| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 17M.2.hl.TZ2.8 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 8 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Soluble acids and bases ionize in water.
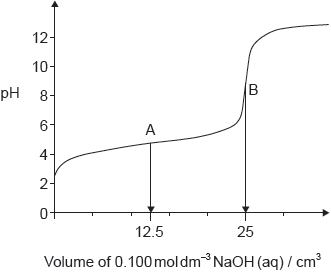
A solution containing 0.510 g of an unknown monoprotic acid, HA, was titrated with 0.100 mol dm–3 NaOH(aq). 25.0 cm3 was required to reach the equivalence point.
The following curve was obtained using a pH probe.
State, giving a reason, the strength of the acid.
State a technique other than a pH titration that can be used to detect the equivalence point.
Deduce the pKa for this acid.
The pKa of an anthocyanin is 4.35. Determine the pH of a 1.60 × 10–3 mol dm–3 solution to two decimal places.
Markscheme
weak AND pH at equivalence greater than 7
OR
weak acid AND forms a buffer region
[1 mark]
calorimetry
OR
measurement of heat/temperature
OR
conductivity measurement
Accept “indicator” but not “universal indicator”.
[1 mark]
«pKa = pH at half-equivalence =» 5.0
[1 mark]
Ka =
[H3O+] = «mol dm–3»
pH = «» 3.57
Award [3] for correct final answer to two decimal places.
If quadratic equation used, then: [H3O+] = 2.459 × 10–4 «mol dm–3» and pH = 3.61
[3 marks]