Question 1
Consider the first-order differential equation
Solve the equation given that when
, giving your answer in the form
.
Consider the first-order differential equation
Solve the equation given that when
, giving your answer in the form
.
Use separation of variables to solve each of the following differential equations:
Use separation of variables to solve each of the following differential equations for which satisfies the given boundary condition:
Radiangast the Beige is chief mathemagician of the wizards’ council. After animals begin falling ill in the forest where he lives, Radiangast realises that an evil magic has begun spreading through the forest. After studying the situation, he believes that at any point in time, , the rate of change of the area,
, affected by the evil magic is inversely proportional to the square root of the area already affected.
At the time when Radiangast first noticed its presence, the evil magic was affecting an area of 16 acres of forest. One week later he noticed that the area has increased to 41 acres.
Radiangast knows that as long as the wizards’ council convenes to weave spells before the area affected by the evil magic exceeds 100 acres, then they will be able to stop the evil magic from spreading further.
After an invasive species of insect has been introduced to a new region, it is estimated that at any point in time the rate of growth of the population of insects in the region will be proportional to the current population size . At the start of a study of the insects in a particular region, researchers estimate the population size to be 1000 individuals. A week later another population survey is conducted, and the population of insects is found to have increased to 1150.
The graph below shows the slope field for the differential equation
in the intervals
and
.
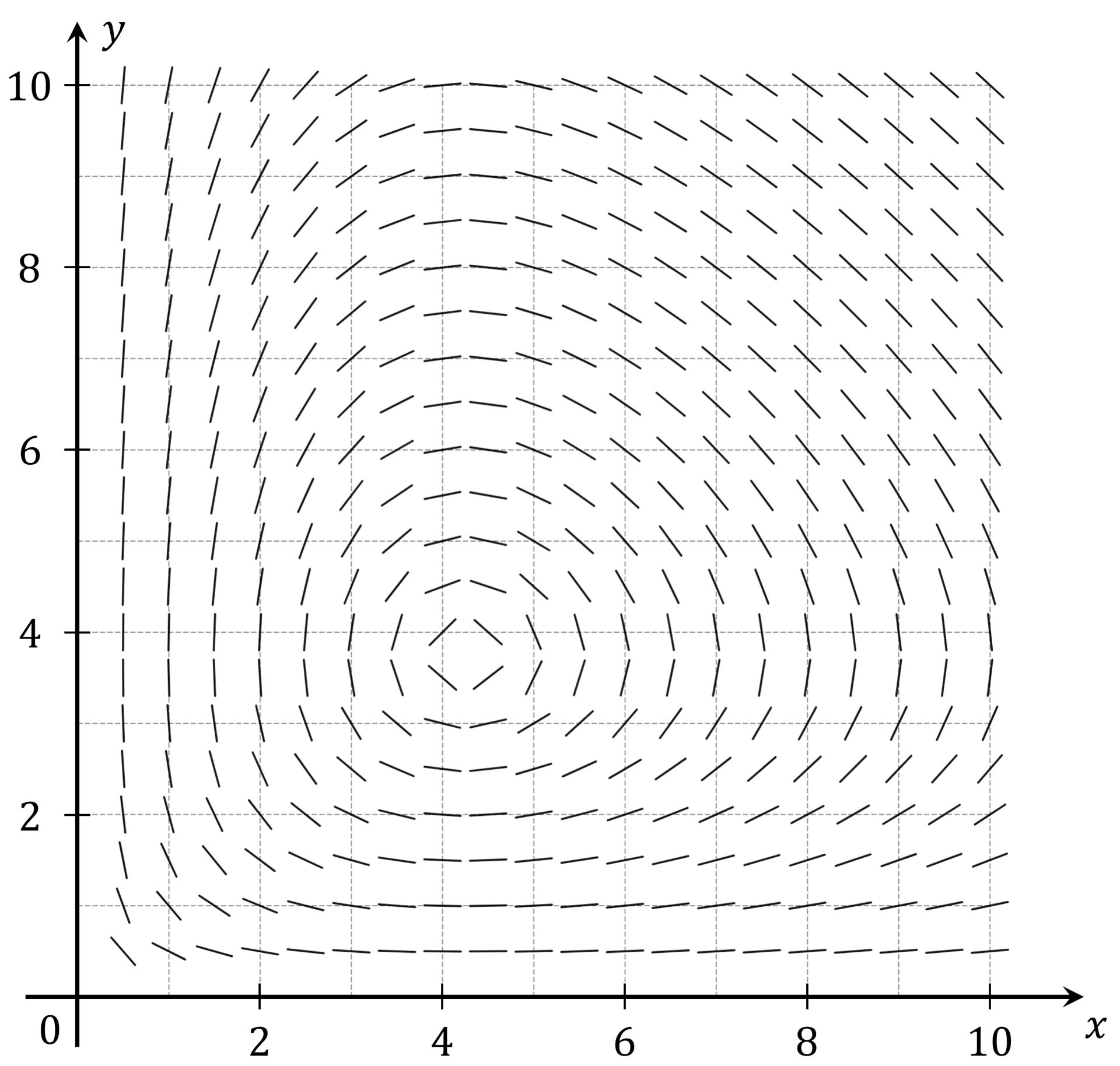
Consider the differential equation
with the boundary condition .
It can be shown that the exact solution to the differential equation with the given boundary condition is
A particle moves in a straight line, such that its displacement at time
is described by the differential equation
At time