| Date | May 2022 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 22M.1.hl.TZ1.27 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Identify | Question number | 27 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
In which set are the salts arranged in order of increasing pH?
A. HCOONH4 < KBr < NH4Br < HCOOK
B. KBr < NH4Br < HCOOK < HCOONH4
C. NH4Br < HCOONH4 < KBr < HCOOK
D. HCOOK < KBr < HCOONH4 < NH4Br
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Not very well done in identifying the set of ionic compounds that were arranged in correct order of increasing pH, with no clear misconception based on the other choices.
Syllabus sections
- 22M.2.hl.TZ1.1d(ii): Ammonia is added to water that contains a few drops of an indicator. Identify an indicator...
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.iv:
The following curve was obtained using a pH probe.
State, giving a reason, the strength of the acid.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.2d.iv:
Predict whether the pH of an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride will be greater than, equal to or less than 7 at 298 K.
- 22M.1.hl.TZ2.26: A weak base is titrated with a strong acid. Which value of pKb can be estimated from this...
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.27: Which combination of acid and base is most likely to have a pH of 8.5 at the equivalence...
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.2d.i:
The graph represents the titration of 25.00 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 aqueous ethanoic acid with 0.100 mol dm−3 aqueous sodium hydroxide.
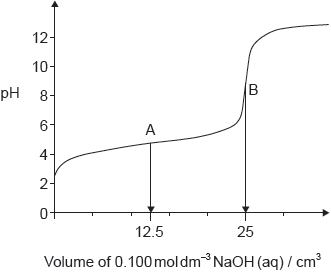
Deduce the major species, other than water and sodium ions, present at points A and B during the titration.
- 18N.1.hl.TZ0.25: What is the order of increasing pH for the following solutions of the same...
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.6c:
Sketch the pH curve for the titration of 25.0 cm3 of ethylamine aqueous solution with 50.0 cm3 of butanoic acid aqueous solution of equal concentration. No calculations are required.
-
16N.1.hl.TZ0.29:
Which salt solution has the highest pH?
A. NH4Cl
B. Ca(NO3)2
C. Na2CO3
D. K2SO4
-
16N.1.hl.TZ0.28:
Which mixture is a buffer solution?
A. 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NH3 (aq) and 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
B. 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NH3 (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
C. 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NaOH (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
D. 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NaOH (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
-
17N.1.hl.TZ0.27:
Which indicator is appropriate for the acid-base titration shown below?
A. Thymol blue (pKa = 1.5)
B. Methyl orange (pKa = 3.7)
C. Bromophenol blue (pKa = 4.2)
D. Phenolphthalein (pKa = 9.6) -
19M.1.hl.TZ2.26:
Where is the buffer region for the titration of a weak acid with a strong base?
-
16N.2.hl.TZ0.7b:
(i) Sketch a graph of pH against volume of a strong base added to a weak acid showing how you would determine pKa for the weak acid.
(ii) Explain, using an equation, why the pH increases very little in the buffer region when a small amount of alkali is added.
-
17M.1.hl.TZ1.27:
A buffer is produced by mixing 20.0 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm−3 ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(aq), with 0.10 mol dm−3 sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq).
What is the volume of NaOH required and the pH of the buffer?
- 17N.1.hl.TZ0.26: Which of the following will form a buffer solution if combined in appropriate molar...
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.5a: A sample of ethanoic acid was titrated with sodium hydroxide solution, and the following pH...
-
19N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(ii):
Describe, using a suitable equation, how the buffer solution formed during the titration resists pH changes when a small amount of acid is added.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.5d(ii):
Suggest a suitable indicator for the titration, using section 22 of the data booklet.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.vi:
Deduce the pKa for this acid.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.5f:
Aqueous sodium hydrogencarbonate has a pH of approximately 7 at 298 K.
Sketch a graph of pH against volume when 25.0cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 NaOH (aq) is gradually added to 10.0cm3 of 0.0500 mol dm−3 NaHCO3 (aq).
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.5d.ii:
Suggest a suitable indicator for the titration of hydrazine solution with dilute sulfuric acid using section 22 of the data booklet.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(i): Identify the most suitable indicator for the titration using section 22 of the data booklet.
- 21M.2.hl.TZ2.5d(i): Sketch the titration curve of methanoic acid with sodium hydroxide, showing how you would...
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(iii):
Suggest, giving a reason, which point on the curve is considered a buffer region.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.5e:
Explain, using appropriate equations, how a suitably concentrated solution formed by the partial neutralization of 2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid with sodium hydroxide acts as a buffer solution.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.5d(i):
Sketch a graph of pH against volume of hydrochloric acid added to ammonia solution, showing how you would determine the pKa of the ammonium ion.
-
18N.1.hl.TZ0.27:
An indicator, HIn, has a pKa of 5.1.
HIn (aq) H+ (aq) + In− (aq)
colour A colour B
Which statement is correct?
A. At pH = 7, colour B would be observed
B. At pH = 3, colour B would be observed
C. At pH = 7, [HIn] = [In−]
D. At pH = 3, [HIn] < [In−] - 21M.1.hl.TZ2.27: Which compound is acidic in aqueous solution? A. KBr B. CH3COONa C. NH4Cl D. Na2CO3
-
21M.2.hl.TZ1.8b:
Sketch the general shape of the variation of pH when 50 cm3 of 0.001 mol dm–3 NaOH (aq) is gradually added to 25 cm3 of 0.001 mol dm–3 CH3CH2COOH (aq).
-
21M.2.hl.TZ2.5d(ii):
Identify an indicator that could be used for the titration in 5(d)(i), using section 22 of the data booklet.
-
21M.2.hl.TZ2.5f:
Identify if aqueous solutions of the following salts are acidic, basic, or neutral.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(i):
Identify the major species, other than water and potassium ions, at these points.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.5d(iii):
Explain, using two equations, how an equimolar solution of ammonia and ammonium ions acts as a buffer solution when small amounts of acid or base are added.
- 20N.2.hl.TZ0.5b(ii): State a suitable indicator for this titration. Use section 22 of the data booklet
- 22M.2.hl.TZ2.7a(iii): Justify whether a 1.0 dm3 solution made from 0.10 mol NH3 and 0.20 mol HCl will form a buffer...
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.4c(iii):
An aqueous solution containing high concentrations of both NH3 and NH4+ acts as an acid-base buffer solution as a result of the equilibrium:
NH3 (aq) + H+ (aq) NH4+ (aq)
Referring to this equilibrium, outline why adding a small volume of strong acid would leave the pH of the buffer solution almost unchanged.
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.11c:
Sketch the neutralisation curve obtained and label the equivalence point.

