabus are Maltose, Sucrose and Lactose.
Which enzymes are responsible for DNA replication?
DNA polymerase builds a DNA polymer, and unwinds the DNA and separates the strands so that each can be used as a template.
It is important to know a few examples of proteins. One example is the light-sensitive pigment found in the rod cells of the eye. It is formed from two molecules, retinal and opsin. What is its name?
Rhodopsin is a light-sensitive pigment found in the rod cells of the eye that is formed from retinal and opsin (a protein)
When bound to the active site, what effect do lactase enzymes have on the bonds holding glucose to galactose in the disaccharide lactose molecules?
They are weakened, making the hydrolysis reaction easier, lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
Which of the following best describes the role of molecular motion in enzyme catalysis?
Reactions happen when substrate and enzyme molecules collide with one another.
Which term best describes the structure of DNA and RNA, both made from long chains of nucleotides?
Polymers is the term that refers to DNA and RNA which are both made from long chains of nucleotides
Which statement best describes DNA helicase?
DNA helicases are enzymes which separate and unwind the two strands in a DNA double helix.
They disturb the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
They are able to move along the DNA molecule and they use ATP.
Why is the DNA code considered to be "universal"?
In which of the following does anaerobic respiration convert pyruvate in the cytoplasm into lactate?
The process of anaerobic respiration in muscle: converts pyruvate in the cytoplasm into lactate
In which of the following metabolic processes is there a large yield of ATP?
There a large yield of ATP in aerobic respiration (in the mitochondria)
Which kind of bonds can form between water molecules?
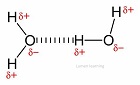
Hydrogen bonds can form between the slightly positive hydrogen and slightly negative oxygen.
Which of the following does not represent the formation of a polymer for energy storage?
Glycogen, lipids and starch are all energy-rich storage molecules, DNA is synthesised for cell reproduction.
Which of the following is not a condensation reaction?
Anabolic reactions are condensation reactions, monomers condensing to form polymers. Breakdown of dimers and polymers is catabolic hydrolysis.
The pH of human blood is maintained between 7.35 and 7.45, why is this important to the function of blood proteins?
Protein function can be affected by changes in pH even if it is a slight change that does not cause denaturation. The other answers are distractors, a slight change in pH will not destroy red blood cells or damage capillaries or affect oxygen solubility.
Which is the best description of this molecule?
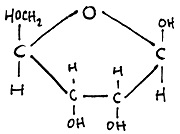
The molecule has 5 carbon atoms so is Ribose (a pentose and a single molecule, monosaccharide).
Cellulose and starch are both polymers of glucose. Why are they different in terms of their structure?
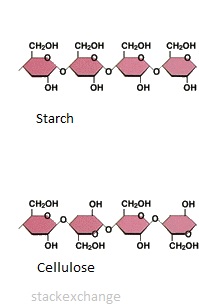
Polymers can vary in structure and function by different bonding of the monomers. These affect the shape of the polymer and its function.
Why is water needed for the process of photosynthesis to produce carbohydrate?
Hydrogen from water is combined in a series of reactions to eventually form carbohydrates.
The genetic code is shown in the illustration. If a point mutation occurs in DNA that changes GGG in the DNA molecule to CGG, what would change in the polypeptide structure produced by this mutation?
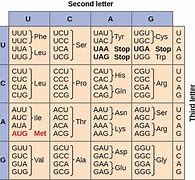
Point mutations occur in DNA, the genetic code altertion occurs in mRNA.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 2 Molecular Biology Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn