DP Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches Questionbank

SL 2.7—Solutions of quadratic equations and inequalities, discriminant and nature of roots
| Path: |
Description
[N/A]Directly related questions
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.S_5:
Let and .
Find the values of so that has no real roots.
-
EXN.1.AHL.TZ0.12d:
Hence find the exact value of .
-
EXN.2.SL.TZ0.5:
The quadratic equation , where , has real distinct roots.
Find the range of possible values for .
-
21N.1.AHL.TZ0.7b:
Consider the case when . The roots of the equation can be expressed in the form , where . Find the value of .
-
21N.1.AHL.TZ0.7a:
Find the possible values for .
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2b.ii:
By substituting , show that where is a constant.
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2a.i:
By solving the differential equation , show that where is a constant.
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2a.ii:
Show that .
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2b.iii:
Hence find as a function of .
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2c.i:
Show that .
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2b.iv:
Hence show that , where is a constant.
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2c.ii:
Find the two values for that satisfy .
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2c.iii:
Let the two values found in part (c)(ii) be and .
Verify that is a solution to the differential equation in (c)(i),where is a constant.
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2a.iii:
Solve the differential equation in part (a)(ii) to find as a function of .
-
21N.3.AHL.TZ0.2b.i:
By differentiating with respect to , show that .
-
22M.3.AHL.TZ1.1a.ii:
The number is a triangular number. Determine which one it is.
-
22M.3.AHL.TZ1.2e:
Deduce from part (d)(i) that the complex roots of the equation can be expressed as .
-
22M.1.SL.TZ2.6b:
The third term in the expansion is the mean of the second term and the fourth term in the expansion.
Find the possible values of .
-
22M.1.SL.TZ2.8a:
Find the coordinates of .
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ2.11c:
Given that , find the value of .
Give your answer in the form , where .
-
22M.2.SL.TZ1.4a:
Show that .
-
22M.2.SL.TZ1.4b:
Find the value of , giving a reason for your answer.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ1.4c:
Hence, find .
-
22M.2.AHL.TZ1.8a:
Write down an expression for the product of the roots, in terms of .
-
22M.2.AHL.TZ1.8b:
Hence or otherwise, determine the values of such that the equation has one positive and one negative real root.
-
22M.1.SL.TZ1.8b.iii:
The sum of the first terms of the series is .
Find the value of .
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10b.iii:
The sum of the first terms of the series is .
Find the value of .
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10b.ii:
Write down in the form , where .
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10b.i:
Show that .
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ2.8:
A continuous random variable has the probability density function
.
The following diagram shows the graph of for .
Given that , find an expression for the median of in terms of and .
-
SPM.2.AHL.TZ0.12b:
Verify that and satisfy the equation .
-
SPM.2.AHL.TZ0.12a:
Show that .
-
SPM.2.AHL.TZ0.12c:
Hence, or otherwise, show that the exact value of .
-
SPM.2.AHL.TZ0.12d:
Using the results from parts (b) and (c) find the exact value of .
Give your answer in the form where , .
-
17M.1.SL.TZ1.S_9c:
The line is a tangent to the curve of . Find the values of .
-
16N.1.AHL.TZ0.H_5:
The quadratic equation has roots and such that . Without solving the equation, find the possible values of the real number .
-
17N.1.SL.TZ0.S_8d:
Find the area of the region enclosed by the graph of and the line .
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.S_1c:
Solve f '(x) = f "(x).
-
17M.1.SL.TZ1.S_10a:
Show that .
-
17M.1.SL.TZ1.S_10b:
Given that , find .
-
17M.1.SL.TZ1.S_10c:
Let , for . The graph of between and is rotated 360° about the -axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
-
16N.2.SL.TZ0.S_4a:
Find the value of and of .
-
16N.2.SL.TZ0.S_4b:
Hence, find the area of the region enclosed by the graphs of and .
-
18N.1.SL.TZ0.S_5:
Consider the vectors a = and b = .
Find the possible values of p for which a and b are parallel.
-
19N.1.SL.TZ0.S_5a:
Show that the discriminant of is .
-
19N.1.SL.TZ0.S_5b:
Given that is an increasing function, find all possible values of .
-
17M.2.AHL.TZ2.H_4a:
Find the set of values of that satisfy the inequality .
-
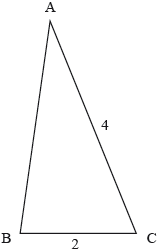
17M.2.AHL.TZ2.H_4b:
The triangle ABC is shown in the following diagram. Given that , find the range of possible values for AB.