Topic 8: Metabolism HL 
This page contains multiple choice questions in the style of Paper 1 of the Biology exams.
They test the breadth of your knowledge of the understandings and skills about HL Metabolism.
To spend more time reviewing the topic before answering these questions, use the revision resources.
Metabolism HL revision resources
This is an introduction to the HL Metabolism topic. It lists understandings and skills expected for Topic 7 including; extra details of enzymes, enzyme inhibitors, cell respiration and photosynthesis. Helpful for revision. Detailed revision...
Learn from any mistakes. Every question has an examiner's explanation that appears when you check your answers.
Cells control metabolic pathways using several different methods?
Which of the following is not a method which is used by cells to control metabolism
Cells can control metabolism using, expression of genes, inhibition, end product inhibition or hormones.
Methylation of DNA may control the expression of genes, but not methylation of enzymes.
What are the reactions which take place in the matrix of mitochondria?
The electron transport chain & chemiosmosis take place on or in the mitochondrion inner membrane.
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm.
The link reaction occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria as does the Krebs cycle.
In the light dependent reactions reduced NADP and oxygen are produced.
Which other important molecule is also synthesised?
ATP is also produced in the light-dependent reactions by ATP synthase and chemiosmosis.
The diagram below shows photosystem II
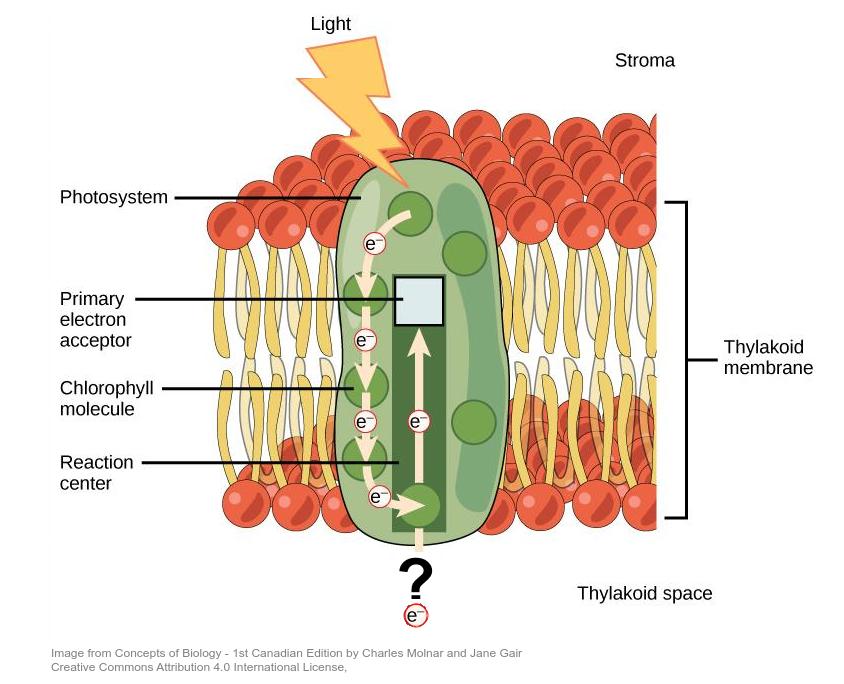
Light energy is harvested by the large collection of chlorophyll molecules in photosystem II to excite an electron. How is this electron replaced?
Light absorbed by photosystem II generates excited electrons.
Photolysis of water produces H+ ions, oxygen atoms and electrons which replace those excited in the light-dependent reactions.
The diagram below shows the Calvin cycle.

At which stage does carboxylation occur?
RuBP carboxylase enzyme (RuBisCO) catalyses the carboxylation of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).

How is the structure of the chloroplast membranes an adaptation to function efficiently?
The structure of the chloroplast is adapted to its function in photosynthesis
There are many membranes because this enables the chloroplast to have many chlorophyll molecules linked to electron carriers, for the light dependant reactions of photosynthesis.
A famous 'lollipop' experiment was performed by Calvin and Benson in the 1950s.
Radioactive carbon dioxide was introduced into the "lollipop" and photosynthesis allowed to continue for just a few seconds, then repeated for longer and longer periods.
The products of photosynthesis were separated by two way chromatography.

What did Calvin and Benson find out using this technique?
- Algae cells were exposed to 14CO2 and light in "lollipop"-shaped flask.
- 14C is radioactive.
- Any molecules containing the 14CO2 carbon atoms will become radioactive and can be detected.
Results of Calvin's work
- When light exposure was only 7 seconds, 12 compounds were radioactively labeled.
- When light exposure was reduced to 2 seconds, most of the radioactive carbon was in just one compound, 3-PGA
- It was concluded PGA must be the first molecule CO2 is fixed to.
Which of the following moves from the cell cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix during aerobic respiration? I Oxygen II ADP III Glucose IV Pyruvate?
Pyruvate (using a transporter protein), oxygen and ADP enter the mitochondrial matrix from the cytoplasm.
How do hydrogen ions travel from the intermembrane space to the mitochondrial matrix?
The inner membrane is only permeable to hydrogen ions through the ATP synthase channels and they travel down their concentration gradient.
Which statement best describes chemiosmosis in mitochondria?
Chemiosmosis is the diffusion of ions through a partially permeable membrane.
In mitochondria the ions are protons (hydrogen ions) and they diffuse through ATP synthase in mitochondrial inner membranes.
ATP synthase makes the inner mitochondrial membrane partially permeable allowing chemiosmosis.
Energy is collected from this process by ATP synthase and used to make ATP, but chemiosmosis is just the diffusion of the protons.
The electron transport chain on the mitochondrial inner membrane carries electrons through membrane proteins.
What other chemical is moved during this process?
The movement of electrons down the electron transport chain provides the energy to pump protons into the intermembrane space.
Which of the following can be produced by anaerobic respiration?
I Lactic acid
II Carbon dioxide
III Ethanol
IV ATP.
Anaerobic respiration in fungi produces ethanol and carbon dioxide. In humans anaerobic respiration produces Lactic acid as a waste product.
Small amounts of ATP are also produced by anaerobic respiration.
What is meant by the term, 'limiting factor' in photosynthesis?
When a process depends on a number of factors, like photosynthesis, its rate is limited by the factor which is in shortest supply. A limiting factor is the one factor out of several factors needed for a process that is actually preventing an increase in the rate of the process. This can be in experimental or natural conditions.
How is ATP produced in photosynthesis?
A proton gradient is generated by electron carriers. ATP synthase is located in the thylakoid membrane and uses the proton gradient to provide energy to synthesise ATP.
What is the triose phosphate produced in the light independent reactions of photosynthesis used for?
Triose phosphate is used to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin cycle and some is used to manufacture glucose and other carbohydrates.
Acarbose, structure shown below, is a competitive reversible inhibitor of pancreatic amylase prescribed to diabetics to lower blood glucose levels after a meal. How would it achieve this effect?
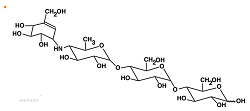
As a competitive reversible inhibitor, acarbose binds temporarily to the active site of amylase and slows digestion of starch. (Read the question carefully, especially when it contains novel information).
Which of the following moves from a muscle cell to the mitochondrial matrix to be during aerobic respiration to be later used for muscular contraction? I Oxygen II ATP III ADP IV Phosphate?

When ATP is used in muscular contraction it forms ADP and phosphate. These enter the mitochondrion to be resynthesised into ATP for further contractions. Oxygen is not directly used for muscular contraction.
Which of the following moves from the thylakoid membranes to the stroma of the chloroplast during daylight?
I NADPH+H+
II ATP
III Glucose
IV Triose phosphate?

ATP and NADPH+H+ are made in the light-dependent reaction in the thylakoid membranes and used in the Calvin Cycle in the stroma to fix carbon dioxide and form carbohydrates.
Which of the following is a function of the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast?
The thylakoid membranes generate ATP and NADPH+ using excited electrons to form proton gradients. The excited electrons are derived from light energy trapped by chlorophyl and replaced from water.
Which molecule transfers energy from aerobic respiration to the electron transport chain?
Reduced NAD transfers electrons (and their energy) to the electron transport chain.
Refresh this page to try a new set of 20 multiple choice questions. The questions will be different next time you visit. Great revision.
How much of Topic 8 Metabolism HL Paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn