- Revision summary list for topic 2.7 DNA Replication
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about an application of DNA replication
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 2.7 DNA replication, transcription and translation quiz 1/1
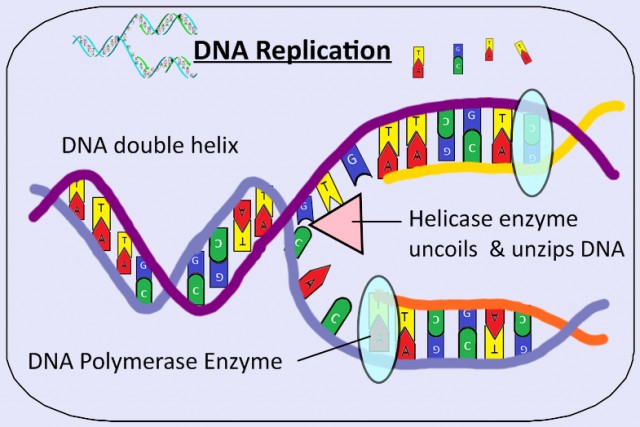 The discovery of the structure of DNA immediately suggested a method of copying the genetic material to Watson and Crick in 1953. This topic looks at these methods, DNA replication making an exact copy of the genetic material as well as Transcription and translation in the expression of a gene to make a protein.
The discovery of the structure of DNA immediately suggested a method of copying the genetic material to Watson and Crick in 1953. This topic looks at these methods, DNA replication making an exact copy of the genetic material as well as Transcription and translation in the expression of a gene to make a protein.Learn and test your biological vocabulary for 2.7 DNA replication using these flash cards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Revision summary list for topic 2.7 DNA Replication
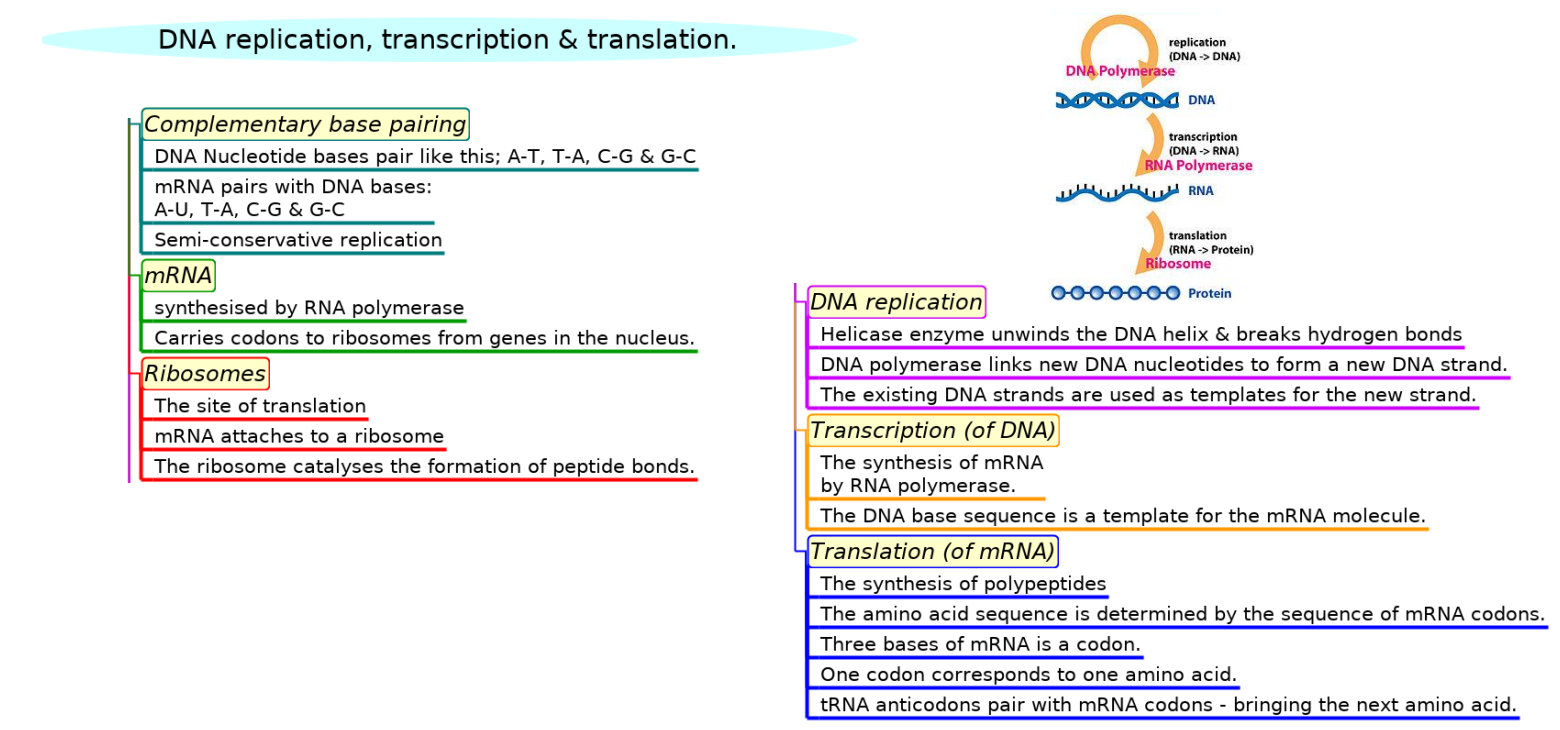
- DNA replication.
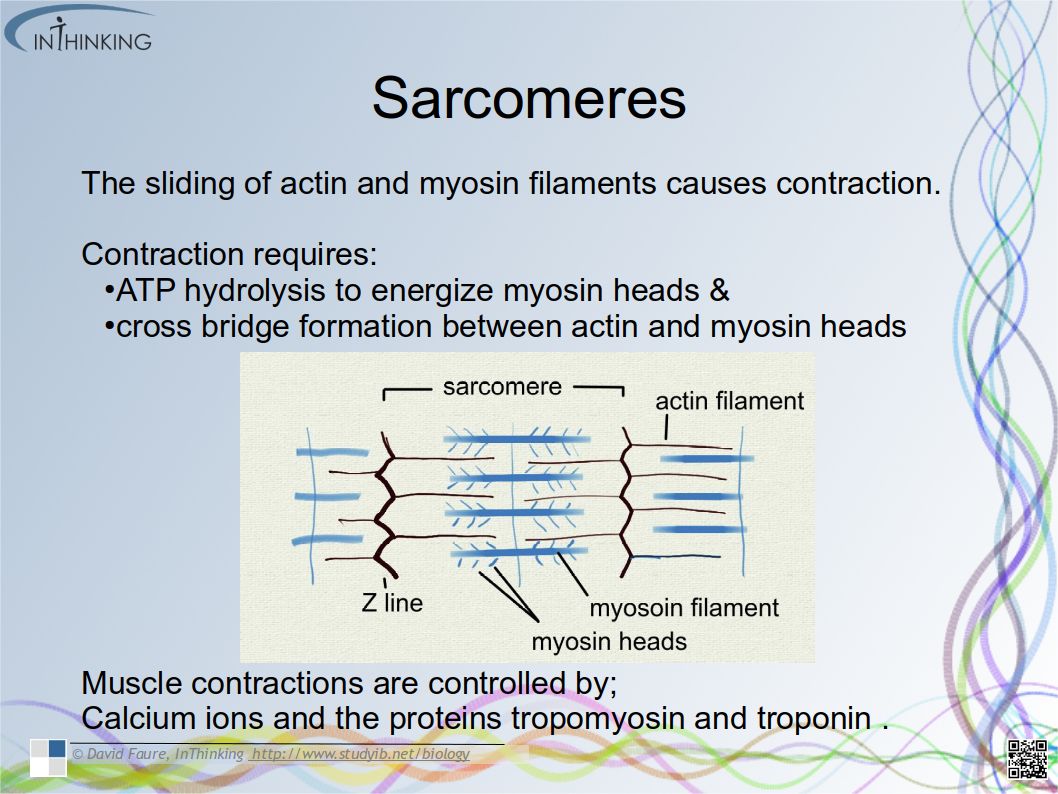
- Complementary base pairing leads to the semi-conservative replication of DNA.
- The enzyme helicase unwinds the double helix and breaks hydrogen bonds which hold the two DNA strands together.
- DNA polymerase (generalised name) links DNA nucleotides together to form a new strand DNA,using the pre-existing strand as a template.
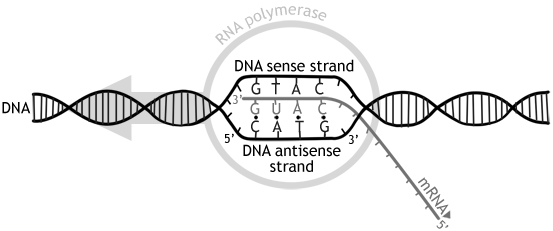
- Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA by RNA polymerase using the DNA base sequence as a template
- Translation is the synthesis of polypeptides on ribosomes.
- The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is determined by mRNA according to the genetic code.
- Three bases of mRNA is called a codon and corresponds to one amino acid in the polypeptide.
- Translation depends on complementary base pairing between codons on mRNA and anticodons on tRNA.
- Awareness that in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) an enzymes called Taq DNA polymerase produces multiple copies of DNA.
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 2.7.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Exam style question about an application of DNA replication
Answer the question below, which addresses one application of DNA replication.
(Thanks to Catarina Gouveia and her students for the question and markscheme).
Outline the role of Taq DNA polymerase in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [4]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
DNA replication
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe DNA replication
parent nucleotides semi-conservative hydrogen base separated new mutations
DNA replication is . The two parent strands are by helicase breaking the bond between complimentary pairs. DNA polymerase then adds complimentary to each of the parent strands.
The two daughter strands consist of one strand and one strand. This method of replication minimises copying errors in the base sequence, .
Explanation: DNA replication is semi-conservative because the two strands produced contain one parent and one new strand each.
The mechanism of transcription needs to be understood and the correct terminology used in a description.
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe transcription.
complimentary covalent reforms ribosome gene gene polymerase Golgi body transfer synthetase messenger single hydrogen pore
Transcription is the synthesis of stranded RNA (mRNA) from the DNA template strand by RNA .
The RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at the start code of a and separates the double helix by breaking the bonds. It then moves along the DNA strand, pairing up the DNA template strand with RNA nucleotides and joining up the backbone to form a single strand of mRNA.
At the end of the , the completed mRNA strand then detaches from the DNA and the double helix . The mRNA moves out of the nucleus through the nuclear and joins to a in the cytoplasm for translation to a polypeptide.
Explanation: A gene is a portion of a DNA strand. DNA polymerase forms an mRNA single strand complimetary to the template strand of DNA corresponding to a gene. (except that Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA).
Translation is an improtant concept and the terminology must be known.
Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to outline translation.
polypeptide end attached three mRNA detach complimentary ribosome genetic code next anticodon amino acids
Translation is the synthesis of a chain with a sequence of corresponding to the sequence of codons in the mRNA.
Codons consist of bases on the mRNA chain. These are translated into an amino acid in the polypeptide sequence according to the , for example the codon GGG on is translated into the amino acid glycine in the polypeptide chain
Translation occurs in the where the codon on the mRNA binds to the on the tRNA by base pairing. The tRNA has the amino acid corresponding to the anticodon previously . The ribosome attaches this amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain and then moves along the mRNA to translate the codon.
When the ribosome reaches the of the mRNA chain, ribosome, mRNA and polypeptide chain from each other.
Examiner hint: This is a basic outline of the process. You will need a more detailed understanding of the genetic code and of the role of the ribosome in translation.
Everyone needs a break or a change of activity from time to time. This activity is a bit of fun, but it's still revision DNA replication, transcription and translation card matching game.
How much of DNA Replication, transcription, translation 2.7 have you understood?




















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn