
Learn and test your biological vocabulary for topic 2.1 molecules to metabolism using these flashcards.
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 2.1 Molecules to metabolism
Carbon based compounds
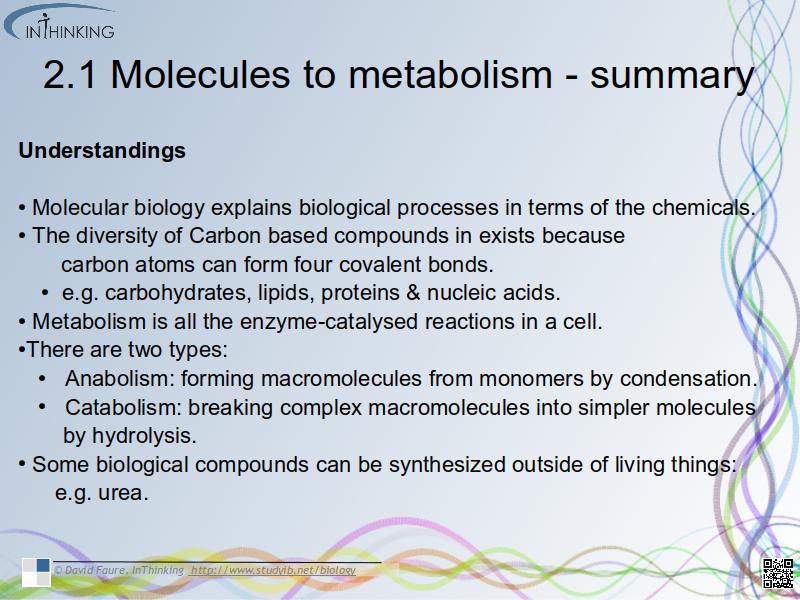
- Molecular biology is explaining biological processes in terms of the chemicals involved.
- There is a diversity of Carbon based compounds in living things because carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds.
e.g. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins & nucleic acids. - All the enzyme-catalysed reactions in a cell make up its metabolism. There are two types:
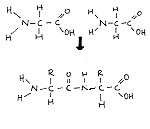
- Anabolism: forming macromolecules from monomers by condensation.
- Catabolism: breaking complex macromolecules into simpler molecules by hydrolysis.
- Some biological compounds can be synthesised outside of living things: e.g. urea.
Skills in drawing molecules
- Draw diagrams of:
- αD-glucose & βD-glucose.
- D-ribose.
- a fatty acid.
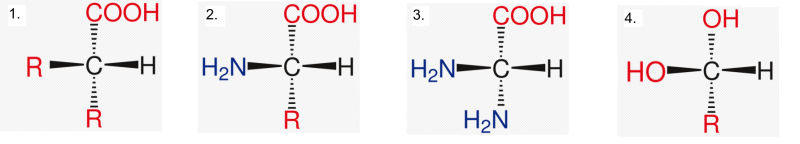
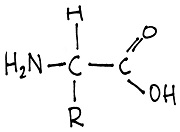
- an amino acid with generalised R-group.
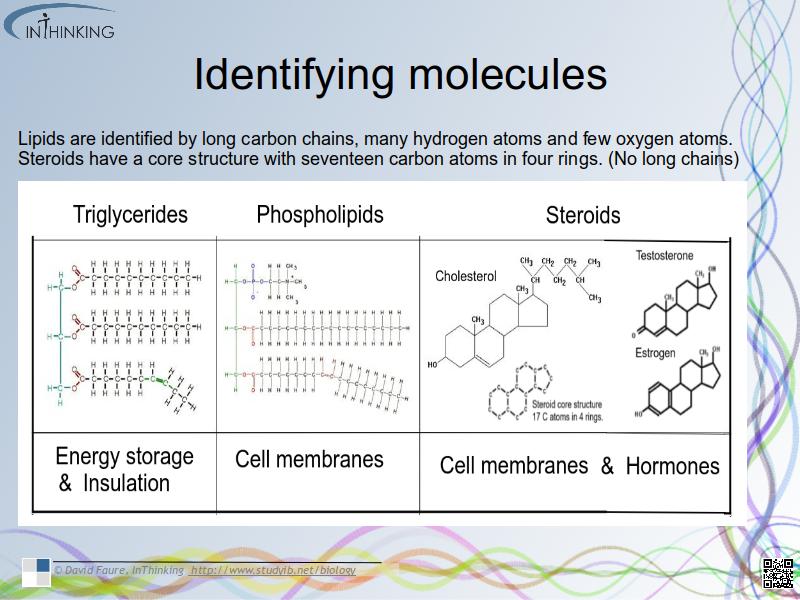
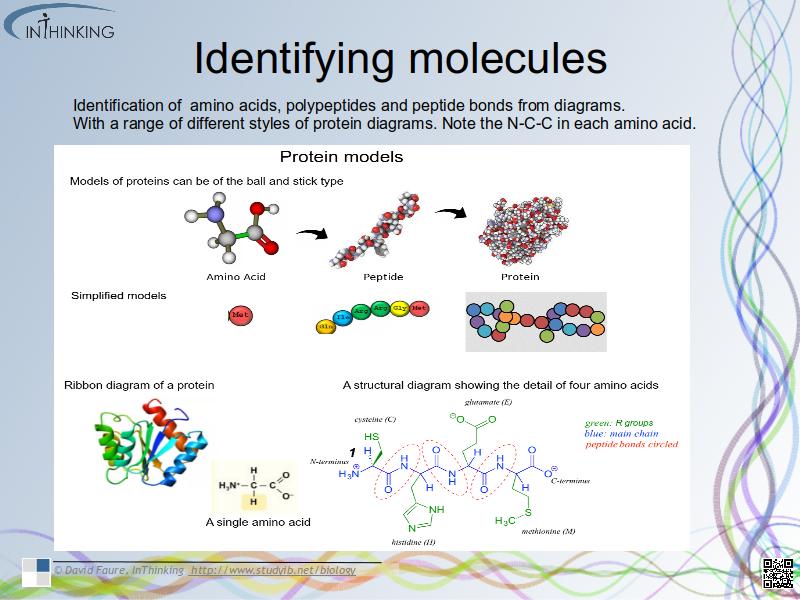
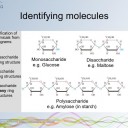
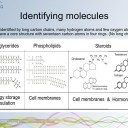
- Identification of biochemicals from diagrams to include:
- monosaccharides.
- disaccharides.
- lipids (triglycerides, phospholipids and steroids)
- amino acids.
- polypeptides and peptide bonds.
- Knowledge of the Benedicts reagent test for reducing sugars and iodine to test for starch.
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 2.1.
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps from memory.
Even better, design your own.
The ability to draw monosaccharide molecules is an important skill in this topic.
Answer the question below, on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
The image shows a diagram of deoxyribose which is a molecule made from five carbon molecules.
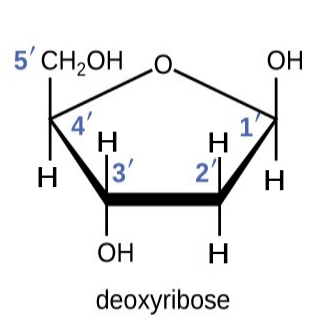
Distinguish between the structure of deoxyribose and the structure of αD-glucose.
(A labelled diagram may be used in the answer). [3]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Test your construction of biological knowledge using the drag and drop questions below.
Metabolism
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe metabolism, anabolism and catabolism.
protein catalysed hydrolysis Anabolism complex water smaller sum water simpler condensation
Metabolism is the of all the enzyme chemical reactions occurring in a cell.
is the synthesis of complex molecules from molecules e.g. synthesis from amino acids. It occurs by reactions between monomers to produce polymers and .
Catabolism is the breakdown of molecules into simpler molecules. It occurs by where the addition of to a chemical bond causes lysis (breaking) of the bond and the polymer breaks down into units.
Explanation/Examiner hint.Metabolism = Anabolism + Catabolism. Polymers are formed by condensation and broken down by hydrolysis.Your understanding of metabolism will improve as it reoccurs throughout the syllabus content.
Click the '+' symbol to open the next explanation.
Everyone needs something a bit light hearted from time to time when revising. That's the aim of this last activity.
Molecules to metabolism arcade games
How much of Molecules to metabolism 2.1 have you understood?

























.jpg)

 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn