- Summary list for topic 2.8 Respiration
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about measuring respiration
- Model answer
- Exam style question about bread making.
- 2.8 Cell Respiration Quiz 1/1
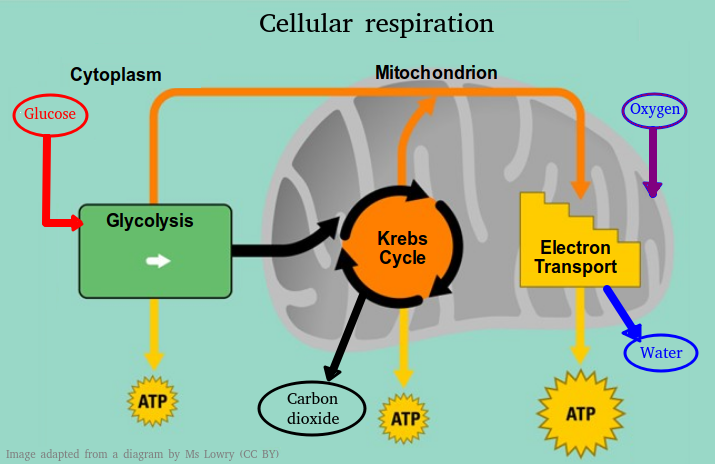 Respiration is one of the seven characteristics of all living things and it is essential for life. This topic covers the basics of aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It is important to know what the role of ATP is in cells and also to have experience of using a respirometer to measure the rate of respiration.
Respiration is one of the seven characteristics of all living things and it is essential for life. This topic covers the basics of aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It is important to know what the role of ATP is in cells and also to have experience of using a respirometer to measure the rate of respiration.These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for topic 2.8 Respiration
- Cell respiration definition,"the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP"
- ATP produced is a source of energy ready for immediate use in the cell.
- Anaerobic cell respiration gives a small yield of ATP from glucose compared to aerobic respiration whose yield is large.
- Aerobic cell respiration also requires oxygen.
- Substrates (e.g. glucose) and final waste products (e.g. water, CO2, lactate, ethanol) should be known.
- Anaerobic cell respiration in yeasts is used to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide in baking.
- In the human body anaerobic respiration is used to maximise the power of muscle contractions & produces lactate.
- Know how to use simple respirometers to measure the rate of respiration.
- to know that an alkali is used to absorb CO2 produced in respirometers, so that reductions in gas volume are due to oxygen use.
- To keep the temperature constant, so that gas volumes don't change through expansion / contraction of gas.
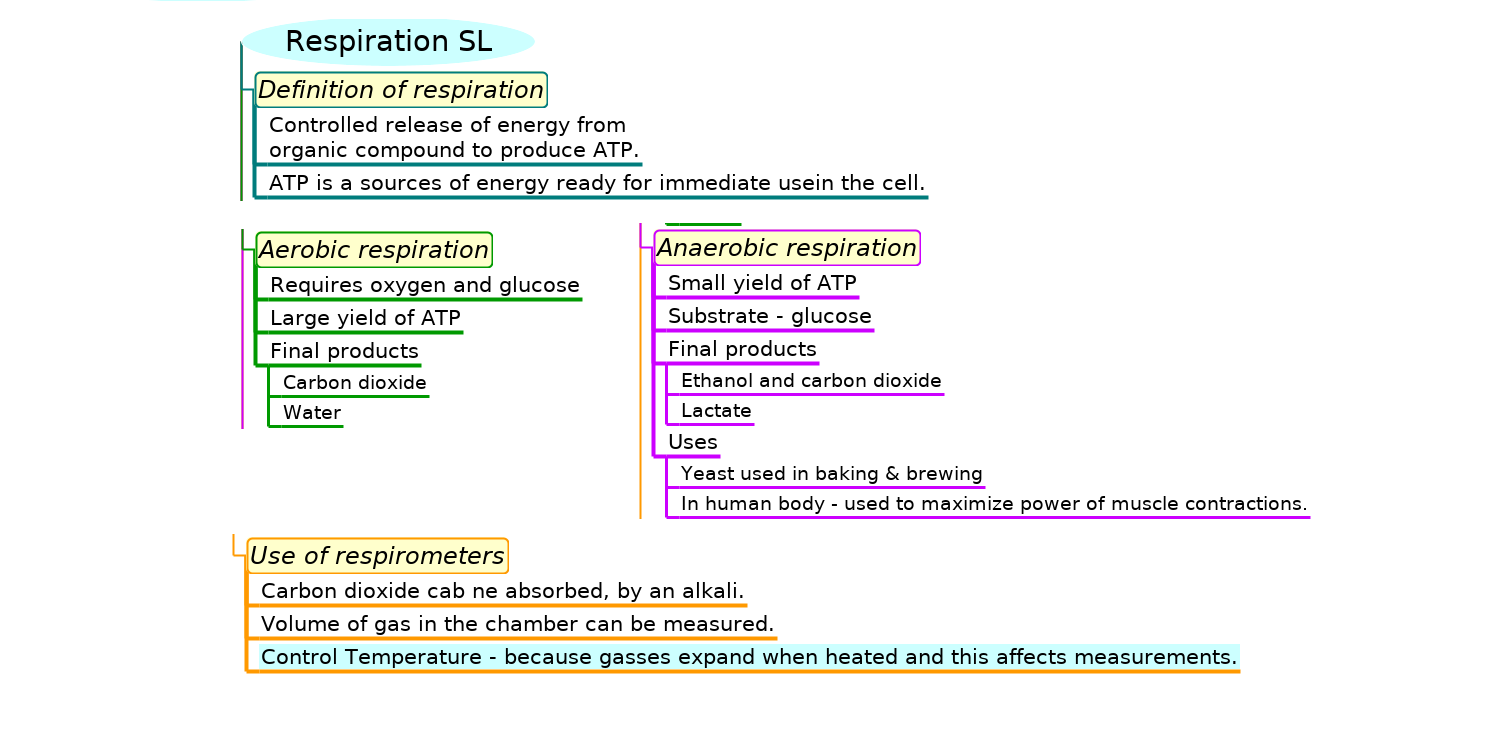
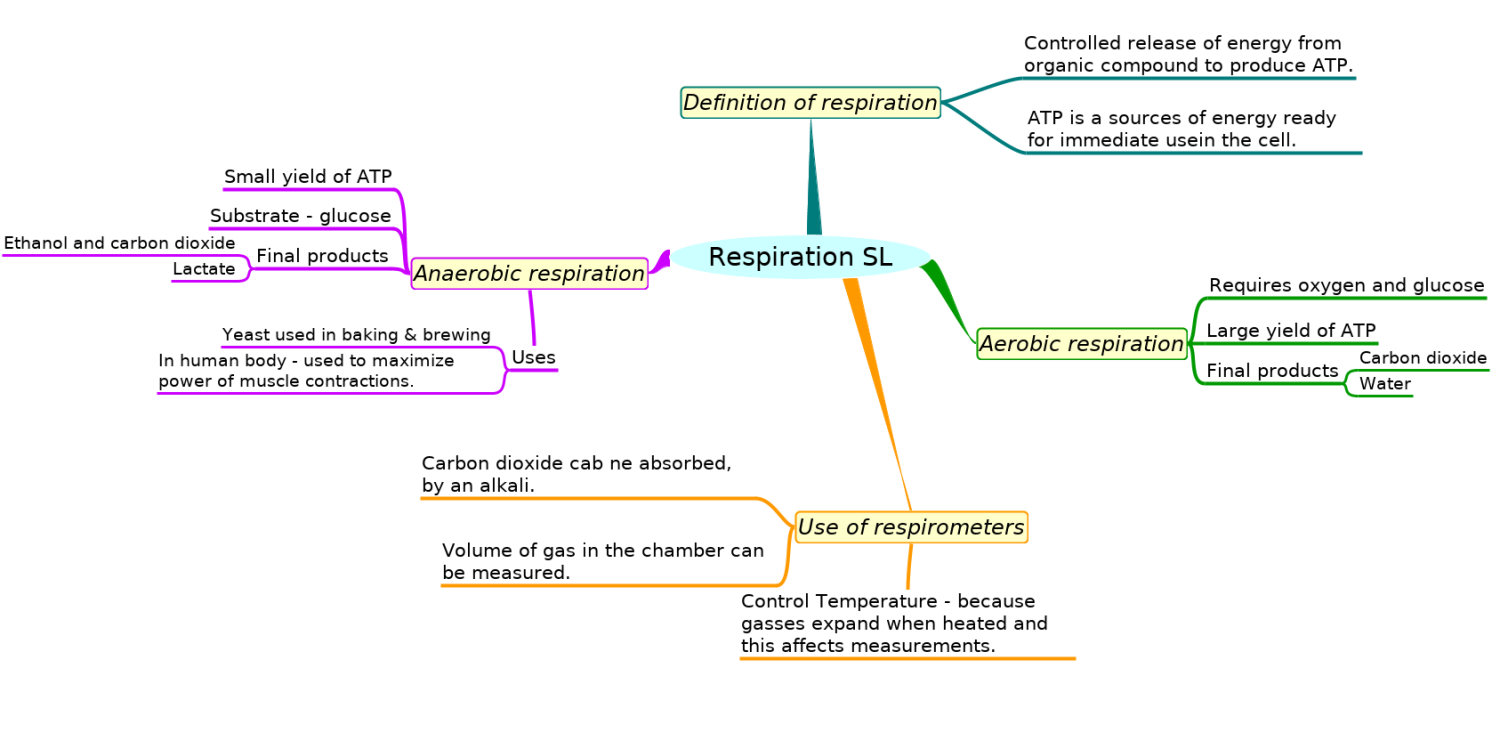
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 2.8.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Exam style question about measuring respiration
Understanding measurements of respiration from experiments with respirometers is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer with the model answer below.
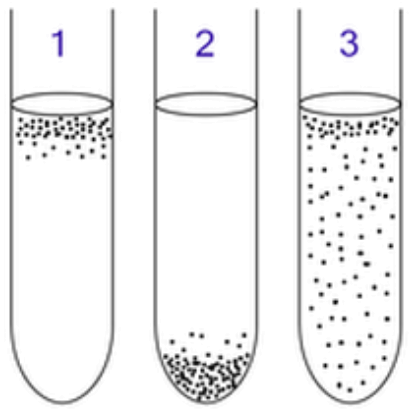
The graph shows the results of an experiment with germinating seeds.
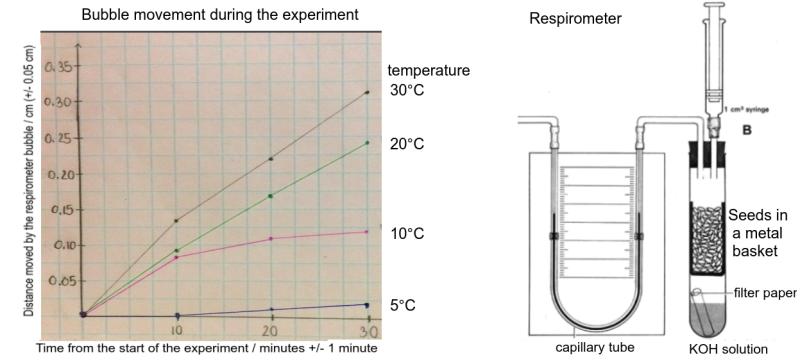
Explain how the respirometer apparatus is used to measure the rate of respiration in germinating seeds. [2]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Calculate the rate of respiration in seeds at 30°C, in cm per minute. [2]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Test your construction of biological knowledge using the drag and drop questions below.
Contrasting aerobic and anaerobic respiration
large cytoplasm ethanol water small amount Aerobic mitochondrion partially carbon dioxide oxygen completely
respiration begins in the cytoplasm and is completed in the . It uses oxygen, breaks down glucose into and and produces a amount of ATP energy.
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the . It does not use and breaks down glucose into or lactic acid and produces a of ATP energy.
Examiner hint: In any compare or compare and contrast response you should use a point of comparison per sentence e.g. aerobic respiration uses oxygen; anaerobic does not. The above paragraphs are written for the drag and drop activity.
This is a little bit of fun. You can choose your favourite game but I prefer the word shoot! Respiration word shoot game
How much of Respiration 2.8 have you understood?


















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn