| Date | May 2011 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 11M.3.hl.TZ2.A2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Deduce | Question number | A2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Infrared spectroscopy is commonly used as an analytical technique by inorganic, physical and organic chemists.
The IR spectrum, mass spectrum and \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum of an unknown compound, X, of molecular formula \({{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\), are as follows.
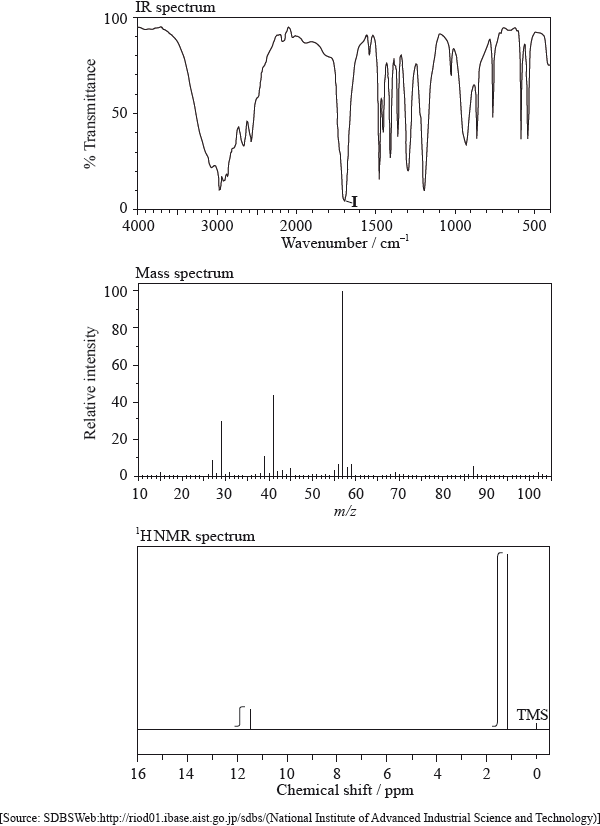
\({\text{HCOOC(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\) is an isomer of X. For the \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum of this isomer, deduce the total number of peaks (excluding the TMS peak at 0 ppm) and the ratio of peak areas. For each peak, deduce whether it is a singlet, doublet, triplet, quartet or shows a more complex splitting pattern.
Number of peaks (excluding the TMS peak at 0 ppm):
Ratio of peak areas:
Splitting patterns:
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) is another isomer of X. For the \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum of this isomer, deduce the total number of peaks (excluding the TMS peak at 0 ppm) and the ratio of peak areas. For each peak, deduce whether it is a singlet, doublet, triplet, quartet or shows a more complex splitting pattern.
Number of peaks (excluding the TMS peak at 0 ppm):
Ratio of peak areas:
Splitting patterns:
Markscheme
Number of peaks: 2;
Ratio of peak areas: 1:9 / 9:1;
Splitting patterns: two singlets / no splitting;
Number of peaks: 4;
Ratio of peak areas: 3:2:2:3;
Accept in any order.
Splitting patterns: two triplets and two quartets;
Examiners report
Most candidates showed good knowledge of IR and MS, sometimes forgetting the charge of the ions in MS. NMR proved a little more difficult, especially in (iv) where information of the integration traces was asked. Students had sometimes difficulty to predict the splitting patterns.
Most candidates showed good knowledge of IR and MS, sometimes forgetting the charge of the ions in MS. NMR proved a little more difficult, especially in (iv) where information of the integration traces was asked. Students had sometimes difficulty to predict the splitting patterns.

