| Date | November 2009 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 09N.3.hl.TZ0.A2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | A2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
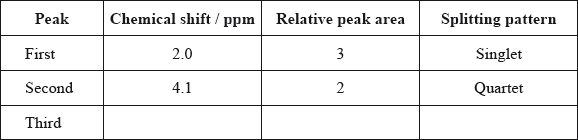
Typical proton chemical shift values are given in Table 18 of the Data Booklet. The \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectrum of X contains three peaks. Details of two of these are shown in the table below.
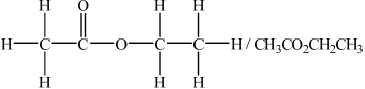
Deduce a possible structure for X that is consistent with the mass, IR and \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectra.
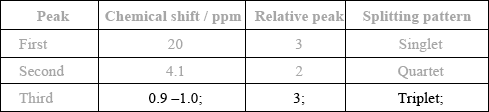
Complete the table above by suggesting the chemical shift of the third peak, and state its relative peak area and splitting pattern.
Explain the splitting pattern of the peak at chemical shift 4.1 ppm.
Markscheme
 ;
;
ECF from structure in (c)(i).
(quartet means) neighbouring C;
has 3 H atoms/protons;
Award [1] for stating CH3CH2.
Award [2] for stating CH3CH2 group and indicating number of protons.
Examiners report
In part (c), most of the better candidates deduced the structure as CH3COOCH2CH3 and subsequently the correct chemical shift, relative peak area and splitting patter for the third peak.
In part (c), most of the better candidates deduced the structure as CH3COOCH2CH3 and subsequently the correct chemical shift, relative peak area and splitting patter for the third peak.
The splitting pattern of the peak at 4.1 ppm was usually well answered. Many students displayed very good knowledge of \(^{\text{1}}{\text{H}}\,{\text{NMR}}\) spectra in this question.

