DP Chemistry Questionbank

18.3 pH curves
Description
[N/A]Directly related questions
-
16N.1.hl.TZ0.28:
Which mixture is a buffer solution?
A. 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NH3 (aq) and 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
B. 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NH3 (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
C. 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NaOH (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
D. 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NaOH (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
-
16N.1.hl.TZ0.29:
Which salt solution has the highest pH?
A. NH4Cl
B. Ca(NO3)2
C. Na2CO3
D. K2SO4
-
16N.2.hl.TZ0.7b:
(i) Sketch a graph of pH against volume of a strong base added to a weak acid showing how you would determine pKa for the weak acid.
(ii) Explain, using an equation, why the pH increases very little in the buffer region when a small amount of alkali is added.
-
17M.1.hl.TZ1.27:
A buffer is produced by mixing 20.0 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm−3 ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(aq), with 0.10 mol dm−3 sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq).
What is the volume of NaOH required and the pH of the buffer?
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.5d.ii:
Suggest a suitable indicator for the titration of hydrazine solution with dilute sulfuric acid using section 22 of the data booklet.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.iv:
The following curve was obtained using a pH probe.
State, giving a reason, the strength of the acid.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.vi:
Deduce the pKa for this acid.
- 20N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(ii): State a suitable indicator for this titration. Use section 22 of the data booklet
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(iii):
Suggest, giving a reason, which point on the curve is considered a buffer region.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(i):
Identify the major species, other than water and potassium ions, at these points.
-
17N.1.hl.TZ0.27:
Which indicator is appropriate for the acid-base titration shown below?
A. Thymol blue (pKa = 1.5)
B. Methyl orange (pKa = 3.7)
C. Bromophenol blue (pKa = 4.2)
D. Phenolphthalein (pKa = 9.6) - 17N.1.hl.TZ0.26: Which of the following will form a buffer solution if combined in appropriate molar ratios? A....
- 21M.1.hl.TZ2.27: Which compound is acidic in aqueous solution? A. KBr B. CH3COONa C. NH4Cl D. Na2CO3
-
21M.2.hl.TZ1.8b:
Sketch the general shape of the variation of pH when 50 cm3 of 0.001 mol dm–3 NaOH (aq) is gradually added to 25 cm3 of 0.001 mol dm–3 CH3CH2COOH (aq).
- 21M.2.hl.TZ2.5d(i): Sketch the titration curve of methanoic acid with sodium hydroxide, showing how you would...
-
21M.2.hl.TZ2.5f:
Identify if aqueous solutions of the following salts are acidic, basic, or neutral.
-
21M.2.hl.TZ2.5d(ii):
Identify an indicator that could be used for the titration in 5(d)(i), using section 22 of the data booklet.
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.27: Which combination of acid and base is most likely to have a pH of 8.5 at the equivalence point in...
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.5e:
Explain, using appropriate equations, how a suitably concentrated solution formed by the partial neutralization of 2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid with sodium hydroxide acts as a buffer solution.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.2d.i:
The graph represents the titration of 25.00 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 aqueous ethanoic acid with 0.100 mol dm−3 aqueous sodium hydroxide.
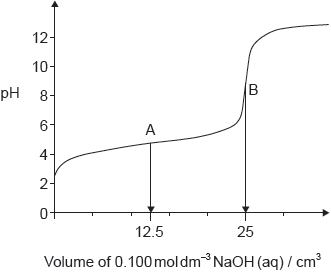
Deduce the major species, other than water and sodium ions, present at points A and B during the titration.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.2d.iv:
Predict whether the pH of an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride will be greater than, equal to or less than 7 at 298 K.
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.11c:
Sketch the neutralisation curve obtained and label the equivalence point.
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.6c:
Sketch the pH curve for the titration of 25.0 cm3 of ethylamine aqueous solution with 50.0 cm3 of butanoic acid aqueous solution of equal concentration. No calculations are required.
-
18N.1.hl.TZ0.27:
An indicator, HIn, has a pKa of 5.1.
HIn (aq) H+ (aq) + In− (aq)
colour A colour B
Which statement is correct?
A. At pH = 7, colour B would be observed
B. At pH = 3, colour B would be observed
C. At pH = 7, [HIn] = [In−]
D. At pH = 3, [HIn] < [In−] - 18N.1.hl.TZ0.25: What is the order of increasing pH for the following solutions of the same concentration? A. ...
- 22M.1.hl.TZ1.27: In which set are the salts arranged in order of increasing pH? A. HCOONH4 < KBr < NH4Br...
- 22M.1.hl.TZ2.26: A weak base is titrated with a strong acid. Which value of pKb can be estimated from this...
- 22M.2.hl.TZ1.1d(ii): Ammonia is added to water that contains a few drops of an indicator. Identify an indicator that...
- 22M.2.hl.TZ2.7a(iii): Justify whether a 1.0 dm3 solution made from 0.10 mol NH3 and 0.20 mol HCl will form a buffer...
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.4c(iii):
An aqueous solution containing high concentrations of both NH3 and NH4+ acts as an acid-base buffer solution as a result of the equilibrium:
NH3 (aq) + H+ (aq) NH4+ (aq)
Referring to this equilibrium, outline why adding a small volume of strong acid would leave the pH of the buffer solution almost unchanged.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.5d(ii):
Suggest a suitable indicator for the titration, using section 22 of the data booklet.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.5d(i):
Sketch a graph of pH against volume of hydrochloric acid added to ammonia solution, showing how you would determine the pKa of the ammonium ion.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.5d(iii):
Explain, using two equations, how an equimolar solution of ammonia and ammonium ions acts as a buffer solution when small amounts of acid or base are added.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.5f:
Aqueous sodium hydrogencarbonate has a pH of approximately 7 at 298 K.
Sketch a graph of pH against volume when 25.0cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 NaOH (aq) is gradually added to 10.0cm3 of 0.0500 mol dm−3 NaHCO3 (aq).
-
19M.1.hl.TZ2.26:
Where is the buffer region for the titration of a weak acid with a strong base?
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(i): Identify the most suitable indicator for the titration using section 22 of the data booklet.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.5a: A sample of ethanoic acid was titrated with sodium hydroxide solution, and the following pH curve...
-
19N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(ii):
Describe, using a suitable equation, how the buffer solution formed during the titration resists pH changes when a small amount of acid is added.
