| Date | May 2009 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 09M.3.hl.TZ1.A2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Deduce | Question number | A2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A feature of some \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectra is the electron-withdrawing effect of electronegative atoms. These atoms cause nearby protons to produce peaks at higher chemical shift values, often in the range 2.5 to 4.5 ppm.
Consider the \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum of an unknown compound, D, which has a molecular formula \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) and is known to have an absorption in its IR spectrum corresponding to a C=O absorption.
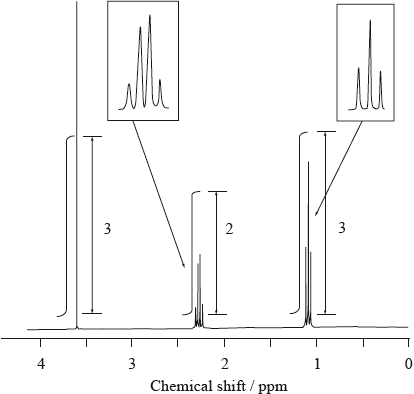
Use this information and the values in Table 18 of the Data Booklet to deduce the structure of D.
Markscheme
D could be \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) or \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\);
this is because there are 3 peaks / 3:2:3 ratio;
explanation of splitting into a singlet a triplet and a quartet;
methyl propanoate/\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) is correct isomer because of higher chemical shift value of singlet (3.6 instead of 2.0–2.5);
Examiners report
From part (a) it is clear that proton NMR is poorly understood in some schools. Whilst many candidates could identify the correct structure, few could write a description of how they had obtained it from the information provided. Very few candidates explicitly mentioned that there were 3 peaks or explained how the structure had been determined, especially neglecting to explain the splitting patterns.

