| Date | May 2009 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 09M.3.sl.TZ1.C2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Discuss | Question number | C2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Liquid crystals are widely used in electrically controlled liquid crystal display (LCD) devices such as calculators, computers and watches.
Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals. State and explain which diagram, I or II, represents molecules that are in a liquid crystalline phase.
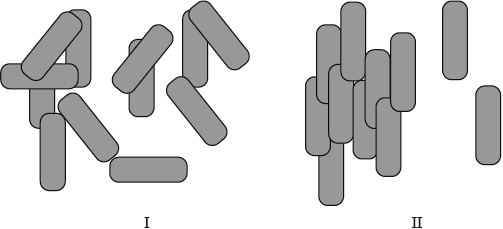
Distinguish between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals and state one example of each type.
Discuss the properties needed for a substance to be used in liquid crystal displays.
Markscheme
liquid crystals are fluids that exhibit orientation of the molecules/an orderly arrangement of molecules;
II, since there is one-dimensional order (characteristic of a liquid crystalline phase);
thermotropic liquid crystals are pure substances that show liquid crystal behaviour over a temperature range (between the solid and liquid states);
example (of thermotropic liquid crystals) is biphenyl nitriles;
lyotropic liquid crystals are solutions that show the liquid crystal state at certain concentrations;
example (of lyotropic liquid crystals) is soap in water;
Award marks for examples, only if they are associated with the correct class of liquid crystals.
chemically stable;
a liquid crystal phase stable over a suitable range of temperatures;
polar in order to change orientation when an electric field is applied;
rapid switching speed;
Examiners report
Candidates were able to define liquid crystals but often confused the two diagrams.
Candidates also had difficulty distinguishing between thermotropic and lyotropic crystals and providing suitable examples for each. This emphasised again that candidates had not learnt definitions accurately with correct chemical terminology.

