Learn and test your biological vocabulary for 2.3 Carbohydrates and Lipids using these flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 2.3 Carbohydrates & Lipids
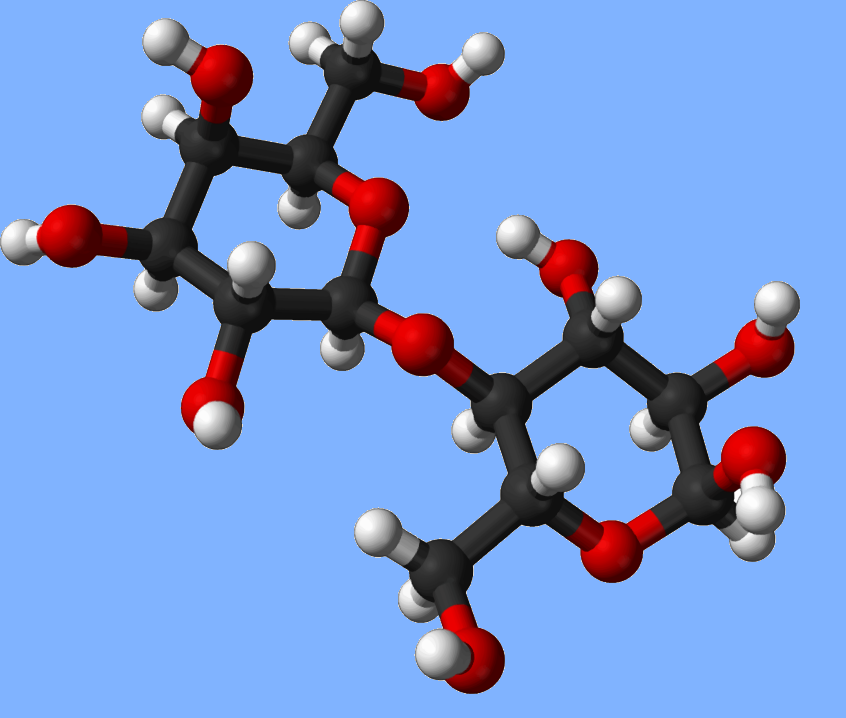
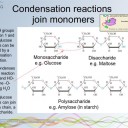
- Condensation reactions link Monosaccharide monomers together to
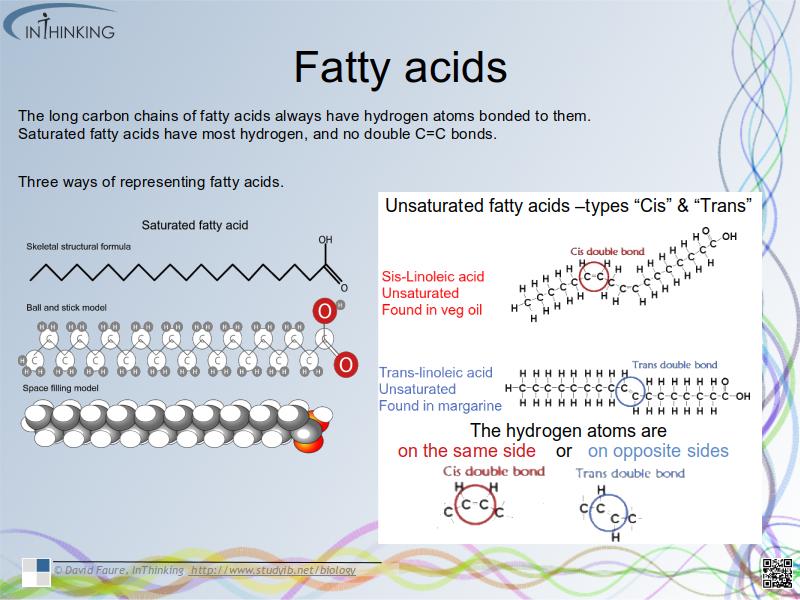
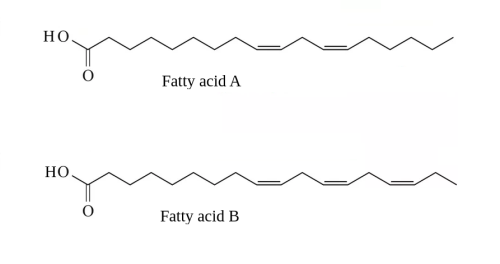
form disaccharides (Sucrose, lactose and maltose) and polysaccharides (cellulose starch and glycogen). - Fatty acids can be saturated, monounsaturated or polyunsaturated.
- and cis or trans isomers if they are unsaturated. (Molecule names not required).
- Three fatty acids and one glycerol molecules can form a Triglycerides by condensation reactions.
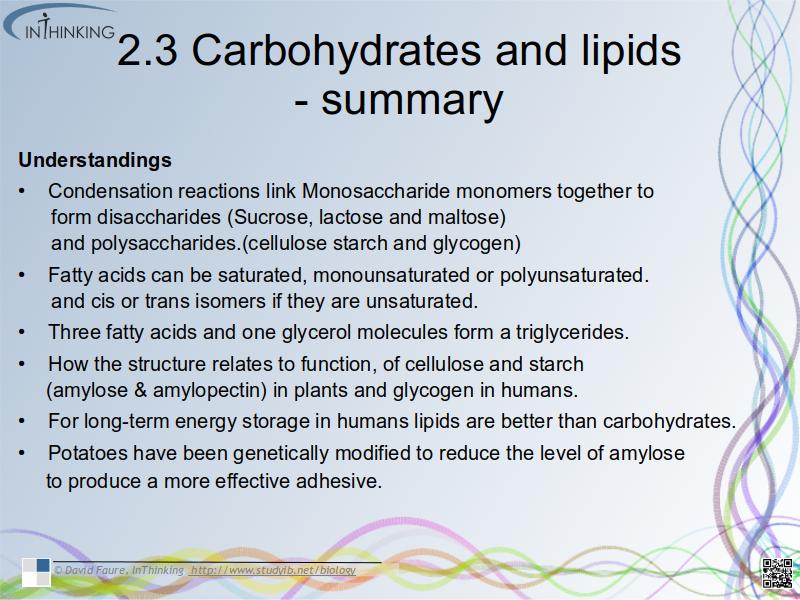
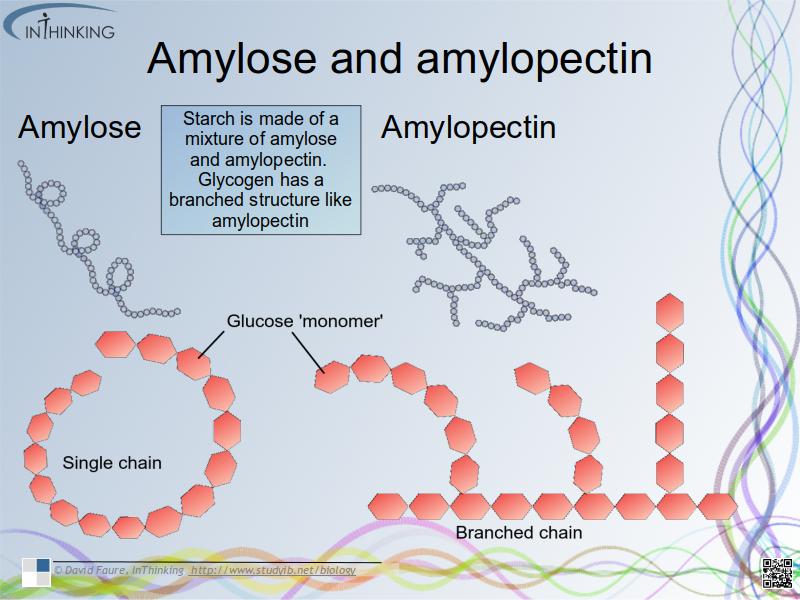
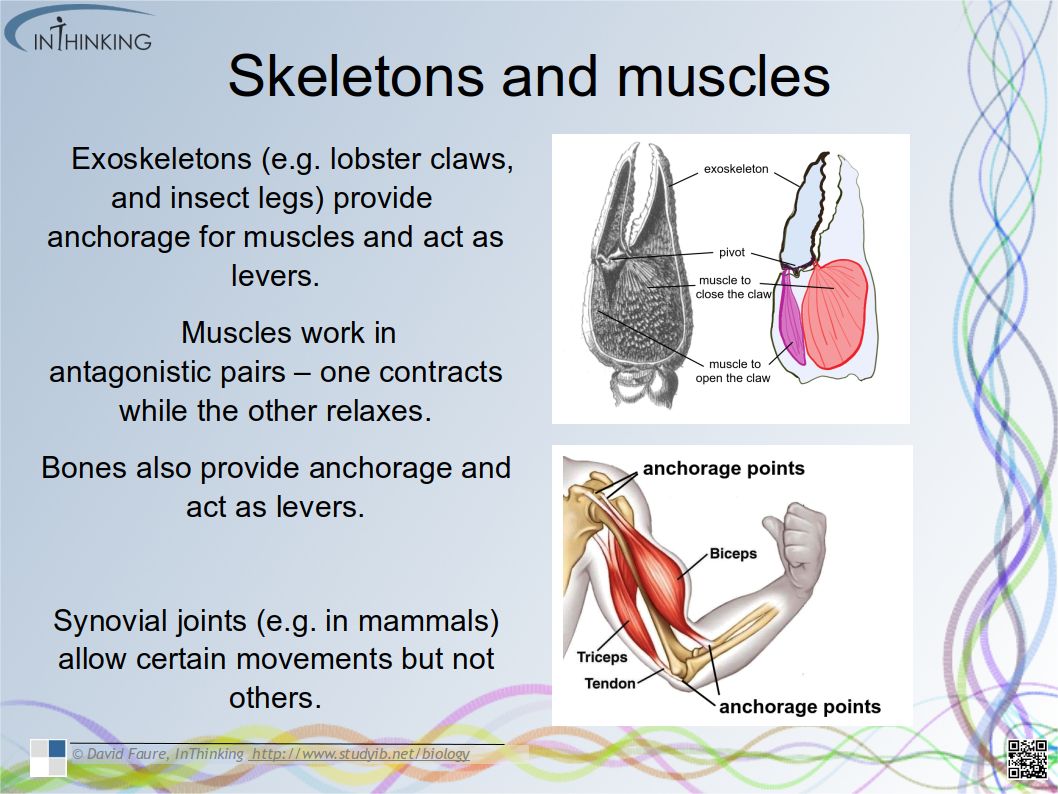
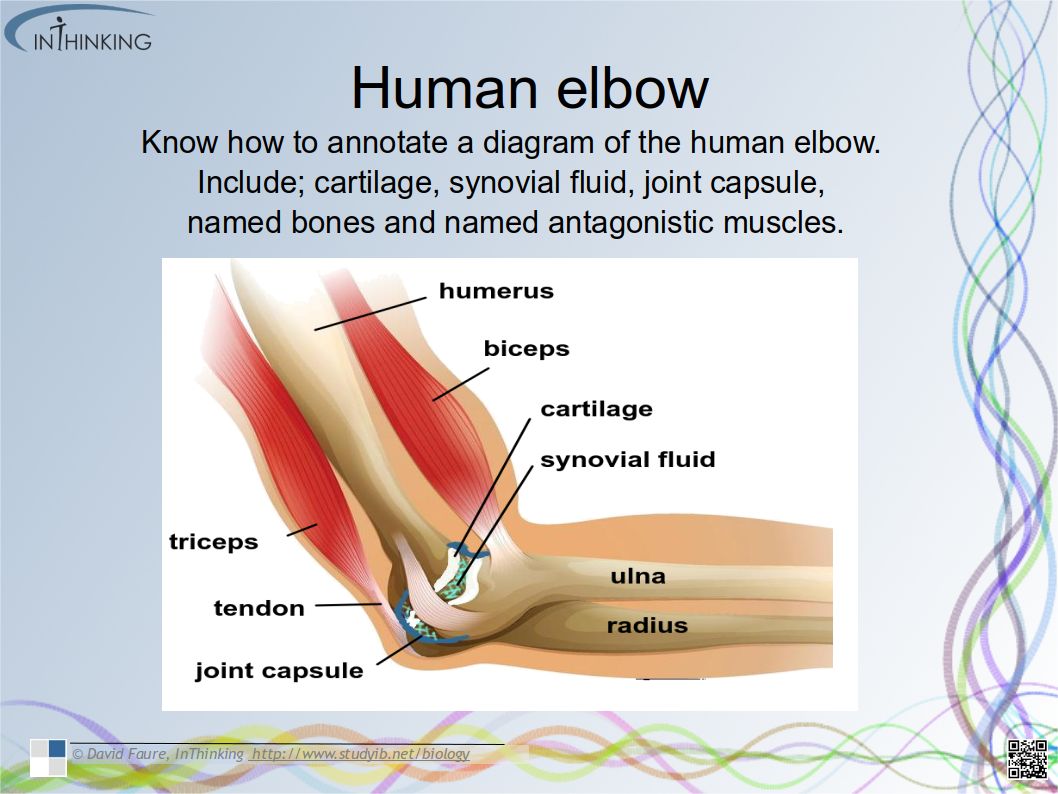
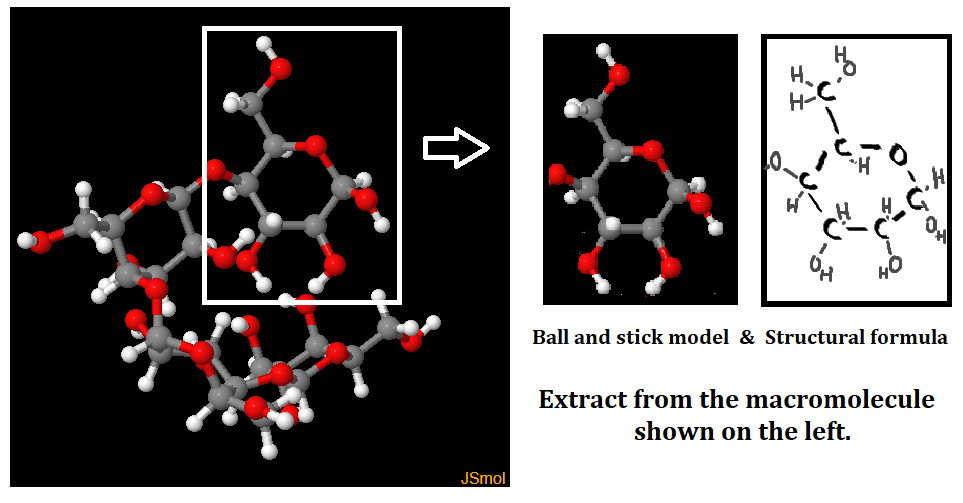
- How the structure of cellulose and starch (amylose & amylopectin) in plants and glycogen in humans relates to function.
- For long-term energy storage in humans lipids are better than carbohydrates.
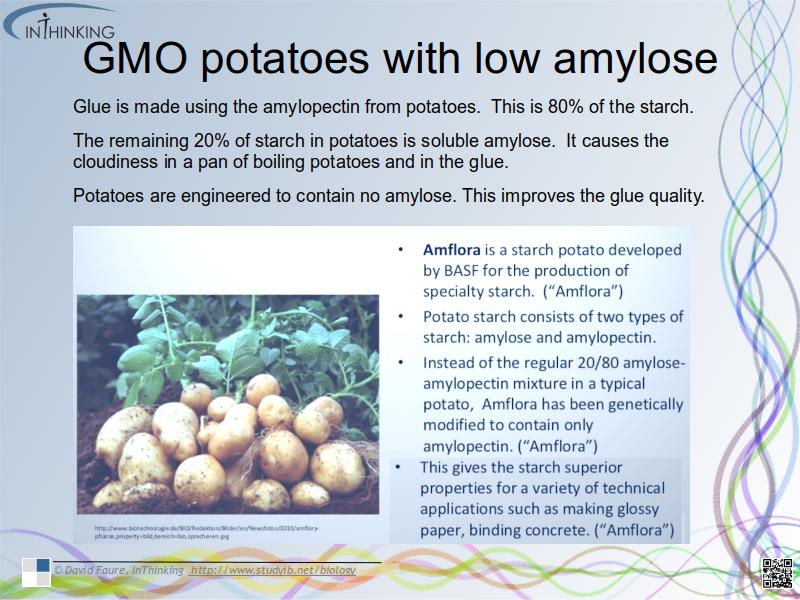
- Potatoes have been genetically modified to reduce the level of amylose to produce a more effective adhesive.
- Evaluate the conflicting evidence for health risks of trans fats and saturated fatty acids and evaluate the methods used.
- Ability to use molecular visualisation software like jmol to compare cellulose, starch and glycogen.
- Ability to work out a BMI using a nomogram or by calculation.
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 2.3.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Even better, design your own.
Exam style question about carbohydrate structure
Understanding the structure of carbohydrates is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer with the model answer below.
There are unsaturated fats in nuts, olive oil, and avocados that are important in a healthy diet. Health authorities around the world encourage people to reduce their consumption of saturated fats, in other types of food.
Compare and contrast the structures of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. [6]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
.
.
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Examples of carbohydrate structure and function
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe the strructure and functions of carbohydrates.
starch galactose storage monomer respiratory aerobic glycogen cellulose milk monosaccharide disaccharide polysaccharide
Glucose is a which is the main substrate, used by mitochondria to make ATP energy by respiration.
Sucrose is a composed of glucose and fructose bonded by a glycosidid bond. It is used in transport in plants.
Lactose is a disaccharide of glucose and found in mammalian .
Polysaccharides of glucose units, depending how the monomer units are bonded, can form for energy in animals, for energy storage in plants and for cell walls in plant cells.
Explanation/Examiner hint. You need to know the structure of simple and complex carbohydrates and some of their roles in living organisms. These examples reoccur throughout the syllabus content.
Just for fun
Everyone needs something a bit light hearted from time to time when revising. That's the aim of this last activity.
Cabohydrates & Lipids - Matching cards memory games
The idea is that this game is fun to do but it still counts as revision.
How much of Carbohydrates & Lipids 2.3 have you understood?



























 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn