- Summary list for 2.5 Enzymes
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about enzyme experiments.
- Model answer
- Exam style question about the lock and key model.
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 2.5 Enzymes 1/1
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Summary list for 2.5 Enzymes
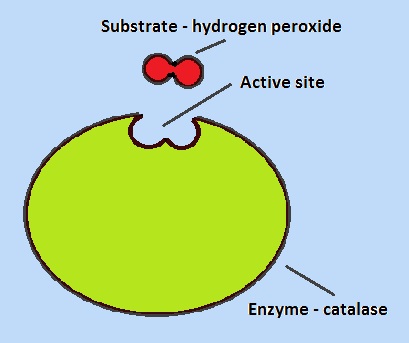
- The role of the active site where specific substrates bind.
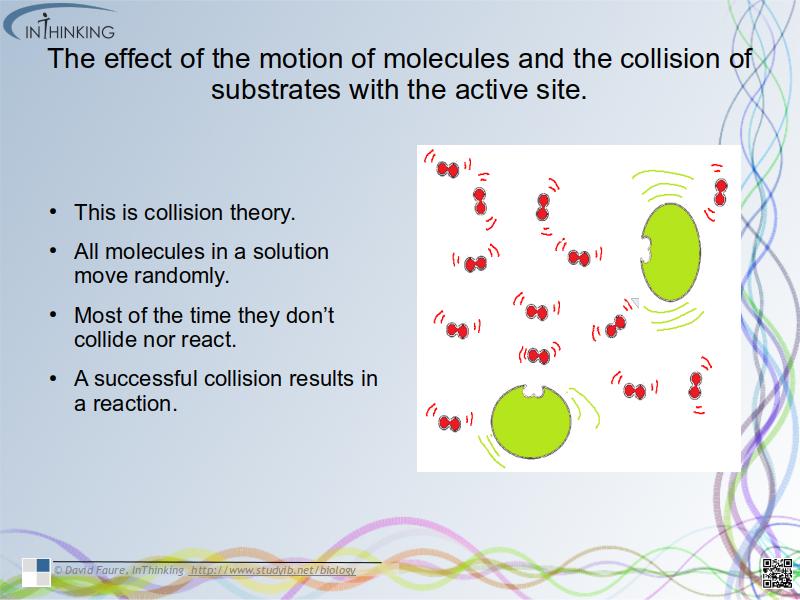
- The effect of the motion of molecules and the collision of substrates with the active site.
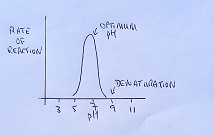
- The effect of Temperature, pH and substrate concentration on the rate of activity of enzymes. (including denaturing)
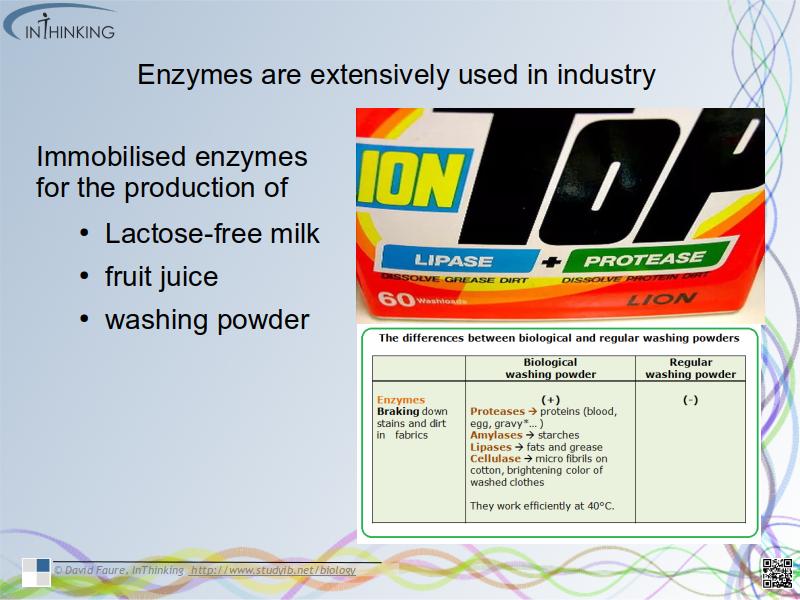
- Enzymes (often immobilised) are extensively used in industry for the production of items including Lactose-free milk, fruit juice and washing powder.
- Advantages of lactose-free milk, and ways of producing it, including immobilization in alginate beads.
- Knowledge of possible designs of experiments to test the effect of temperature, pH and substrate concentration on enzyme activity.
- Practical 3: Investigation of a factor affecting enzyme activity.
- The skill of sketching a graph of expected results in enzymes experiments and the ability to explain reasons for their shapes.
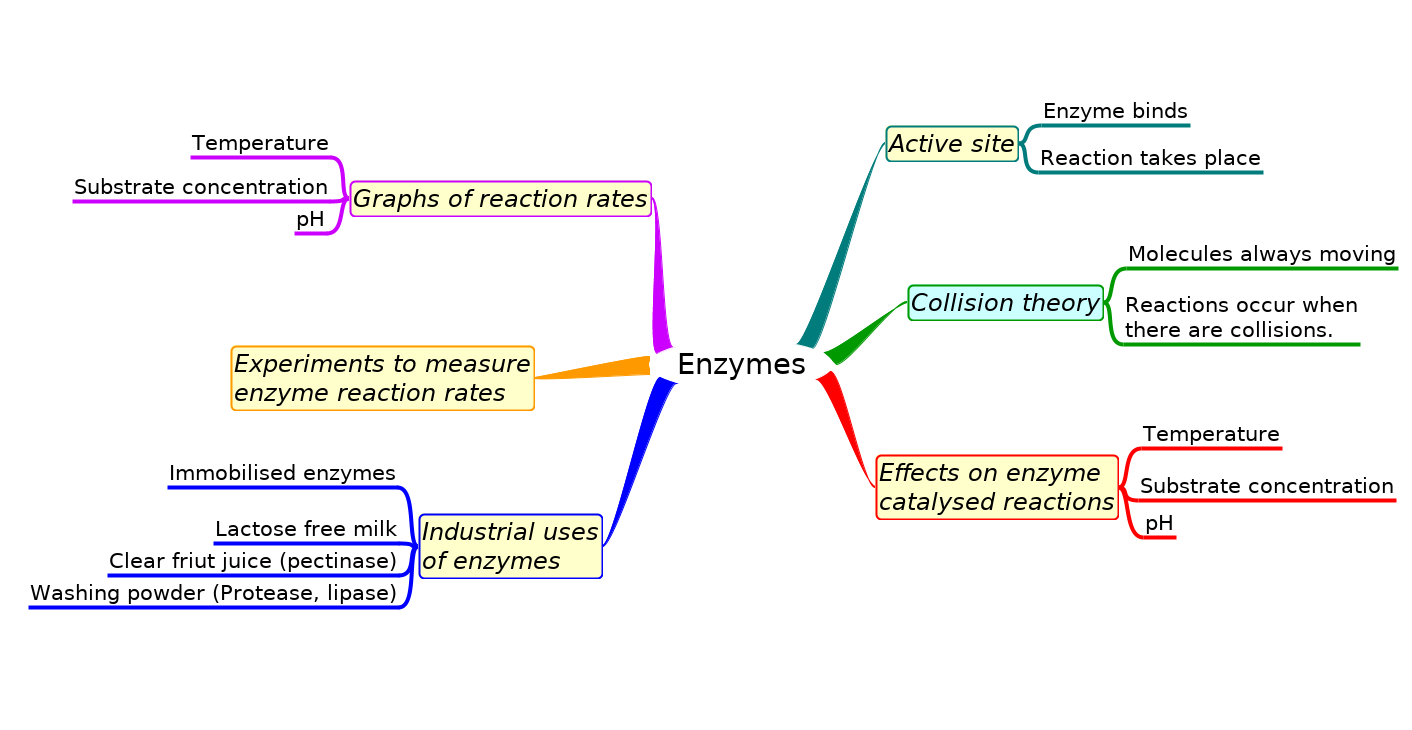
Mindmaps
This diagram summaries the main sections of topic 2.5
Test if you can draw something like these concept maps yourself from memory.
Exam style question about enzyme experiments.
Understanding how to design experiments to test the rate of activity of enzymes is important in this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer with the model answer.
Explain why it is important to keep factors such as; enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, and temperature constant when designing the method for an experiment to measure the effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction. [4]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Enzyme functions and pH
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe how pH can affect enzyme function.
extremophiles stomach optimum above or below damaged (neutral) maximal active site denatured
An enzyme has an pH at which the reaction rate is , the rate drops when the pH is a little the optimum. At too high or low a pH, bonds in the protein are and the shape of the changes and the enzyme becomes .
Most enzymes have an optimum pH of around 7 but stomach pepsin has an optimum of pH 2 (the pH of the ).
There are organisms adapted to extreme pH and temperatures, , which have enzymes that are also adapted to that environment.
Examiner hint. You could include a graph in your response to this question.
Enzyme investigation variables.
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe the control of variables in enzyme investigations.
controlled substrate decrease independent volumes concentration pH broken down concentrations drops
When carrying out an enzyme experiment, there are four variables to be considered which can either be the variable or the variables.
The four variables are enzyme , concentration, and temperature.
In practice, of enzyme and substrate solutions must also be kept constant as these affect .
During an enzyme-controlled reaction in vitro (laboratory conditions), as the substrate is , it’s concentration , and the reaction rate will gradually until all the substrate has been used up.
Examiner hint. You also need to be able to explain why these variables affect the rate of enzyme controlled reactions.
.
Just for fun
If you want to review key terminology and have some fun with your revision try this.
How much of Enzymes 2.5 have you understood?


















.jpg)
 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn